Single Remote Sensing Image Super-Resolution via a Generative Adversarial Network With Stratified Dense Sampling and Chain Training
- Fanen Meng, Sensen Wu, Yadong Li, Zhe Zhang, Tian Feng, Renyi Liu, Zhenhong Du
- IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, vol. 62, pp. 1-22
- https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10375518
- checkpoint: https://pan.baidu.com/s/1eUANo6besXp5HctEqqRVOA?pwd=0115 or https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1_ncUya30a-AwaDXkys56AMj2m8eSJjfH?usp=sharing
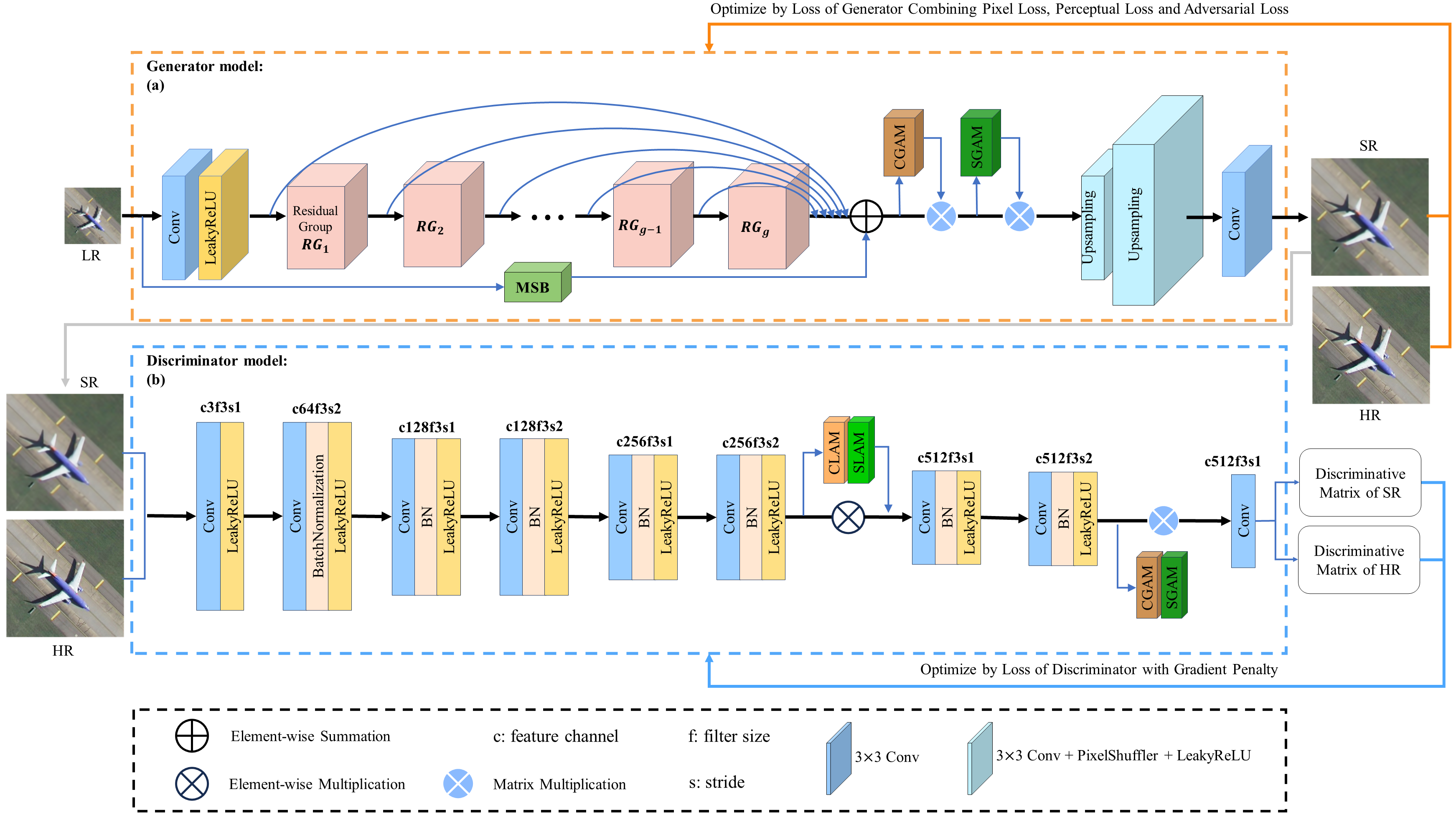 Fig. 1. Structure of our proposed SRADSGAN. (a) Generator model. (b) Discriminator model.
