One of the powers of Zimbra is the ability to be extended with custom functionality. The Zimbra front-end can be extended with JavaScript Zimlets and the back-end can be extended with Java extensions. This article is a practical guide to writing Preact Zimlets for Zimbra 9 and above.
Zimbra 9 introduced the so-called Modern UI. The Modern UI is fully responsive and based on Preact. Preact itself is based on React and that is a framework for building applications on Node JS.
You will need to understand the basics of React, have some knowledge of ES6 JavaScript and NodeJS to be able to understand the sample code in this article. A good online course that can help you with these fundamentals can be found at https://www.udemy.com/course/the-complete-react-fullstack-course/
This article is part of a series. There is also a guide for back-end extensions at https://github.com/Zimbra/zm-extension-guide.
To follow the steps in this article you need a Zimbra test server. You also need a version of Zimbra that includes the Modern UI. The Modern UI is included in Zimbra Network Edition version 9 and higher. You can set this up in a Virtual Machine in the cloud or you can install it on your local computer inside VirtualBox/KVM/Parallels etc. If you decide to set it up on your local computer you need at least an i5 with 16GB of RAM and a SSD. Your test server needs to be accessible over SSH. Instructions on how to set up your Zimbra server: https://blog.zimbra.com/2018/01/install-zimbra-collaboration-8-8-ubuntu-16-04-lts/ make sure to install the latest patches. You can find instructions on how to install patches at https://wiki.zimbra.com/wiki/Zimbra_Releases
This article uses the Mytest back-end from the guide for back-end extensions at https://github.com/Zimbra/zm-extension-guide. Install a pre-compiled version to be sure you have it on your development server:
sudo rm -Rf /opt/zimbra/lib/ext/mytest
sudo mkdir /opt/zimbra/lib/ext/mytest
sudo wget https://github.com/Zimbra/zm-extension-guide/releases/download/0.0.8/mytest.jar -O /opt/zimbra/lib/ext/mytest/mytest.jar
su - zimbra
zmmailboxdctl restart
You need to deploy and enable the Zimlet Sideloader on your development server. You only have to do this step once.
sudo yum install zimbra-zimlet-sideloader
sudo apt install zimbra-zimlet-sideloader
su - zimbra
zmmailboxdctl restart
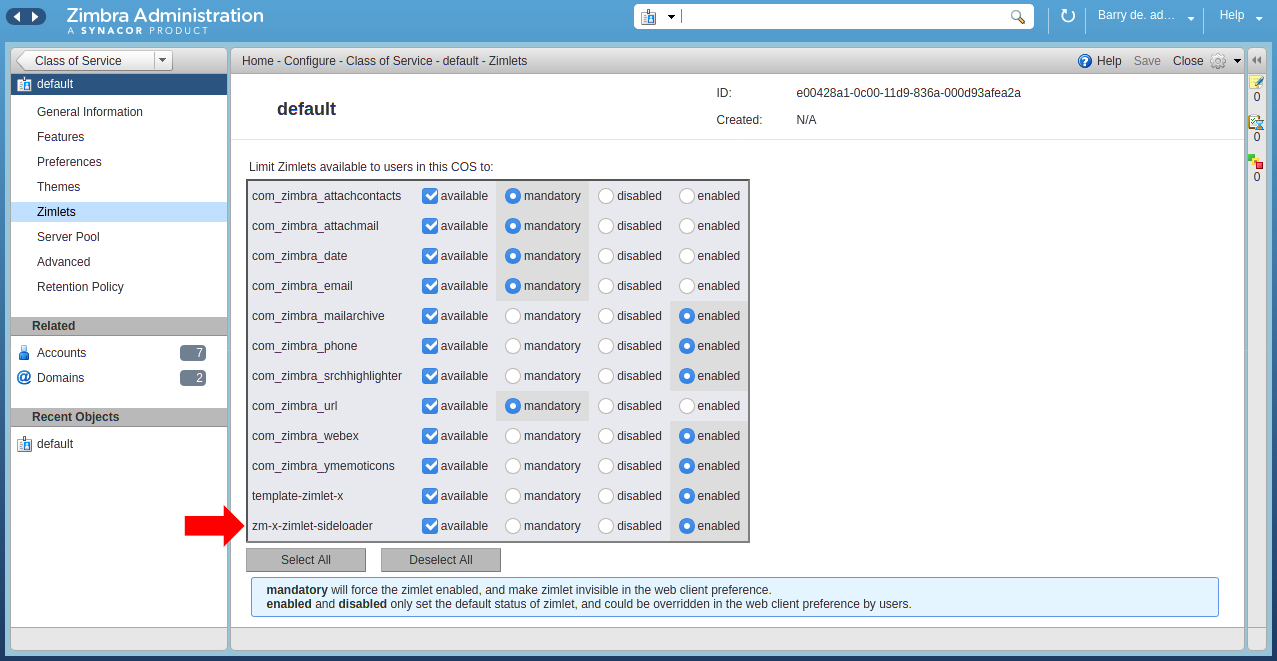 Verify that the Sideloader Zimlet is available and enabled for your Zimbra Class of Service (CoS) by logging into the Admin UI -> Home -> Configure -> Class of Service.
