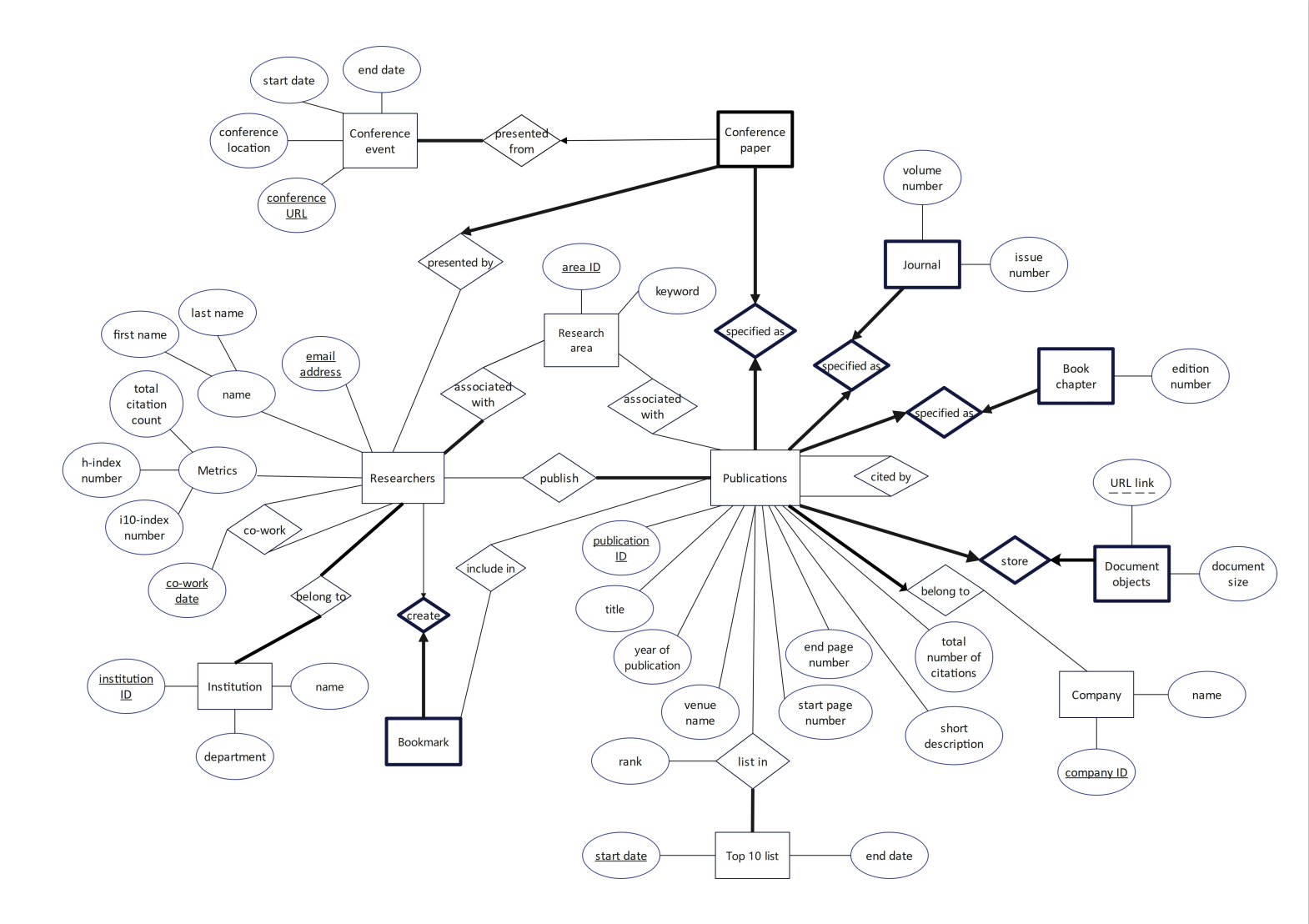
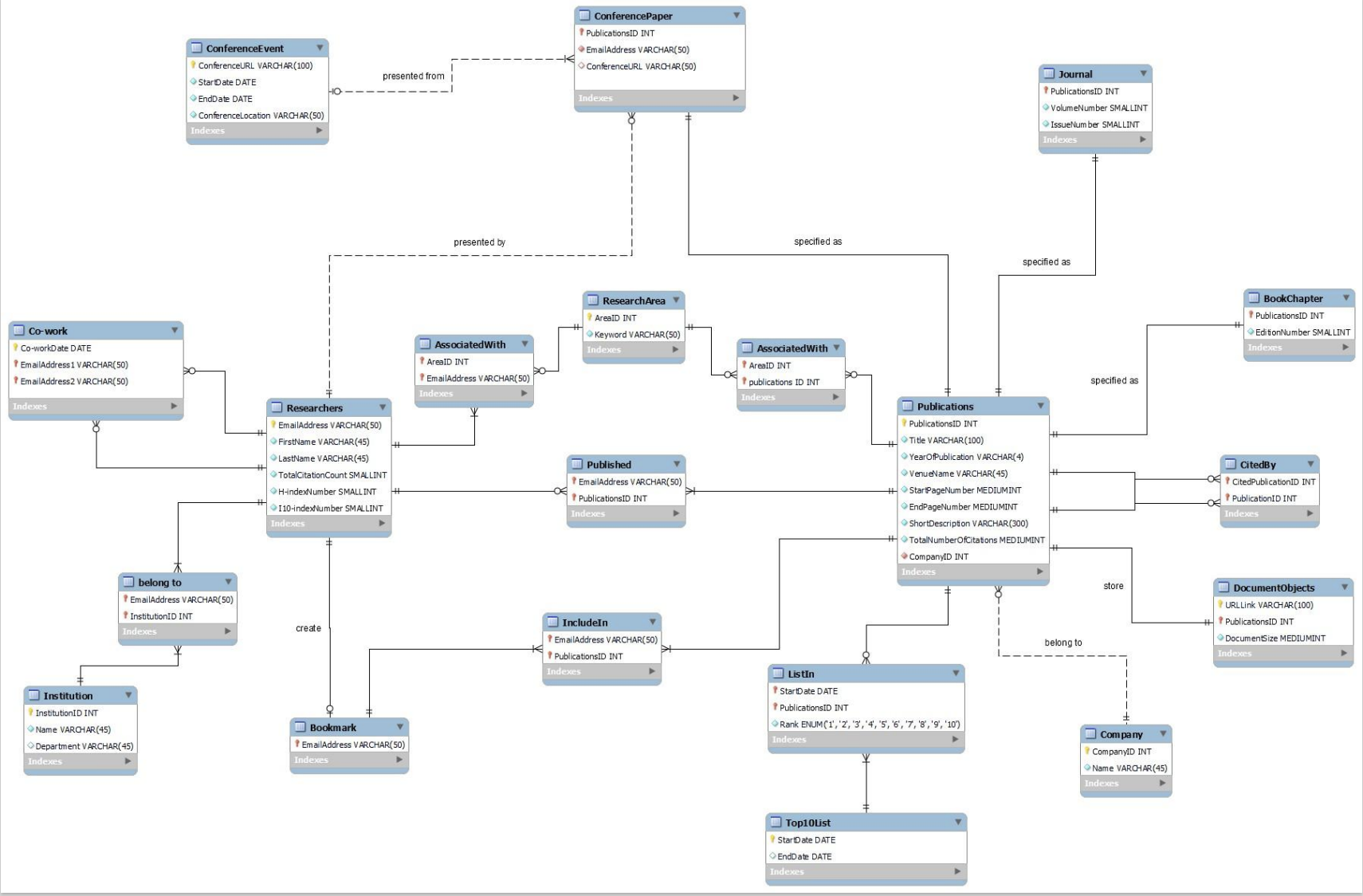
Google scholar is a free accessible web search engine that provides a broad range of information on scholarly publications. It also provides information on researchers, relations among scholarly publications and researchers, and different metrics to measure impact of publications. Your team has been asked to design a MySQL database to store information about the researchers, the details of the publications, and relations among researchers and publications. With your design, Google scholar hopes to improve access and searching of the data. The following specifications have been provided to your team to assist in your design.