Fig. 1. Structure of our proposed SRADSGAN. (a) Generator model. (b) Discriminator model.
Our folder structure is as follows:
├── dataset (dataset used by SRADSGAN)
│ ├── sradsgan
│ │ ├── AID
│ │ ├── DOTA
│ │ ├── LoveDA
│ │ ├── RSSCN7_2800
│ │ ├── SECOND
│ │ ├── UCMerced_LandUse
├── SRADSGAN (code)
│ ├── data
│ ├── GDP_x0
│ ├── img
│ │ ├── GF2_HR.tif
│ │ ├── GF2_LR.tif
│ │ ├── Sentinel2.tif
│ ├── model
│ │ ├── amssrn.py (amssrn model)
│ │ ├── drcan.py (drcan model)
│ │ ├── dssr.py (dssr model)
│ │ ├── edsr.py (edsr model)
│ │ ├── hat.py (hat model)
│ │ ├── ndsrgan.py (ndsrgan model)
│ │ ├── sradsgan.py (sradsgan model)
│ │ ├── sragan.py (sragan model)
│ │ ├── srgan.py (srgan model)
│ ├── utils
│ ├── main_amssrn.py
│ ├── main_drcan.py
│ ├── main_dssr.py
│ ├── main_edsr.py
│ ├── main_hat.py
│ ├── main_ndsrgan.py
│ ├── main_sradsgan.py