Verify that the Sideloader Zimlet is available and enabled for your Zimbra Class of Service (CoS) by logging into the Admin UI -> Home -> Configure -> Class of Service.
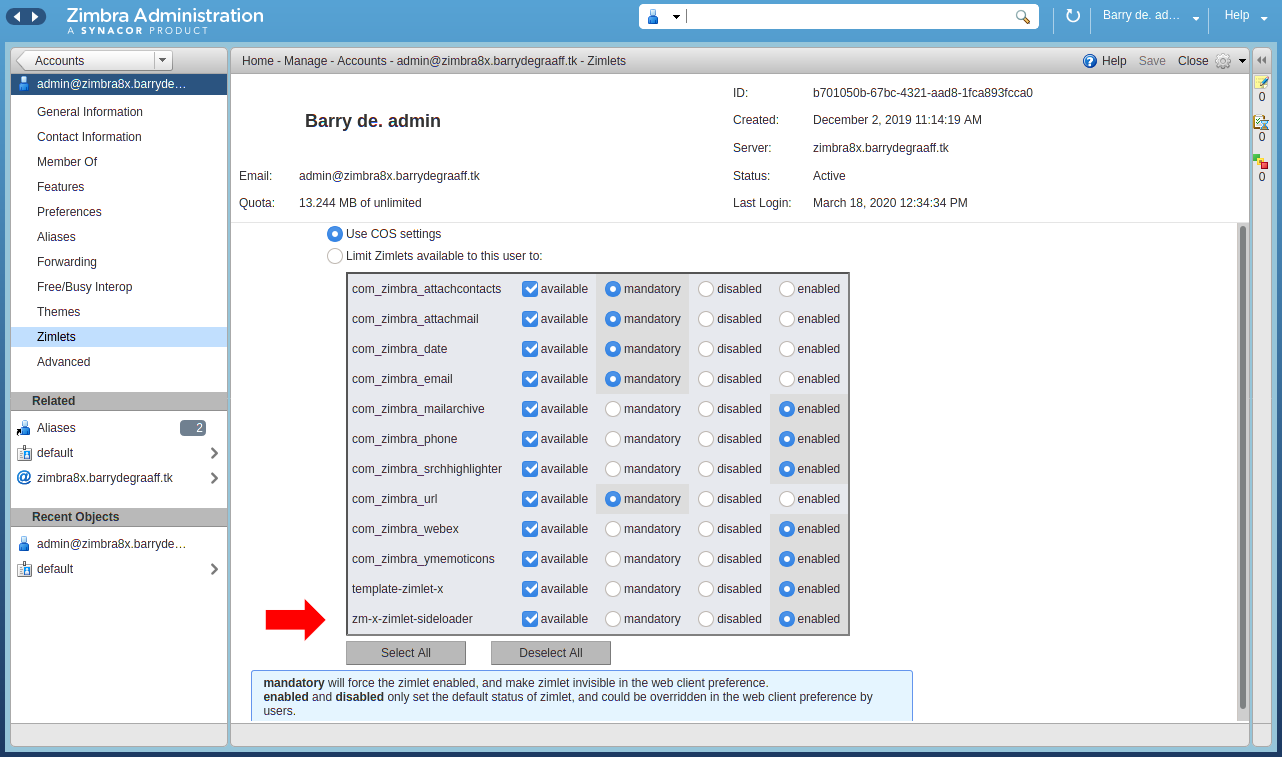 Verify that the Sideloader Zimlet is available and enabled for your Zimbra and account by logging into the Admin UI -> Home -> Manage -> Accounts.