For each researcher profile, Google scholar records the researcher’s details such as first name, last name, a unique email address tied to the researcher, and the institution(s) the researcher is affiliated with. A researcher can be affiliated with one or multiple institutions. For each institution, the name of the department, if exists (e.g., Computing and Information Systems), and the name of the institution (e.g., The University of Melbourne) are stored. Each researcher can also be associated with a few keywords representing their ‘research area’, such as Databases, Machine learning, Psychology, Medicine, etc. Each researcher is also associated with multiple metrics providing insight on their research quality. A researcher has a total citation count number (e.g., 203) that denotes the total number of times their publications have been cited by other publications (see ‘Publications’ for the details on citations), an h-index number (e.g., 15) and an i10- index number (e.g., 12). An h-index value of 15 means that this researcher has 15 publications that have each been cited at least 15 times (similarly an h-index of 14 implies that the researcher has 14 publications that have each been cited at least 14 times). An i10-index value is the number of publications with at least 10 citations.
Google scholar maintains three types of publications: conference papers, journals, and book chapters. For each publication, Google scholar stores its title, year of publication, publication venue name, a list of authors (there can be multiple authors of a publication, where each author is a researcher), start page number (e.g., 475), end page number (e.g., 500), a short description (which is denoted as its abstract), and publisher company (assume only one publisher company per publication). Google scholar may also store a few keywords such as Databases, Machine learning, Psychology, etc for the ‘research area’ of each publication. Each publication has a list of references (i.e., it “cites” other publications), where each reference is another publication. If publication A is in the reference list of another publication B, then B is “cited by” A. For each publication, Google scholar also shows the total number of its citations, which denotes the number of times that the publication was cited by other publications. The following figure shows an example publication with its basic information and its list of references.
Google scholar database will not store the actual publications, but rather a link to the document objects. Each publication is linked to one document object. For each document object, Google scholar stores the URL link and the document size in KB. For each journal, the volume number and the issue number of the journal publication are also stored. Each book chapter has an edition number. Each conference paper is associated with a conference event where one of the authors (researchers) of the paper needs to make an oral presentation of the paper. Multiple conference papers can be presented in the same conference event, but a conference paper can be presented in only one conference event. Google scholar stores the following information for each conference event: the location (e.g., Melbourne, Australia) of the conference, the start date, the end date of the conference, and the URL to the conference event website. For each conference paper, the author who presents that paper in the conference, is also stored.
For each researcher, Google scholar stores their list of publications. The researchers who author a publication together are called ‘co-authors’. A researcher can create a list of publications as ‘bookmark’ that they find important. A publication can be added or removed from the ‘bookmarked’ list of a researcher, but Google scholar does not record the history of bookmarks. Only the publications that are currently in the ‘bookmarked’ list for a researcher, are stored.
Google scholar manually curates a list of top 10 publications every fortnight depending on the number of citations of the publications. A publication can make it to top 10 more than once over time. We must be able to determine how many times a publication has been in the top 10 (but we do not need to know the rationale why this is the current ranking, i.e. we do not need to track publication citations throughout time). A publication can stay in the top 10 at the same or different rank. For example, the publication entitled “Learning to index” can be number 1 from January 1st – January 14th, 2022 but the rank drops to number 3 from January 15th-January 31st, 2022. For each such rank, we must keep a record of start date when a publication reached that position and end date when it was removed from the position (and potentially from the list altogether).