│ ├── main_sragan.py
│ ├── main_srgan.py
│ ├── Scene_classification_mfe.py (scene classification)
-
SRADSGAN (traditional generative model architecture)
The HAT model uses python 3.8, pytorch 1.9, tensorflow-gpu 2.1.0, and the environment of other models is in requirements.txt
pip install -r requirements.txtWe used six datasets to train our model. After secondary processing, we obtained a total of about 35,000 images of 216*216 size.
-
Train
- ["AID", "DOTA", "LoveDA", "RSSCN7_2800", "SECOND"]
-
Test
-
["UCMerced_LandUse"]
-
Link: https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1e4VRUgFL4bDRfrb0CS6-Y9f7bTZhBqiV?usp=sharing or
https://pan.baidu.com/s/1cXkKu-CI6Q8EF_7Kbfxodg?pwd=w5t8 提取码:w5t8
- Prepare environment, datasets and code.
- Run training / evaluation code. The code is for training on 1 GPU.
# sradsgan
cd SRADSGAN
python main_sradsgan.py
---------------------------------------------------------------
net.train() # train
net.mfeNew_validate() # test
net.mfeNew_validateByClass() # classes test
net.mfe_test_single() # infer
---------------------------------------------------------------
# GDP_x0
cd GDP_x0
python sr_mfe.py -p train -c config/gdp_train_27_216.json # train
python sr_mfe.py -p val -c config/gdp_test_27_216.json # test
python sr_mfe.py -p val -c config/gdp_GF2_x3.json # infer
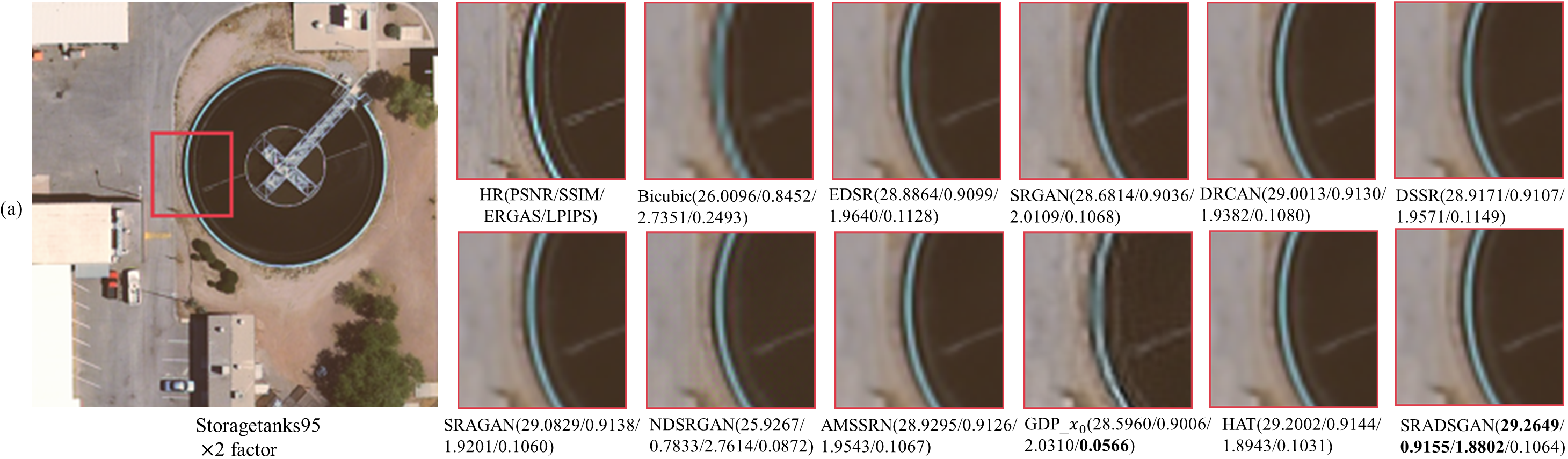
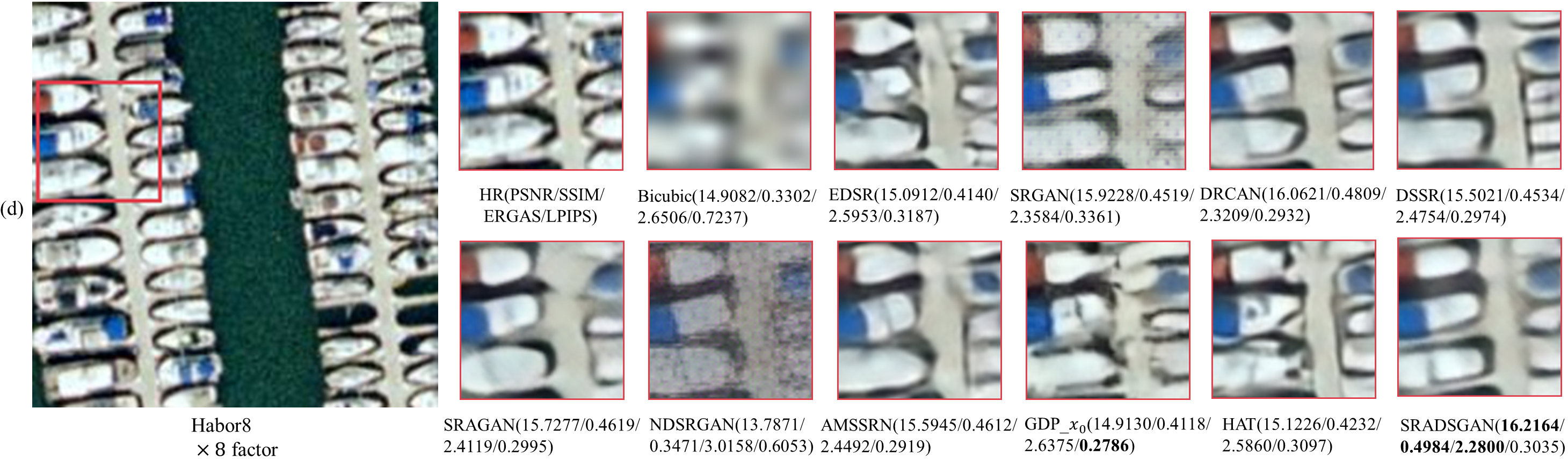
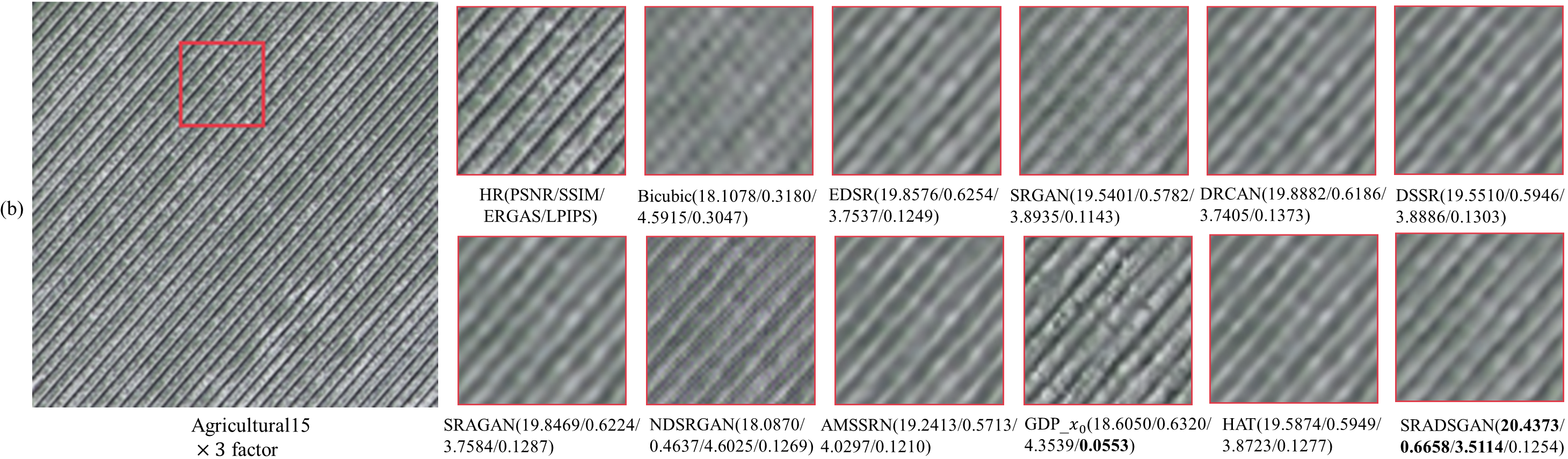
Fig. 5. Visualization of different methods on UC Merced dataset. From (a) to (e) are x2, x3, x4, x8 and x9 SR results, respectively.
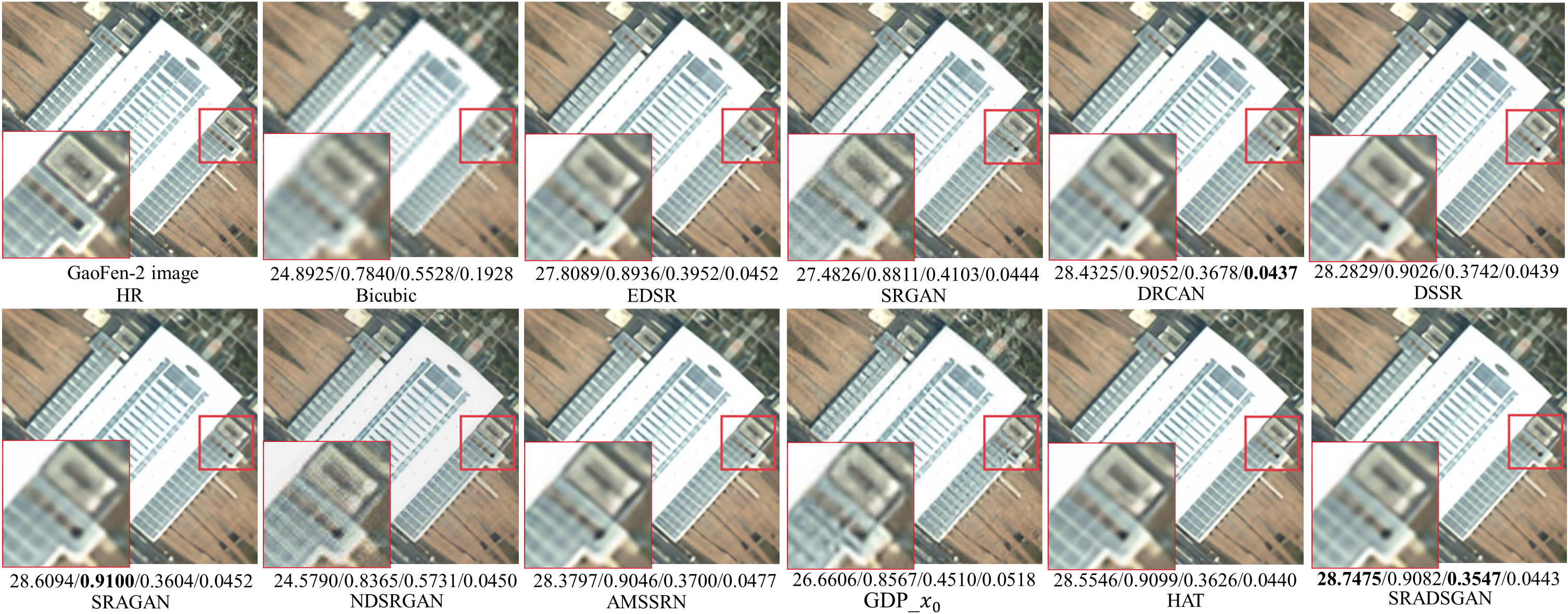
Fig. 8. 3-time super-resolution results of different methods on GaoFen-2 remote sensing image.