Verify that the Sideloader Zimlet is available and enabled for your Zimbra and account by logging into the Admin UI -> Home -> Manage -> Accounts.
You can develop Zimbra Zimlets on any OS supported by NodeJS (https://nodejs.org/en/download/). This article will include Linux commands you can run on CentOS/Fedora/Redhat and Ubuntu. If you run on a different OS reading these commands should help you understand what you must do to get started.
Zimbra provides a tool called Zimlet CLI that is based on Webpack. It is used for building/packaging your Zimlet and for working with Zimlet templates. Install it on your local computer:
As root:
yum install nodejs
apt install nodejs
npm install -g @zimbra/zimlet-cli
⚠️ Make sure to install nodejs version 14.x or higher.
After installing Zimlet CLI you will have the zimlet command that you can run from the command line. Use --help to get access to the built in documentation.
zimlet --help
Zimlet client tool for developing and building Zimlets.
Type "zimlet [commmand] --help" for command specific usage information
Commands:
zimlet create [template] [dest] Create a new zimlet.
zimlet watch Start a development server
zimlet build Compile a zimlet
zimlet package Package a zimlet for deployment
You can also get command specific usage information:
zimlet create --help
zimlet create [template] [dest]
Create a new zimlet.
Options:
--version Show version number [boolean]
--help Show help [boolean]
--cwd A directory to use instead of $PWD. [default: "."]
--name The zimlet's name
--force, -f Force `dest` directory to created if it already exists; will
overwrite! [boolean] [default: false]
--yarn Install with `yarn` instead of `npm` [boolean] [default: false]
--git Initialize a `git` repository [boolean] [default: false]
--install, -i Install dependencies [boolean] [default: true]
--template Remote template to clone (user/repo#tag)
--dest Directory to create the zimlet
Create a folder on your local computer to store the MyTest Zimlet:
mkdir ~/zimbra_zimletx_course
cd ~/zimbra_zimletx_course
git clone https://github.com/Zimbra/zm-zimlet-guide
cd zm-zimlet-guide
cd advanced
npm install
zimlet watch
The output of this command should be:
Compiled successfully!
You can view the application in browser.
Local: https://localhost:8081/index.js
On Your Network: https://192.168.1.100:8081/index.js
Visit https://localhost:8081/index.js in your browser and accept the self-signed certificate. The index.js is a packed version of the MyTest Zimlet. More information about using SSL certificates can be found below.
Have you already used Zimlet Cli in the past? Make sure to update it using sudo npm install -g @zimbra/zimlet-cli. You can check your version using zimlet --version. You will need version 12.8.0 of Zimlet Cli for this Zimlet to work.
Log on to your Zimbra development server and make sure that you are seeing the modern UI. Then click the Jigsaw puzzle icon and Zimlets Sideloader. If you are not seeing the Zimlet Sideloader menu. You have to run apt/yum install zimbra-zimlet-sideloader on your Zimbra server and enable the Sideloader Zimlet in your Class of Service.
Sideload the
mytestZimlet by clicking Load Zimlet. The Zimlet is now added to the Zimbra UI in real-time. No reload is necessary.
Click on the mytest tab. If you followed the guide for back-end extensions this should look familiar. As what we see is an iframe that loads the extension from /service/extension/mytest.
Click the Send JSON button to send the HTML form to the back-end. The server will respond with a copy of the JSON data with added JSON elements for each file you uploaded.
