Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Large Language Models (LLM) with Fine-Tuning LLM and make Question answering (QA) with LoRA and Flan-T5 Large
In this notebook we're going to Fine-Tuning LLM:
Many LLMs are general purpose models trained on a broad range of data and use cases. This enables them to perform well in a variety of applications, as shown in previous modules. It is not uncommon though to find situations where applying a general purpose model performs unacceptably for specific dataset or use case. This often does not mean that the general purpose model is unusable. Perhaps, with some new data and additional training the model could be improved, or fine-tuned, such that it produces acceptable results for the specific use case.
Fine-tuning uses a pre-trained model as a base and continues to train it with a new, task targeted dataset. Conceptually, fine-tuning leverages that which has already been learned by a model and aims to focus its learnings further for a specific task.
It is important to recognize that fine-tuning is model training. The training process remains a resource intensive, and time consuming effort. Albeit fine-tuning training time is greatly shortened as a result of having started from a pre-trained model.
T5 Model
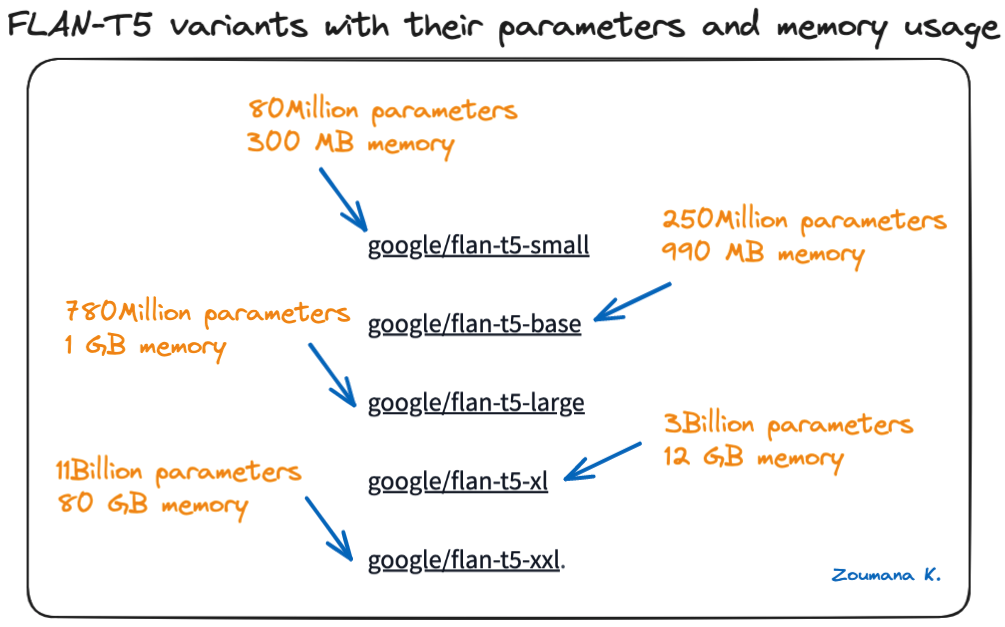
Multiple formats of FLAN-T5 models are available on Hugging Face, from small to extra-large models, and the bigger the model, the more parameters it has.
Below are the different model sizes available from the Hugging Face model card:
FLAN-T5 variants with their parameters and memory usage
Choosing the right model size The choice of the right model size among the variants of FLAN-T5 highly depends on the following criteria:
- The specific requirements of the project
- The available computational resources
- The level of performance expected
Fine-Tuning with LoRA
Fine-tuning, a crucial aspect of adapting pre-trained models to specific tasks, has witnessed a revolutionary approach known as Low Rank Adaptation (LoRA). Unlike conventional fine-tuning methods, LoRA strategically freezes pre-trained model weights and introduces trainable rank decomposition matrices into the Transformer architecture's layers. This innovative technique significantly reduces the number of trainable parameters, leading to expedited fine-tuning processes and mitigated overfitting.
