This repository contains the code for the lnmux service. The problem that lnmux solves is fail-over for incoming Lightning payments. BOLT11 invoices are bound to a single node. If that node goes down, the invoice is no longer payable. The same is true for the node or its peers running out of inbound liquidity.
What lnmux allows you to do is set up a cluster of nodes where each of these nodes can settle any invoice. If a node is unable to accept payments for one of the reasons above, senders will still be able to pay the invoice via one of the other nodes.
Even with all nodes in the cluster available, it can be advantageous for the sender to have multiple routing options to better utilize liquidity and minimise fees. If needed, multi-part payments can be completed through more than one cluster node.
For the setup, it is assumed that there are multiple LND nodes running with connections to the wider Lightning network and sufficient inbound liquidity. The minimally required version of lnd is v0.15.0-beta.
-
Run the
lndnodes with the--requireinterceptoroption. This ensures that HTLCs are always offered to interceptor applications eventually, even when there are momentary disconnects. Not running with this option can lead to HTLCs failing after the invoice that they pay to has been marked as settled. -
Create a postgres database. Note that
lnmuxuses stateless invoices. This means that the database only contains settled invoices. -
Create a config file for
lnmuxdnamedlnmux.yml. An example can be found in this repository. The config file contains the following elements:- LND nodes configuration: TLS certificate, macaroon, address and pubkey. Pubkey is configured as a protection against unintentionally connecting to the wrong node.
- Postgres connection string for the database created above.
- 32-byte Identity PRIVATE key. This key is used to generate invoices and decode incoming htlcs. In a production environment, this key must be protected carefully.
-
Initialize the database:
go run ./cmd/lnmuxd -c lnmux.yml migrate init -
Migrate the database to the latest version:
go run ./cmd/lnmuxd -c lnmux.yml migrate up -
Run
lnmuxd:go run ./cmd/lnmuxd -c lnmux.yml run. This opens connections to all LND nodes via the HTLC interceptor API. Incoming htlcs are collected and assembled into sets. When a set is complete, an external application connected tolnmuxdecides whether to settle the invoice. If the application sends a settle request, the invoice is marked as settled in thelnmuxdatabase and a settle action is returned to the LND instance(s) holding the HTLC(s). -
Invoice generation is taken over by
lnmuxd. It is no longer a responsibility of the LND nodes. To generate an invoice, run:grpcurl -plaintext -v -d '{"amt_msat":20000, "expiry_secs":600}' localhost:19090 lnmux.Service.AddInvoice.If you decode the invoice, you'll find route hints from each node in the cluster to the
lnmuxdpublic key.lnmuxdacts as a virtual node without real channels.The invoice is not stored in the
lnmuxdatabase and does not take up any disk space. This makeslnmuxparticularly suitable for scenarios where large numbers of invoices are generated.Below is an example invoice generated by
lnmuxd.
{
"destination": "03422175ba6fed348de4f273cf81627c26d5ab2a78bfdc1a39e6f9c06354dd9371",
"payment_hash": "fd3b0f9a077006697ba8f82cc5673d1511cb11d1d1012662bf0c0b3c93f4245e",
...
"route_hints": [
{
"hop_hints": [
{
"node_id": "020723c6f2203f1072336bd0e71bf4d11e367ab0b3010ce60c080abef0d4770db8",
"chan_id": "12345",
"fee_base_msat": 0,
"fee_proportional_millionths": 0,
"cltv_expiry_delta": 40
}
]
},
{
"hop_hints": [
{
"node_id": "026ff75cb2ff49b864833aa3c93970069070231a9ad64819252e190406dd0a6976",
"chan_id": "12345",
"fee_base_msat": 0,
"fee_proportional_millionths": 0,
"cltv_expiry_delta": 40
}
]
}
],
"payment_addr": "8f135e331fed1858e467f775fa644751a2b0da17ee0676ebb1bc8a994d667be6",
"num_msat": "6000",
"features": {
...