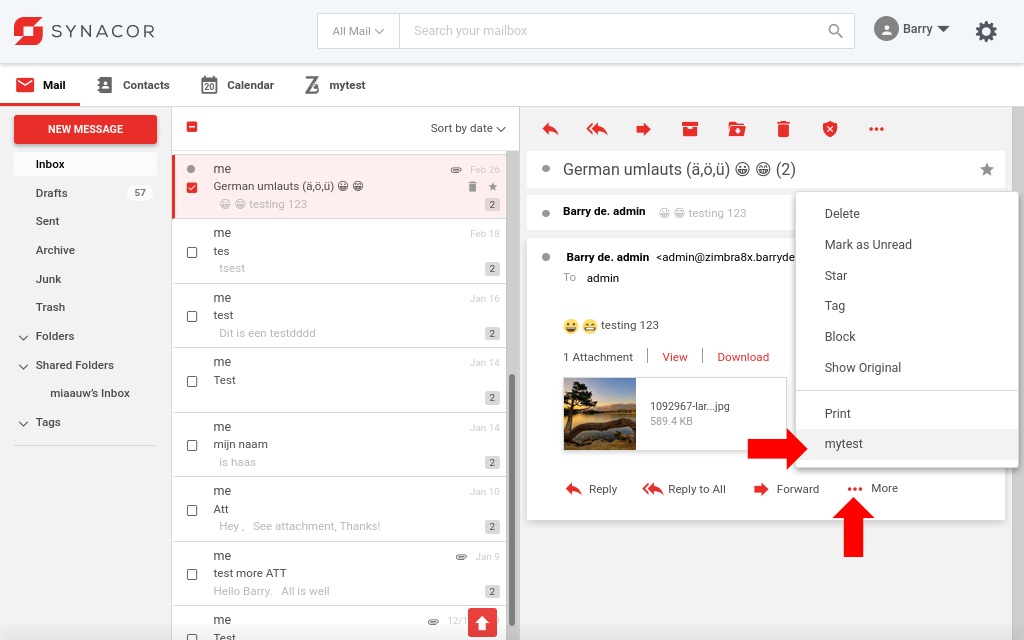 Click the
Click the mytest menu item in the More menu.
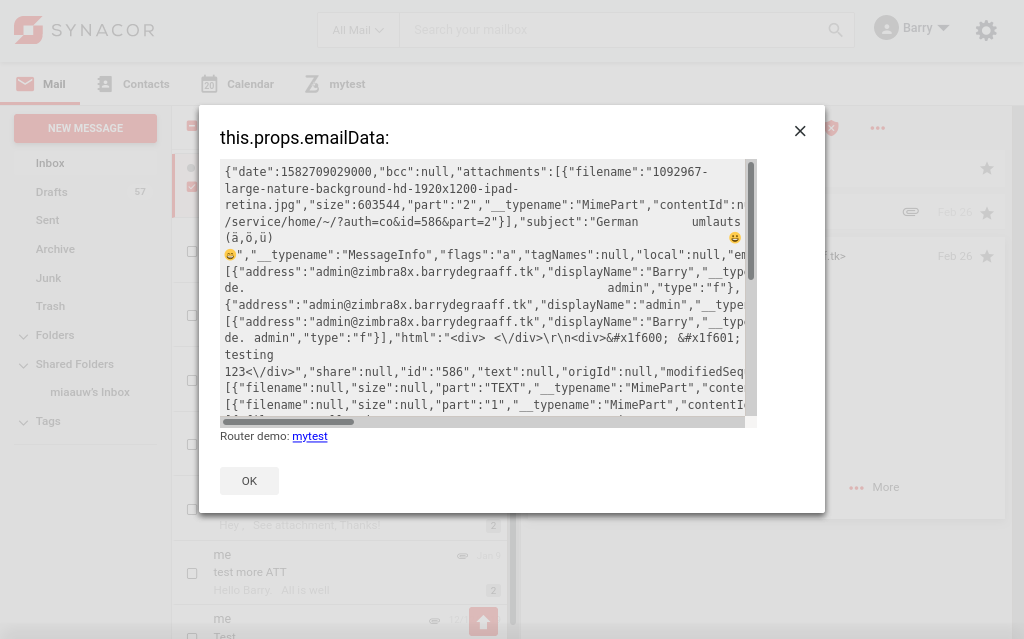 The selected email is sent to the back-end in JSON format, and the contents is displayed in the modal dialog.
The selected email is sent to the back-end in JSON format, and the contents is displayed in the modal dialog.
