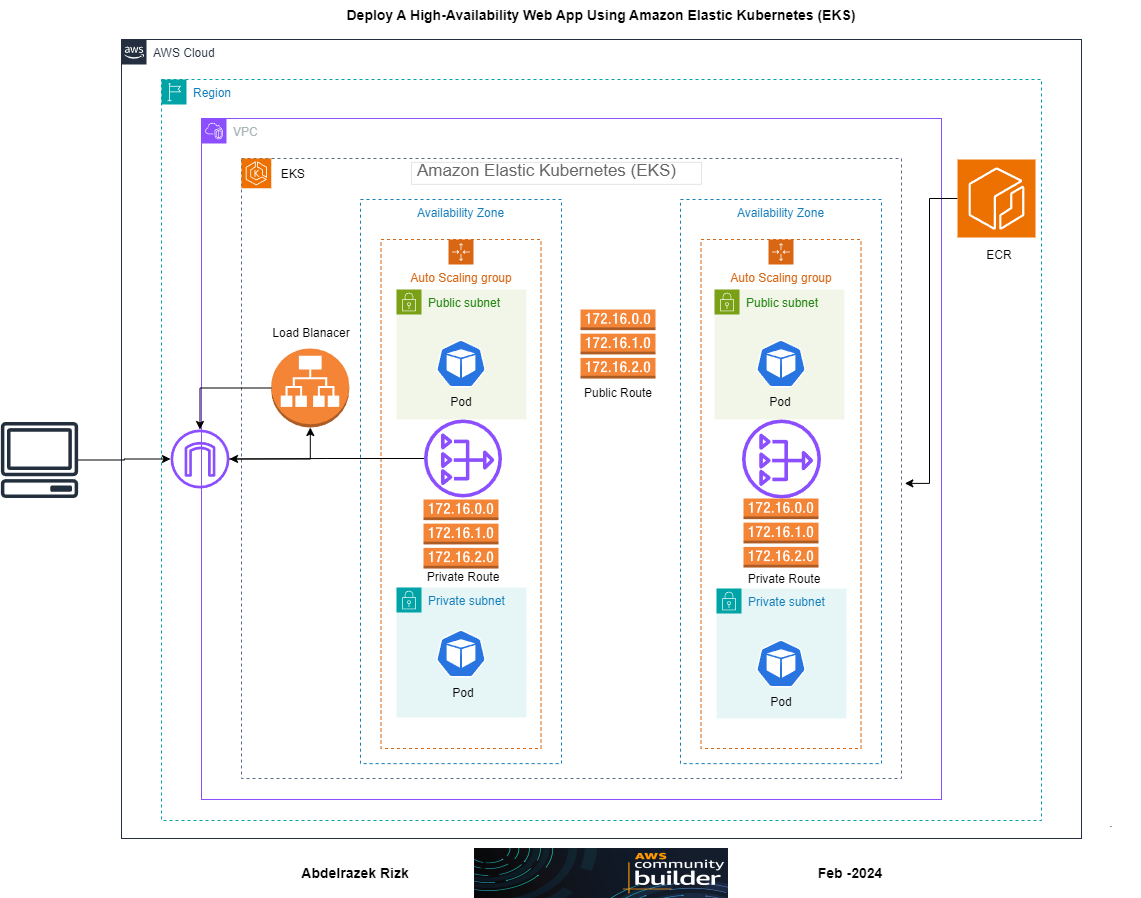
Architecture Diagram:
This is a guide on how to Developing and Deploying a Basic Web Application on Amazon EKS
- Gain hands-on experience with containerization using Docker.
- Understand how to use Amazon ECR to store and manage container images.
- Learn the basics of creating and managing an Amazon EKS cluster.
- Explore Kubernetes concepts like Deployments, Services, and Horizontal Pod Autoscaling.
- Implement multi-AZ deployment to ensure high availability.
Whether you are new to Amazon EKS or looking to level up your skills, this repository has you covered.
Note: that Tutorial using AIM with Administrative User.
Below are the steps to follow:
- Step 1: Create a Flask Web Application
- Step 2: Create a Dockerfile
- Step 3: Create a requirements.txt File
- Step 4: Preparing Your Environment
- Step 5: Build and Push Docker Image to Amazon ECR
- Step 6: Step 6: Create Amazon ECR Repository
- Step 7: Setup Amazon EKS Cluster Requirements
- Step 8: Creating an Amazon EKS cluster
- Step 9: Create a Node Group
- Step 10: Create a Kubernetes Deployment
- Step 11: Test The Application
- Step 12: Cleanup
Create a basic Flask web application.
app.py:
Create a Dockerfile to containerize the Flask application.