}
}
-
It should be possible to pay this invoice as long as at least one node in the cluster is available.
-
When the payment comes in, an event is generated. Events can be listened for via:
grpcurl -plaintext -v -d '{"hash":"EgR0u/TAjFXNGId9PEHVnryFl1sy/UwB2uN+YxC8S80="}' localhost:19090 lnmux.Service.SubscribeSingleInvoice(replace base64 hash)
-
To request settlement of the invoice, invoke:
grpcurl -plaintext -v -d '{"hash":"EgR0u/TAjFXNGId9PEHVnryFl1sy/UwB2uN+YxC8S80="}' localhost:19090 lnmux.Service.SettleInvoice
If you've set up lnmuxd correctly, output similar to what is shown below is expected.
- Interception is started on all of your nodes
- When an HTLC comes in, it is matched against the invoice database. If there is a match, the invoice is loaded into memory.
- The total amount of the HTLC set is tracked. When the total amount matches the invoice amount, HTLC settle resolutions are sent to LND.
2022-04-19T08:39:09.333+0200 INFO Succesfully connected to LND {"node": "020723c6f2203f1072336bd0e71bf4d11e367ab0b3010ce60c080abef0d4770db8"}
2022-04-19T08:39:09.339+0200 INFO Succesfully connected to LND {"node": "026ff75cb2ff49b864833aa3c93970069070231a9ad64819252e190406dd0a6976"}
2022-04-19T08:39:09.347+0200 INFO InvoiceRegistry starting
2022-04-19T08:39:09.347+0200 INFO Press ctrl-c to exit
2022-04-19T08:39:09.347+0200 DEBUG Starting htlc interception {"node": "026ff75cb2ff49b864833aa3c93970069070231a9ad64819252e190406dd0a6976"}
2022-04-19T08:39:09.347+0200 DEBUG Starting htlc interception {"node": "020723c6f2203f1072336bd0e71bf4d11e367ab0b3010ce60c080abef0d4770db8"}
2022-04-19T08:39:09.347+0200 DEBUG Starting main event loop