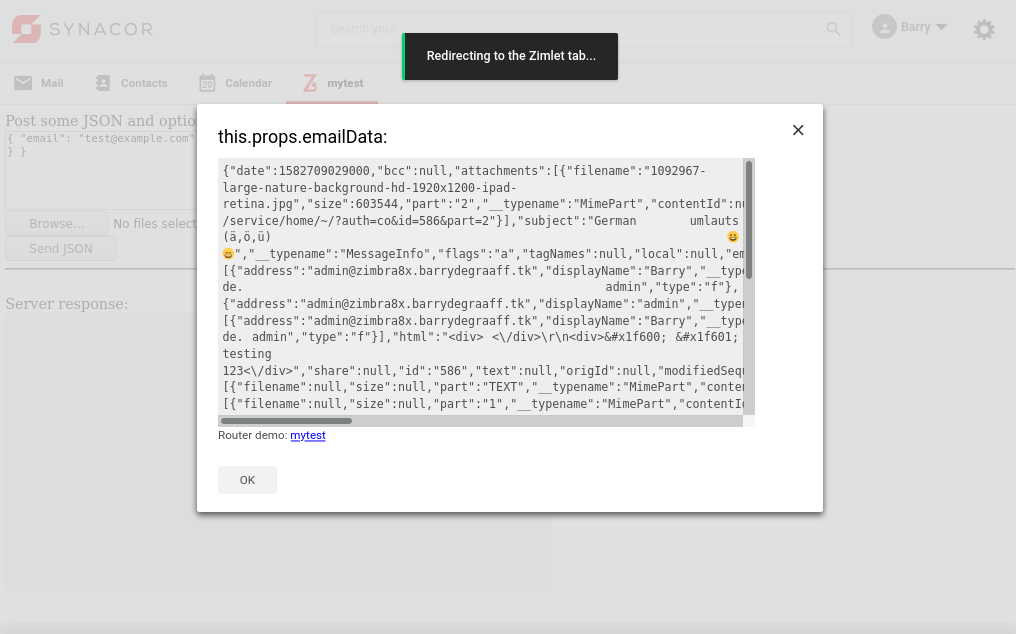 Click the
Click the mytest link in the dialog. This will show a demo toaster notification and switch to the mytest tab.
Summary of the functionality implemented in the mytest Zimlet:
- Create a new tab in the UI
- Implement a More menu item
- Show a modal dialog
- Show a toaster notification
- Redirect users by clicking a link
Visual Studio Code is an integrated development environment (IDE). It supports React out of the box and it will check your code for errors while you type it. It also has code auto-completion and automatic formatting of source files. There is a tutorial that shows you all NodeJS/React features: https://code.visualstudio.com/docs/nodejs/reactjs-tutorial
Go to https://code.visualstudio.com/ and install Visual Studio Code on your local computer.
To open the mytest Zimlet in Visual Studio Code click File -> Open Folder and select ~/zimbra_zimletx_course/zm-zimlet-guide/advanced/
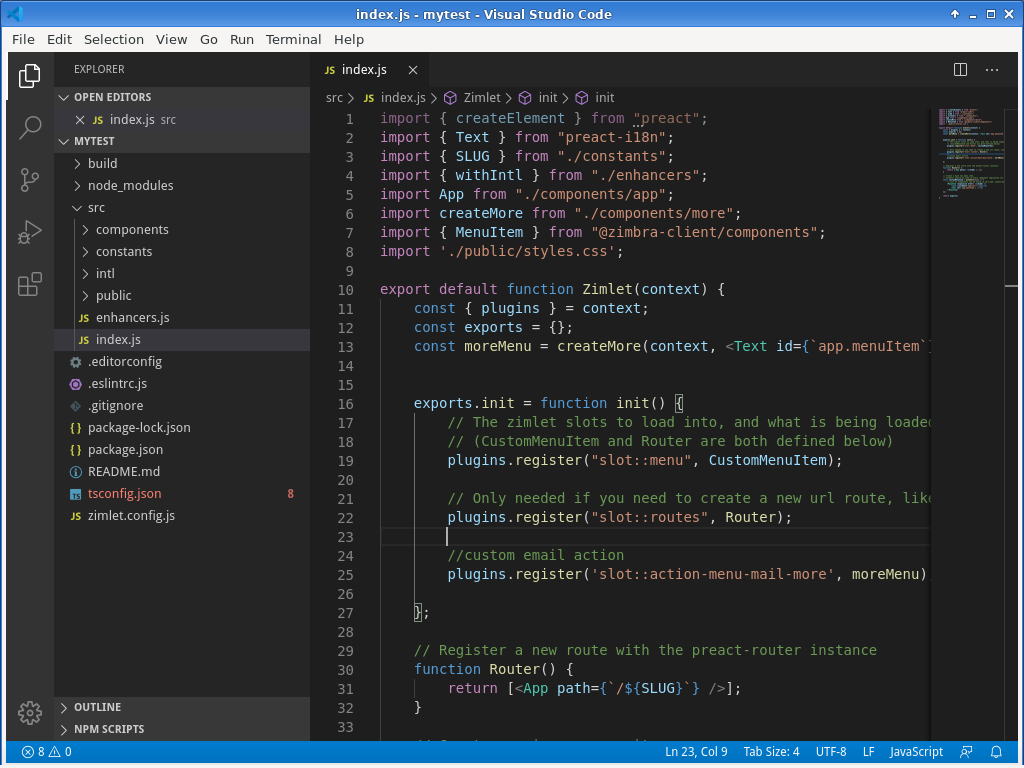 Visual Studio Code with the
Visual Studio Code with the mytest Zimlet loaded, pretty much works out of the box.
