Project code for CS6250 (Computer Networking) at Georgia Tech for fall 2014, lectures freely available through Udacity. Work done using Mininet to simulate network environments.
Nam Pho (npho3@gatech.edu)
Forked from https://github.com/OMS6250/gt-cs6250 on 9/4/14
Final thoughts: this was my first Gtech OMSCS course and I loved the quality of the lecture content. The hw assignments were relevant and fun although I felt (as was confirmed by many of my classmates on Piazza) that the quiz questions were sometimes confusingly worded.
##Table of Contents
- Notes
- assignment-1 Mininet Setup (10/10)
- assignment-2 Mininet Topology (10/10)
- assignment-3 Parking Lot (11.5/10)
- assignment-4 Learning Switch (9.5/10)
- assignment-5 Buffer Bloat (8/10)
- assignment-6 TCP Fast Open (9/10)
- assignment-7 SDN and Firewalls (10/10)
- assignment-8 SDN and DoS Attacks (9.5/10)
- assignment-9 Replicating Research (18/20)
Final Grade = (0.5*hw1 + sum(hw2-hw9))/95 * 100 = 95.26%
Hw assignments were equal parts coding and quiz questions. All the code in this repo is correct for the assignments and points lost were exclusively from quiz questions.
####Notes 1. Clone the original OMS6250 repo and fork it.
$ git clone https://github.com/OMS6250/gt-cs6250.git
2. Adjust the repo to point to your fork and then upstream as the original.
$ git remote set-url origin git@github.com:nampho2/CS6250.git
$ git remote add upstream https://github.com/OMS6250/gt-cs6250.git
3. Keep fork in sync with original from Github docs.
$ git fetch upstream
$ git checkout master
$ git merge upstream/master
4. Adjust PYTHONPATH environment variable to include helpful cross-assignment imports.
export PYTHONPATH=`pwd`/lib/:$PYTHONPATH
or
export PYTHONPATH=/home/mininet/gt-cs6250/lib/:$PYTHONPATH
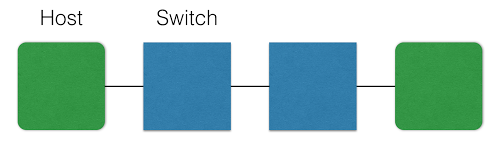
####assignment-2: Mininet Topology
- Run
topology.shand review output. - Modify
mntopo.pyto insert an additional switch between the hosts. Helpful to review Mininet documentation on this. - Rerun
topology.sh, output should be similar. - Test latency by running the ping wrapper,
ping.py. Should get ~6ms. - Increase the latency delay from 1ms to 10ms in
mntopo.py. - Re-test latency. Should get ~60ms.
- Increase the bandwidth from 10Mbps to 50Mbps in
mntopo.py. - Re-run
topology.shand review output.
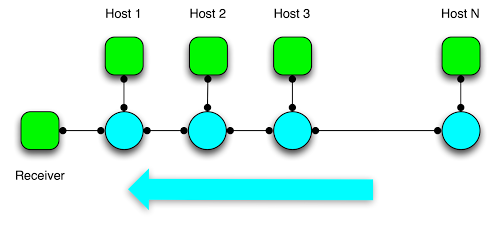
####assignment-3: Parking Lot
- Complete the
__init__function of theParkingLotTopoclass to generalize this for any number of hosts, n > 0. The resulting topology is as shown in the figure above. - Complete the
run_parkinglot_exptfunction to generate TCP flows usingiperf. - Final result is running
sudo ./parkinglot-sweep.shto test various parameters ofn = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5. - Run my additional
submit.shscript to collect the output ofparkinglot-sweep.shwrapper per submission specifications. Submit allbwm.txtfiles. - Complete additional quiz questions in
quiz.txt.
####assignment-4: Learning Switch
- Code
learn_route()function inlearning-switch.pycode to generate ARP tables. - Run topology with commands:
# symbolically link topology to pyretic
$ ln -s ~/CS6250/assignment-4/learning-switch.py ~/pyretic/pyretic/modules/
# run pyretic first
$ cd ~/pyretic/
$ python pyretic.py -m p0 pyretic.modules.learning-switch
# run mininet in separate terminal
$ cd ~/CS6250/assignment-4/
$ sudo python learning-switch-topo.py
# pingall hosts
mininet> pingall
- Answer some quiz questions in
hw4.txt. - Note: use
arpingto send single ARP packets and watch the learning switch in action to answer quiz.