Dockerfile:
Create a requirements.txt file to list the Python dependencies.
requirements.txt:
Assuming you have an Docker and Kubectl. if not
Below are the steps to follow:
sudo apt-get update
apt list --upgradable
sudo apt upgrade -y
sudo apt-get install docker.io -y
- Start the Docker service.
sudo systemctl enable docker
sudo systemctl start docker
-
Add the
ubuntu userto thedocker groupso you can execute Docker commands without usingsudo.sudo usermod -aG docker ubuntu -
Log out and log back in again or restart your EC2 to pick up the new docker group permissions.
-
Verify that the ubuntu can run Docker commands without sudo.
docker run hello-world -
Troubleshoot Docker Engine installation.
permission denied while trying to connect to the Docker daemon socket
at unix:///var/run/docker.sock: Post "http://%2Fvar%2Frun%2Fdocker.sock/v1.24/containers/create":
dial unix /var/run/docker.sock: connect: permission denied.
- Run the follow command:
sudo chmod 666 /var/run/docker.sock
Note: that Tutorial using EC2 with ubuntu-jammy-22.04-amd64-server Operation System
Docker version 24.0.5, build 24.0.5-0ubuntu1~22.04.1
For other Operation System Follow the Official Docker Documunts here.
Assuming you have an AWS account, follow these steps:
-
AWS CLI install and update
curl "https://awscli.amazonaws.com/awscli-exe-linux-x86_64.zip" -o "awscliv2.zip" unzip awscliv2.zip sudo ./aws/install
before that step you may need to install unzip using sudo apt install unzip
-
Confirm the installation.
aws --version
output: aws-cli/2.15.13 Python/3.11.6 Linux/6.2.0-1017-aws exe/x86_64.ubuntu.22 prompt/off
-
Configure the AWS CLI.
aws configure
AWS Access Key ID [None]:<your AWS Access Key ID>
AWS Secret Access Key [None]:<your-AWS Secret Access Key>
Default region name [None]:<your-region>
Default output format [None]:
-
Open a terminal or command prompt and navigate to the directory containing the Dockerfile and run the following command:
docker build -t my-eks-web-app . -
Run the newly built image.
docker run -p 5000:5000 my-eks-web-app -
Running Docker locally, point your browser to
http://localhost:5000/orhttp://127.0.0.1:5000/
- Create an ECR repository to store your Docker images.
- Make note of the repository URI.
- Verify that your IAM user or role has the necessary permissions to access the ECR repository.
The required permissions include:
ecr:GetAuthorizationToken
ecr:BatchCheckLayerAvailability
You can attach the AmazonEC2ContainerRegistryPowerUser policy to your IAM user or role to grant these permissions.
-
Authenticate a private repository.
aws ecr get-login-password --region <your-region> | docker login --username AWS --password-stdin <aws_account_id>.dkr.ecr.<your-region>.amazonaws.com -
Replace:
<your-region>with your region.
<aws_account_id>with your aws_account_id
aws ecr create-repository \
--repository-name <repository-name> \
--region <your-region>
- Replace:
<repository-name>with your repository-name.
<your-region>with your region.
-
Tag the image to push to your private repository.
-
List the images you have stored locally to identify the image to tag and push.
docker images -
Tag the image to push to
Amazon ECR privaterepository.docker tag <image-name:tag> <aws_account_id>.dkr.ecr.<your-region>.amazonaws.com/<repository-name:tag> -
Push the image.
docker push <aws_account_id>.dkr.ecr.<your-region>.amazonaws.com/<repository-name:tag> -
Replace:
<image-name:tag>with your image-name:tagex: hello-world:latest
<aws_account_id>with your aws_account_id.
<your-region>with your region.
<repository-name>with your repository-name.
Note: ECR repository URI=<aws_account_id>.dkr.ecr.<your-region>.amazonaws.com/<repository-name:tag>
Follow the Official Documunts Amazon Quick start: Publishing to Amazon ECR Pprivate repository using the AWS CLI here.
-
Authenticate a public repository.
aws ecr-public get-login-password --region <your-region> | docker login --username AWS --password-stdin public.ecr.aws -
Create a public repository.