Zimlets are essentially Preact components that run in a sandbox within the Zimbra web application. Throughout the Zimbra application, there are hooks made available to Zimlets for injecting components into the application. These hooks are called ZimletSlots.
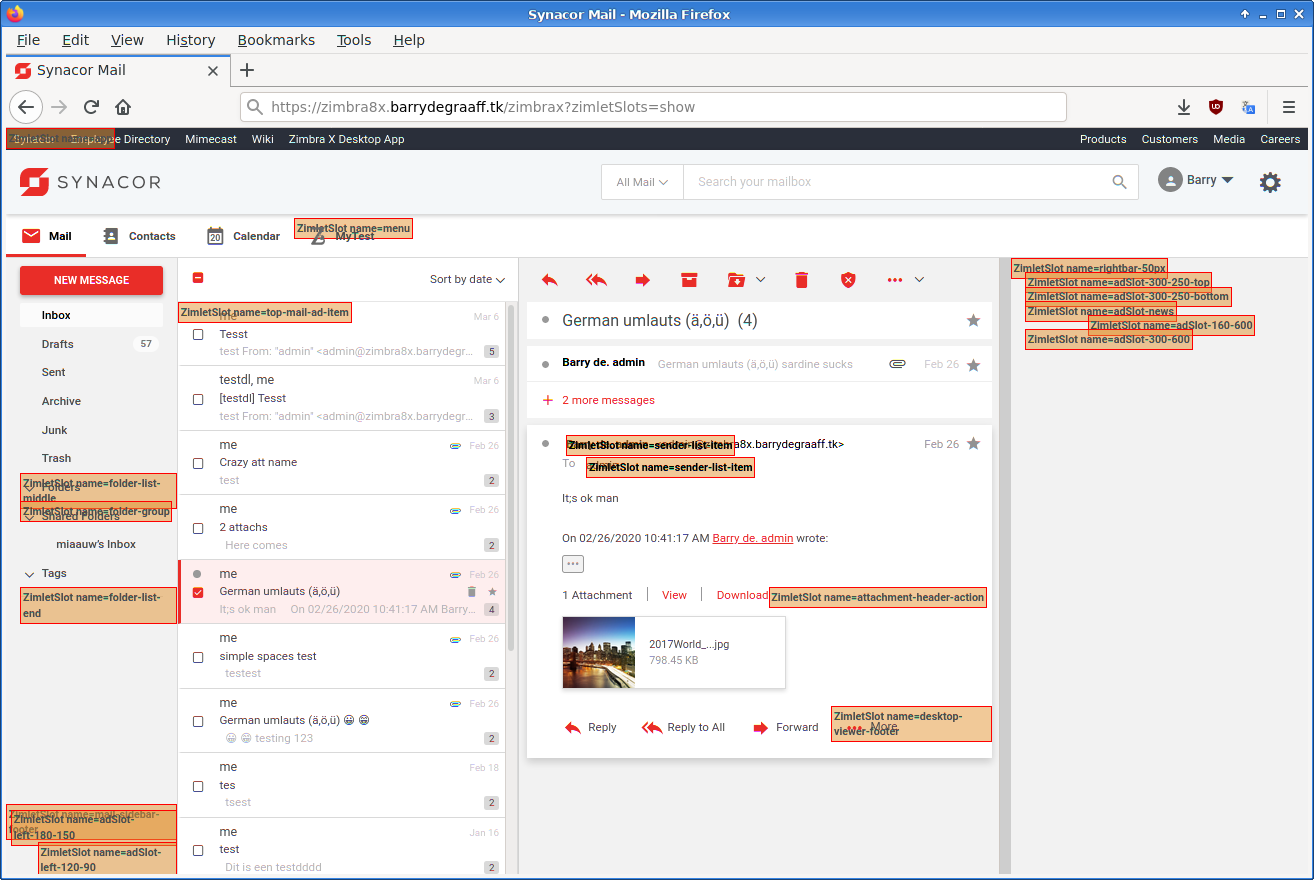
To see which slots are available in the UI, add ?zimletSlots=show to the end of the URL of Zimbra. This will show all of the places in the active UI where ZimletSlots are available.