# install arping in Ubuntu
$ sudo apt-get install arping
# 0. h2 ping (ICMP) h6
mininet> h2 ping h6
# 3. h2 ARP request to h6
mininet> h2 arping -B -c 1 h6
# 4. h6 ARP reply to h2
mininet> h6 arping -b -c 1 -t 00:00:00:00:00:02 h2
# 5. h6 ARP request to h3
mininet> h6 arping -B -c 1 h3
# 6. h3 ARP reply to h6
mininet> h3 arping -b -c 1 -t 00:00:00:00:00:06 h6
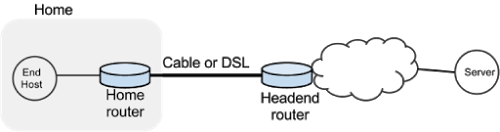
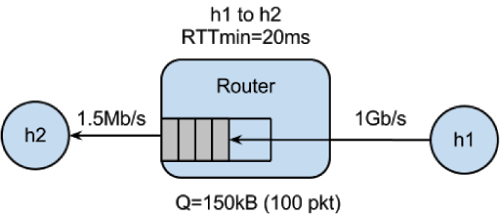
####assignment-5: Buffer Bloat
Simulate buffer bloat as seen on typical home ISP connection as seen in the figure below:
The corresponding abstract Mininet topology is represented below:
1. Run select Mininet topology with various buffers and sizes.
# 100 packet router buffer
$ sudo ./run.sh
# smaller 20 packet router buffer
$ sudo ./run-minq.sh
# 2 queue router buffer
$ sudo ./run-diff.sh
2. Run monitoring script if desired, cwnd data saved to <title of run>_tcpprobe.txt file.
$ ./monitor.sh <title of run>
3. Saturate the router bandwidth using iperf script from h1 to h2, watch the packet flow for ~70s for equilibrium and then request data under resource contention and saturated bandwidth using wget.
# run iperf script
mininet> h1 ./iperf.sh
# watch packets, wait ~70s
mininet> h2 tail -f ./iperf-recv.txt
# get data under saturated bandwidth using wget
mininet> h2 wget http://10.0.0.1
4. Visualize how router handles resource contention, go to http://<IP>:8000.
$ sudo ./plot_figures.sh <title of run>
####assignment-6: TCP Fast Open
1. Read the original TCP Fast Open (TFO) paper [PDF] to answer quiz questions. Additional useful slides here.
2. Run the simulation and record as observations.txt file, basically should show that there are web performance enhancements under TFO vs not TFO. Experiment inspired from other assignment.
# install pre-req packages
$ sudo apt-get update
$ sudo apt-get install vnc4server
$ sudo apt-get install libnss3-dev
$ sudo easy_install termcolor
# run simulation
$ vnc4server
$ sudo ./run.sh
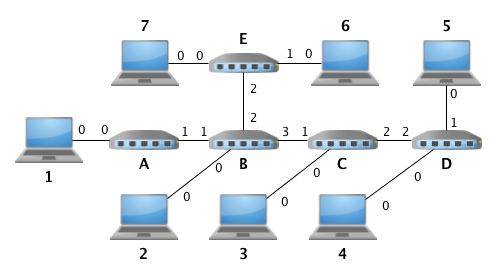
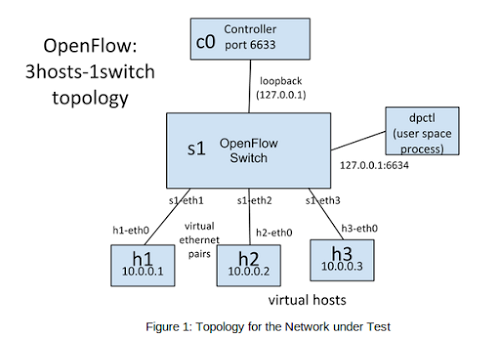
####assignment-7: SDN and Firewalls
Work with Software Defined Networking (SDN) controllers in Python, specifically POX and Pyretic languages. Use the SDN languages to implement a firewall based on L2 and L3 headers (i.e., IP and MAC addresses) between h1 and h2 as shown in the diagram below.