Text Generation vs Text2Text Generation
Text Generation:
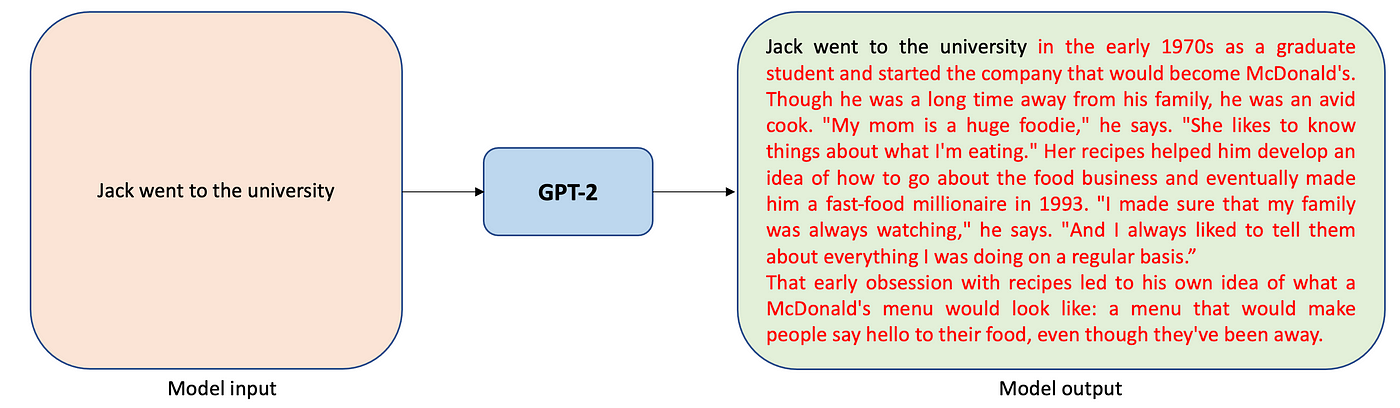
Text Generation, also known as Causal Language Modeling, is the process of generating text that closely resembles human writing.
It utilizes a Decoder-only architecture and operates in a left-to-right context. Text Generation is often employed for tasks such as sentence completion and generating the next lines of poetry when given a few lines as input. Examples of Text Generation models include the GPT family, BLOOM, and PaLM, which find applications in Chatbots, Text Completion, and content generation.
from transformers import pipeline
task = "text-generation"
model_name = "gpt2"
max_output_length = 30
num_of_return_sequences = 2
input_text = "Hello, "
text_generator = pipeline(task, model=model_name)
text_generator(input_text, max_length=max_output_length, num_return_sequences=num_of_return_sequences)Text2Text Generation:
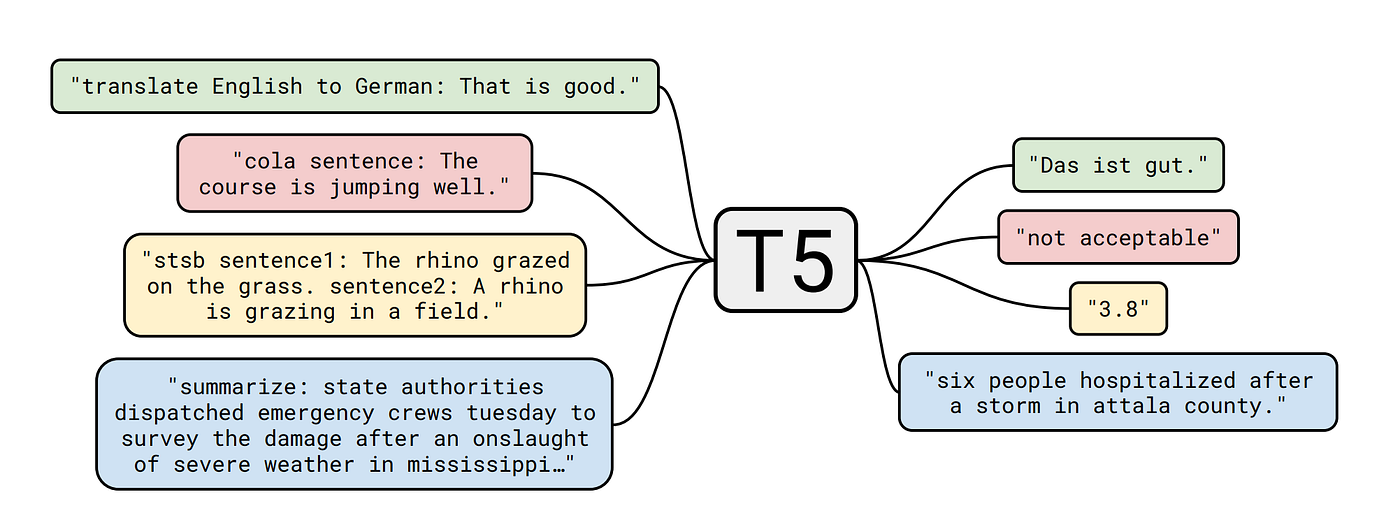
Text-to-Text Generation, also known as Sequence-to-Sequence Modeling, is the process of converting one piece of text into another.