2022-04-19T08:39:23.166+0200 INFO Htlc received {"hash": "fd3b0f9a077006697ba8f82cc5673d1511cb11d1d1012662bf0c0b3c93f4245e", "source": "026ff75cb2ff49b864833aa3c93970069070231a9ad64819252e190406dd0a6976", "circuitKey": "1161084279062528:7"}
2022-04-19T08:39:23.224+0200 DEBUG Loaded invoice from db {"hash": "fd3b0f9a077006697ba8f82cc5673d1511cb11d1d1012662bf0c0b3c93f4245e"}
2022-04-19T08:39:23.225+0200 DEBUG Hodl subscribe for 1161084279062528:7
2022-04-19T08:39:23.225+0200 DEBUG Htlc accepted: hash=fd3b0f9a077006697ba8f82cc5673d1511cb11d1d1012662bf0c0b3c93f4245e, amt=6000 mSAT, expiry=1110, circuit=1161084279062528:7, mpp=total=6000 mSAT, addr=8f135e331fed1858e467f775fa644751a2b0da17ee0676ebb1bc8a994d667be6
2022-04-19T08:39:23.237+0200 DEBUG Sending settle resolution {"hash": "fd3b0f9a077006697ba8f82cc5673d1511cb11d1d1012662bf0c0b3c93f4245e", "source": "026ff75cb2ff49b864833aa3c93970069070231a9ad64819252e190406dd0a6976", "circuitKey": "1161084279062528:7", "outcome": "settled"}
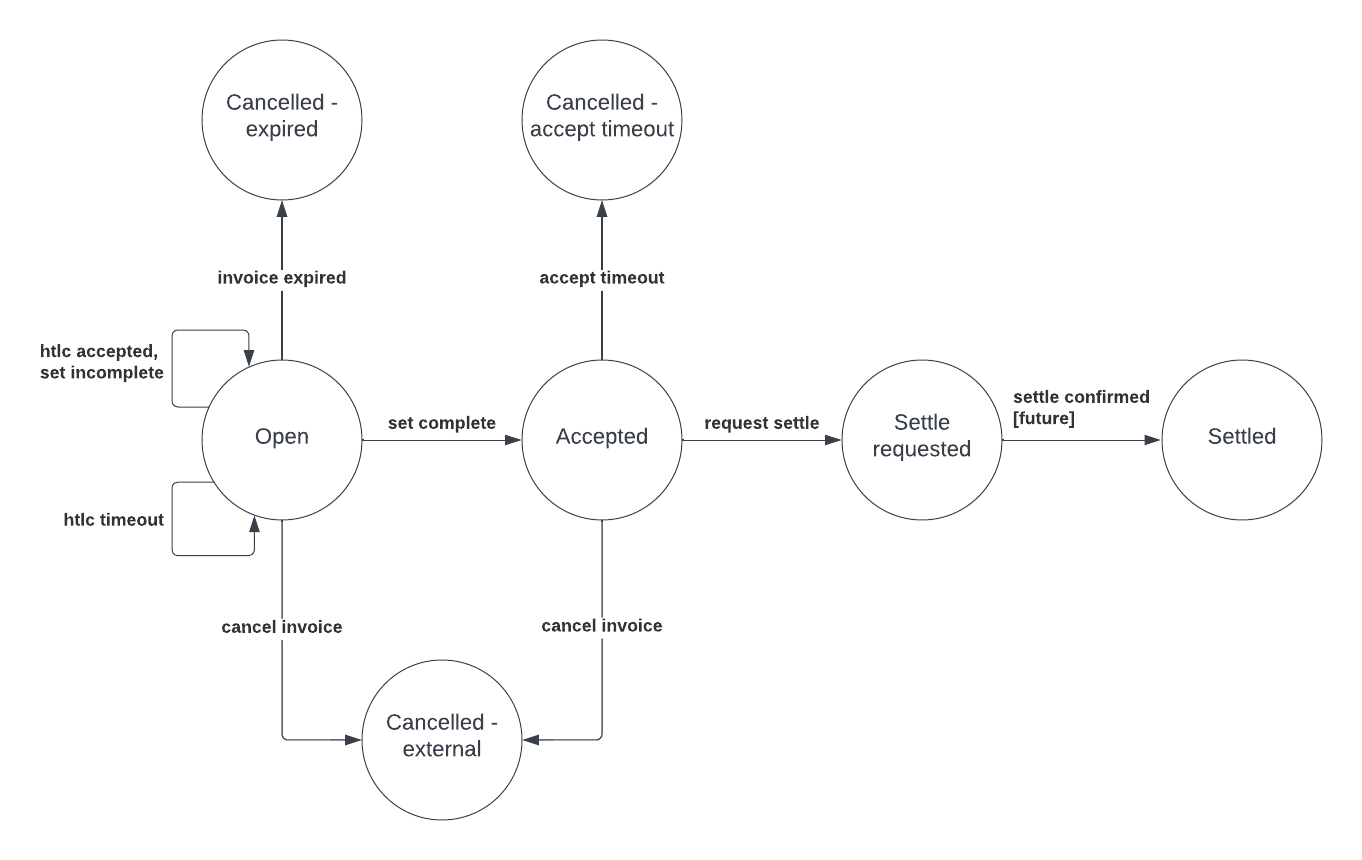
Note that only the states accepted, settle requested and settled are published to callers of the SubscribeSingleInvoice rpc.
The transition from settle requested to settled is marked as [future]. This transition is happening already, but not backed by an actual final settle event from lnd. See lightningnetwork/lnd#6208.
The minimal setup to test on regtest is to create three LND nodes A, B and C. Create channels between B and A and between B and C. Connect lnmuxd to the nodes A and C. Pay invoices from node B, while experimenting with online status and liquidity of A and C.
This software is in an experimental state. At this stage, breaking changes can happen and may not always include a database migration. Use at your own risk.