Slots that are not visible, such as the routes slot which allows for adding URL routes to screens in the app, will present a message in the browser console, such as:
non-visible ZimletSlot name=routes
non-visible ZimletSlot name=searchInputPlaceholder
The ZimletSlots will remain visible until the page is refreshed without zimletSlots=show in the URL.
Zimbra passes the Zimlet context object into every Zimlet when they are created. Context allows the Zimlet to interact with the main application by registering plugins. It allows the main application to pass data into the Zimlet. Zimbra passes the context only to the component defined in src/index.js. You need to pass the context to any additional components that need it.
Here are some examples that show you how to work with context:
//getAccount() is a function in the context object. It returns an object with current account name, id, display name and other account attributes:
context.getAccount()
//Get an object with the name 'plugins' from context and define it in the current scope:
const { plugins } = context;
//Call the register function from the 'plugins' object to register a Zimlet slot:
plugins.register('slot::action-menu-mail-more', moreMenu);
//Get a function with the name 'dispatch' from an object with the name 'store' and define in the scope
const { dispatch } = context.store;
//Call the dispatch function to show a modal dialog defined in this.modal.
dispatch(context.zimletRedux.actions.zimlets.addModal({ id: 'addEventModal', modal: this.modal }));Re-usable components from the Zimbra application are made available to the Zimlet via shims. You can find the latest shims in context.shims. To use the ModalDialog function from the @zimbra-client/components shim you would import it like this:
import { ModalDialog } from '@zimbra-client/components';Please be aware that when you sideload a Zimlet, the shims are provided by Zimlet CLI from your local machine. These shims may differ from the ones in the Zimbra application. This will happen for example if outdated Zimlet CLI/shims and (node) modules are available on your local machine. It is recommended to test your work from time to time in a fresh environment.
Take a look at package.json and make sure you do not include dependencies that are already shimmed. Be aware that package-lock.json gets generated automatically from your package.json and as long as package-lock.json exists the dependencies from that file take precedence over package.json. package-lock.json does not automatically regenerate if you make changes to package.json!
- A lot of React code examples use setState to trigger re-rendering of components. Be careful when using it as it works asynchronous and avoid it if you can.
- The Zimlet is Sandboxed and runs in a separate environment that feels like an iframe. Global variables like window.location can be accessed using window.parent.location.
- Interacting with the DOM directly will not work in most cases as that is abstracted away by the framework. If you really must you can do things like window.parent.querySelectorAll and window.parent.document.body.appendChild.
Now that you have created a Zimlet and see it running in the UI. You can use Visual Studio Code to analyze the code to understand how the example Zimlet mytest works. Import statements can import components, json data, stylesheets etc. These imports can be dependencies provided by the Zimbra application/Zimlet CLI or be components from your Zimlet. Usually when an import starts with ./ or ../ it is a component from your Zimlet. Otherwise it is a dependency.
//This is a dependency loaded from Zimbra:
import { createElement } from "preact";
//These are dependencies from our Zimlet sources:
import createMore from "./components/more";
import MoreMenu from '../more-menu';The index.js in the root of your src folder will be called by Zimbra to load your Zimlet. This is where you configure what Zimlet slots to use and what routes to add to the application. A route is a location in the URL of your browser. Read the comments in code to learn more:
//Load components from Zimbra
import { createElement, Fragment } from 'preact';
import { Text } from 'preact-i18n';
import { provide } from 'preact-context-provider';
import { withIntl } from './enhancers';
import { MenuItem, GenericMobileUISidebar, GenericMobileUIToolbar } from '@zimbra-client/components'; // Sidebar/Toolbar are so nav menu is accessible in mobile
import { Button } from '@zimbra-client/blocks';
import { useCallback } from 'preact/hooks';
//Load the createMore function from our Zimlet component
import createMore from './components/more';
//Load a style static stylesheet (Preact will not change this)
import './public/styles.css';
const App = () => {
const handleClick = useCallback(() => alert('Test OK!'), []);
return (<Fragment>
<GenericMobileUIToolbar />
<GenericMobileUISidebar />
<Button onClick={handleClick}>Zimlet Callback Test</Button>
<iframe class={'MyTestWrapper'} src="/service/extension/mytest"/>
</Fragment>);
};
//Create function by Zimbra convention
export default function Zimlet(context) {
//Get the 'plugins' object from context and define it in the current scope
const { plugins, store, zimbraBatchClient } = context;
const { dispatch, zimletRedux } = store;
const exports = {};
exports.init = function init() {
// The zimlet slots to load into, and what is being loaded into that slot
// (CustomMenuItem and Router are both defined below)
plugins.register('slot::integrations-tab-item', CustomMenuItem);
// Only needed if you need to create a new url route, like for a menu tab, or print, etc
plugins.register('slot::routes', Router);
//Here we load the moreMenu Zimlet item into the UI slot:
plugins.register('slot::action-menu-mail-more', provide(context)(createMore));
};
// Register a new route with the preact-router instance
function Router() {
return [<App path={'/integrations/MyTest'} />];
}
// Create a main nav menu item.