- Implement the firewall policies in
firewall-policies.csvby editingpox_firewall.pyandpyretic_firewall.py, a good POX resource for this assignment is and a good Pyretic resource. - Clean up your environment between every run.
- Run your respective controller w/firewall in POX or Pyretic.
- Create networking environment (i.e., run mininet).
- Test if firewall rules are actually implemented in each controller by running
ping(below).
# clean up environment
$ sudo fuser -k 6633/tcp
$ sudo mn -c
# POX setup
$ ln -s ~/CSCS6250/assignment-7/firewall-policies.csv ~/pox/pox/misc/
$ ln -s ~/CSCS6250/assignment-7/pox_firewall.py ~/pox/pox/misc/
$ pox.py log.level --DEBUG forwarding.l2_learning misc.pox_firewall &
# Pyretic setup
$ ln -s ~/CSCS6250/assignment-7/firewall-policies.csv ~/pyretic/pyretic/examples/
$ ln -s ~/CSCS6250/assignment-7/pyretic_firewall.py ~/pyretic/pyretic/examples/
$ pyretic.py pyretic.examples.pyretic_firewall &
# create network
$ sudo mn --topo single,3 --controller remote --mac
# h1 and h2 should drop packets
mininet> h1 ping -c1 h2
mininet> h2 ping -c1 h1
# h3 should not
mininet> h1 ping -c1 h3
mininet> h3 ping -c1 h1
mininet> h2 ping -c1 h3
mininet> h3 ping -c1 h2
####assignment-8: SDN and DoS Attacks
- Use sFlowRT to monitor network traffic.
- Use PyResonance to alter network traffic in response to events (e.g., DoS attack).
### 1st window (create network)
# start 3 node mn
$ sudo mn --controller=remote --topo=single,3
### 2nd window (monitoring agent)
# create sFlow agent
$ sudo ovs-vsctl -- --id=@sflow create sflow agent=eth0 target=\"127.0.0.1:6343\" sampling=2 polling=20 -- -- set bridge s1 sflow=@sflow
# start sFlowRT
$ ./start.sh
### 3rd window (SDN switch)
# copy policy files to pyretic/pyresonance/apps/
# copy config file to pyretic/pyresonance/
# run pyretic switch
$ ./pyretic.py pyretic.pyresonance.main --config=./pyretic/pyresonance/global.config --mode=manual
- Make changes to the
dos_policy.pyfile to drop DDoS attack connections. - Test below.
# confirm all 3 hosts can ping each other
mininet> pingall
# get console on h1
mininet> xterm h1
# start DoS sttack from h1
$ sudo ping 10.0.0.2 -i .05
# confirm that h1 now blocked from all other hosts
mininet> pingall
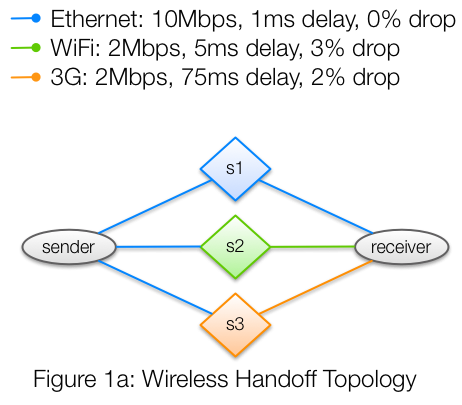
####assignment-9: Replicating Research
- This is an experiment in Multipath TCP (MPTCP).
- Implement the network topology below by completing TODO sections.
- Additional quiz questions.
# upgrade kernel
$ sudo ./install_mptcp_raring.sh
# confirm testing env
$ sudo ./test_mptcp.py --bw 10 --mptcp -n 2
# run experiments
$ sudo ./mptcp_handoff.sh
$ sudo ./mptcp_sweep.sh