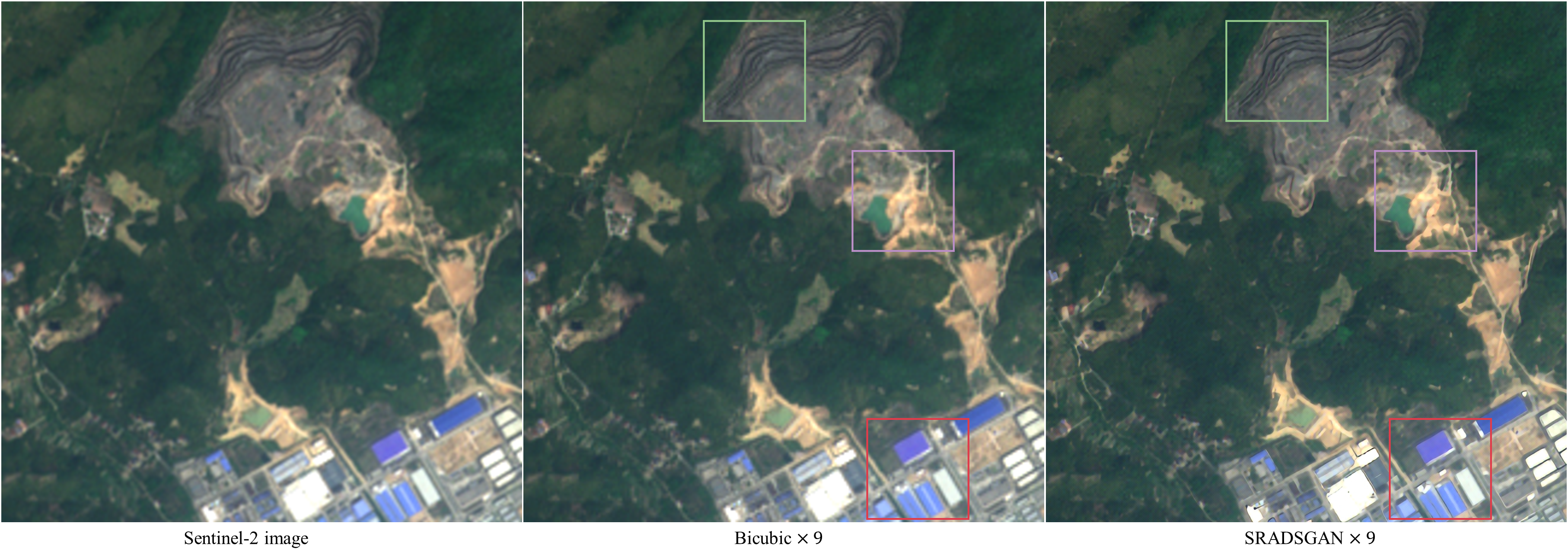
Fig. 9. 9-time super-resolution results on Sentinel-2 remote sensing image without downsampling.
If our code helps your research or work, please consider citing our paper.
F. Meng et al., "Single Remote Sensing Image Super-Resolution via a Generative Adversarial Network With Stratified Dense
Sampling and Chain Training," in IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, vol. 62, pp. 1-22, 2024, Art no. 5400822,
doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2023.3344112.