// withIntl should be used on every component registered via plugins.register(). You will see this in the App index.js file as well
const CustomMenuItem = withIntl()(() => (
// List of components can be found in zm-x-web, zimlet-manager/shims.js, and more can be added if needed
<MenuItem responsive href={'/integrations/MyTest'}>
<span className='appIconMyTest'></span><b>
<Text id={'zimbra-zimlet-mytest.menuItem'} /></b>
</MenuItem>
));
return exports;
}
If you do not understand the use of <> and {} take a look at the at https://www.udemy.com/course/the-complete-react-fullstack-course/.
The mytest item in the More menu is registered in the main index.js with these lines of code:
import createMore from './components/more';
...
plugins.register('slot::action-menu-mail-more', provide(context)(createMore));createMore is imported from src/components/more/index.js.
Open src/components/more-menu/index.js to find out how to:
- Show a modal dialog
- Show a toaster notification
- Redirect users by clicking a link
Similar to to more menu a new tab is added to the UI. The mytest tab is registered in the main index.js with these lines of code:
plugins.register('slot::integrations-tab-item', CustomMenuItem);
// Register a new route with the preact-router instance
function Router() {
return [<App path={'/integrations/MyTest'} />];
}
// Create a main nav menu item.
// withIntl should be used on every component registered via plugins.register(). You will see this in the App index.js file as well
const CustomMenuItem = withIntl()(() => (
// List of components can be found in zm-x-web, zimlet-manager/shims.js, and more can be added if needed
<MenuItem responsive href={'/integrations/MyTest'}>
<span className='appIconMyTest'></span><b>
<Text id={'zimbra-zimlet-mytest.menuItem'} /></b>
</MenuItem>
));CustomMenuItem holds the HTML loaded into the slot and has the HTML link to our tab. <MenuItem> is a component that returns HTML and SLUG is a static string loaded from src/constants/index.js. The Router() function is what ties an instance of App to the url location of our tab.
To find out more about adding menu items to vericals in Zimbra see the AnyFrame Zimlet: https://github.com/Zimbra/zimbra-zimlet-anyframe
To create a Zimlet zip file to be used with zmzimletctl deploy you can use zimlet package command. The zip will be in the pkg folder:
zimlet build
zimlet package -v 0.0.1 --zimbraXVersion ">=0.0.1" -n "mytest-zimlet" --desc "A Zimlet to learn about Zimbra Zimlets" -l "Test Zimlet"
By default Zimlet-CLI will generate a self-signed certificate. Web browsers will give you the option to temporary trust the certificate by clicking Accept the risk or Proceed to localhost (unsafe). From time to time browsers will require you to re-confirm trusting the certificate. Since the Sideloader Zimlet cannot answer trusts questions it will fail in the background when this happens. If you want you can install a trusted certificate so your work is not interrupted. This example uses Let's Encrypt:
#stop your dev server by hitting CTRL+C or `killall node`
cat /etc/letsencrypt/live/zimlets.example.com/privkey.pem >
'/usr/local/lib/node_modules/@zimbra/zimlet-cli/node_modules/webpack-dev-server/ssl/server.pem'
cat /etc/letsencrypt/live/zimlets.example.com/cert.pem >>
'/usr/local/lib/node_modules/@zimbra/zimlet-cli/node_modules/webpack-dev-server/ssl/server.pem'
export HOST=zimlets.example.com && zimlet watch
Now that you have completed your Zimlet, don't forget to test it
- on the latest version of Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and MS Edge, and
- with multiple languages.
Please take a look at Web Accessibility and see what you can do so that people with disabilities can use your Zimlet.