-
Open a terminal or command prompt and navigate to the ECR directory and run the following command:.
aws ecr-public create-repository \ --repository-name <repository-name> \ --catalog-data file://repositorycatalogdata.json \ --region <your-region> -
Replace:
<repository-name>with your repository-name.
<your-region>with your region. -
Tag and Push an image to
Amazon ECR Publicrepository.
List the images you have stored locally to identify the image to tag and push.docker images -
Tag the image to push to your repository with your
public repository URI
which was in the response to thecreate-repositorycall you made in the previous step.docker tag <image-name:tag> public.ecr.aws/registry_alias/<repository-name> -
Push the image to the Amazon ECR.
docker push public.ecr.aws/registry_alias/<repository-name> -
Pull the image from the Amazon ECR.
docker pull public.ecr.aws/g7p1j8g3/hello-flask:v.1 -
Replace:
<registry_alias>with your registry_alias.
<repository-name>with your repository-name.
Follow the Official Amazon Quick start: Publishing to Amazon ECR Public using the AWS CLI here.
-
Follow the official Documunts
Amazon EKS Getting Started guideto create an Amazon EKS cluster. -
Download the kubectl binary for your cluster's Kubernetes version from Amazon S3.
-
Kubernetes 1.29
curl -O https://s3.us-west-2.amazonaws.com/amazon-eks/1.29.0/2024-01-04/bin/linux/amd64/kubectl -
Apply execute permissions to the binary.
chmod +x ./kubectl -
Copy the binary to a folder in your PATH.
mkdir -p $HOME/bin && cp ./kubectl $HOME/bin/kubectl && export PATH=$HOME/bin:$PATH
-Verify EKS Version.
kubectl version --client
-
Create IAM Policy Role.
-
Create a cluster IAM role and attach the required
Amazon EKS IAM managed policyto it. -
Open a terminal or command prompt and navigate to the EKS directory and run the following command:.
aws iam create-role \ --role-name <Policy-Role-Name> \ --assume-role-policy-document file://"eks-cluster-role-trust-policy.json" -
Attach Policy Role.
-
Attach the required Amazon EKS managed IAM policy to the role.
aws iam attach-role-policy \ --policy-arn arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AmazonEKSClusterPolicy \ --role-name EKS-Cluster-trust-policy-role
-
Create an Amazon VPC with public and private subnets that meets Amazon EKS requirements.
-
Open a terminal or command prompt and navigate to the cloudformation directory and run the following command:.
aws cloudformation create-stack \ --region <your-region> \ --stack-name <stack-name> \ --template-body file://amazon-eks-vpc-private-subnets.yaml -
Replace:
<your-region>with your region.
<stack-name>with your stack-name. -
Navigate to the
cloud-formation outputsMake note and write down:
- Subnets IDs in the VPC<PrivateSubnet01>, <PrivateSubnet02>, <PublicSubnet01>, <PublicSubnet02>
- SecurityGroups<Security group>
aws eks create-cluster --region <your-region> --name <cluster-name> --kubernetes-version 1.29 \
--role-arn arn:aws:iam::<aws_account_id>:role/myAmazonEKSClusterRole \
--resources-vpc-config subnetIds=<PrivateSubnet01>,<PrivateSubnet02>,<PublicSubnet01>,<PublicSubnet02>,securityGroupIds=<Security-group>
- Replace:
<your-region>with your region.
<cluster-name>with your cluster name.
<aws_account_id>with your aws_account_id.
<PrivateSubnet01>,<PrivateSubnet02>,<PublicSubnet01>,<PublicSubnet02>with your public and private subnets fromcloud-formation outputs.
<Security-group>with your Security group
aws eks update-kubeconfig --region <your-region> --name <cluster-name>
kubectl get svc
-
Create a node IAM role and attach the required Amazon Node IAM managed policy to it.
-
Open a terminal or command prompt and navigate to the
EKS directoryand run the following command:.aws iam create-role \ --role-name AmazonEKSNodeRole \ --assume-role-policy-document file://"node-role-trust-relationship.json" -
Attach Policy Role.
-
Attach the required
Amazon EKS Worker NodeAmazon and EC2 Container Registry ReadOnlyPolicy to the role.
aws iam attach-role-policy \
--policy-arn arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AmazonEKSWorkerNodePolicy \
--role-name AmazonEKSNodeRole
aws iam attach-role-policy \
--policy-arn arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AmazonEC2ContainerRegistryReadOnly \
--role-name AmazonEKSNodeRole
-
Determine the IP family of your cluster.
aws eks describe-cluster --name my-cluster | grep ipFamily
depending on which IP family you created your cluster IPv4 or IPv6.
-
IPv4
aws iam attach-role-policy \ --policy-arn arn:aws:iam::aws:policy/AmazonEKS_CNI_Policy \ --role-name AmazonEKSNodeRole
Follow the Official Documunts Amazon EKS node IAM role using the AWS CLI here
-
Provision compute capacity for your cluster by adding a Managed node group.
aws eks create-nodegroup \ --cluster-name <cluster-name> \ --nodegroup-name <nodegroup-name> \ --scaling-config desiredSize=(integer),minSize=(integer),maxSize=3 \ --subnets <PrivateSubnet01> <PrivateSubnet02> <PublicSubnet01> <PublicSubnet02> \ --instance-types t2.micro \ --disk-size 8 \ --ami-type AL2_x86_64 \ --node-role arn:aws:iam::<aws_account_id>:role/<nodegroup-role> -
Replace:
<cluster-name>with your cluster name.
<nodegroup-name>with your nodegroup-name.
<desiredSize>with The current number of nodes that the managed node group should maintain should not behigher thanthe maxSize.
<minSize>with The minimum number of nodes that the managed node group can scale in to.
<maxSize>with The maximum number of nodes that the managed node group can scale out to.
<subnets>with your subnetIds to use for the Auto Scaling group that was created for your node group from previous step Create an Amazon VPC.
<instance-types>with the instance types for a node group.
<aws_account_id>with your aws_account_id.
<nodegroup-role>with your AmazonEKSNodeRole AIM Role from previous step Create a Node AIM Policy Role.
10.1. Create a Kubernetes deployment file.
deployment.yaml:
- Replace:
<your-ecr-repository-uri>with your ECR repository URI.
-
Apply the Kubernetes Deployment:
kubectl apply -f deployment.yaml
Wait for the LoadBalancer service to be assigned an external IP address:
- Obtain the Load Balancer URL:
kubectl get svc my-eks-web-app -w
- output
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
my-eks-web-app LoadBalancer 10.100.190.72 a47bd5cd4514f4f1428151bbd6f3446c-4482297959.us-west-1.elb.amazonaws.com 80:30606/TCP 2d4h
Once the external IP is available, you can access your web application in a browser using that IP.
- Cleaning up your resources is an important part of managing your cloud environment.
- By following these steps, you can ensure that your resources are always clean and tidy and it will also help you to avoid unnecessary costs.
kubectl delete deployment <deployment-name>
- Replace:
<deployment-name>with your deployment-name.
kubectl get svc --all-namespaces
- These services are fronted by an Elastic Load Balancing load balancer,
and you must delete them in Kubernetes to allow the load balancer and associated resources to be properly released.
kubectl delete svc <service-name>
- Replace:
<service-name>with your service-name.
aws eks delete-nodegroup \
--cluster-name <cluster-name> \
--nodegroup-name <nodegroup-name> \
--region <your-region>
- Replace:
<cluster-name>with your cluster name.
<nodegroup-name>with your nodegroup-name.
<your-region>with your region.
aws eks delete-cluster \
--name <cluster-name>
- Replace:
<cluster-name>with your cluster name.
aws cloudformation delete-stack \
--stack-name <stack-name>
- Replace:
<stack-name>with your stack-name.
- To stop an EC2 instance:
aws ec2 stop-instances \
--instance-ids <instance-id>
- To terminate an EC2 instance:
aws ec2 terminate-instances \
--instance-ids <instance-id>
-
Replace:
<instance-id>with your instance-ids. -
Remember to always follow the best practices and guidelines provided by your cloud provider to ensure a smooth and efficient cleanup process.
-
Regularly reviewing and optimizing your resource utilization can not only save costs but also improve the overall performance and efficiency of your cloud infrastructure.
Follow the Official Documunts Deleting an Amazon EKS cluster here
Keep in mind that this example is minimal and focuses on the basic steps.
In a production scenario, you would likely include more features, security measures, and configurations.
Additionally, you might want to explore tools like Helm for managing Kubernetes manifests more efficiently.