Text-to-Text Generation involves transforming input text into a desired target text, making it a versatile approach. It is commonly used in tasks such as language translation, summarization, and question-answering.
Examples of Text-to-Text Generation models include Transformer-based architectures like T5 (Text-to-Text Transfer Transformer) and BART (Bart is not just another Reformatter).
from transformers import pipeline
task = "text2text-generation"
model_name = "t5-small"
max_output_length = 50
num_of_return_sequences = 2
input_text = "Translate the following English text to French: 'Hello, how are you?'"
text_generator = pipeline(task, model=model_name)
text_generator(input_text, max_length=max_output_length, num_return_sequences=num_of_return_sequences)In this example, we use the T5 model from Hugging Face to perform text-to-text generation. The input text is an English sentence that we want to translate into French. The model is capable of generating multiple possible translations.
What is LoRA?

LoRA represents a paradigm shift in fine-tuning strategies, offering efficiency and effectiveness. By reducing the number of trainable parameters and GPU memory requirements, LoRA proves to be a powerful tool for tailoring pre-trained large models to specific tasks. This article explores how LoRA can be employed to create a personalized chatbot.


PeftModel vs get_peft_model?
Note: 1. `PeftModel.from_pretrained`: - By default, the adapter of the PEFT model is frozen (non-trainable). - You can change this by adjusting the `is_trainable` configuration.
-
get_peft_modelfunction:- Parameters are not frozen by default.
- Result: you obtain a trainable PEFT model for the SFT task.
-
Fine-tuning an already fine-tuned PEFT model:
- Utilize
from_pretrained. - Set
is_trainable = Trueto enable training of the previously fine-tuned model.
- Utilize
What is ROUGE score?
ROUGE stands for Recall-Oriented Understudy for Gisting Evaluation. Some key components of ROUGE for question-answering include: - ROUGE-L: Measures the longest common subsequence between the candidate and reference answers. This focuses on recall of the full text. - ROUGE-1, ROUGE-2, ROUGE-SU4: Compare unigram, bigram, 4-gram overlaps between candidate and reference. Focus on recall of key parts/chunks
Higher ROUGE scores generally indicate better performance for question answering. Scores close to or above 0.70+ are considered strong. When using this metric, processing like stemming, and removing stopwords can help improve the overall performance
The utilization of chat prompts during the fine-tuning of a T5 model holds crucial significance due to several inherent advantages associated with the conversational nature of such data. Here is a more detailed explanation of using chat prompts in this context:
-
Simulation of Human Interaction: Chat prompts enable the simulation of human interactions, mirroring the dynamics of a real conversation. This approach facilitates the model's learning to generate responses that reflect the fluidity and coherence inherent in human exchanges.
-
Contextual Awareness: Chat prompts are essential for capturing contextual nuances in conversations. Each preceding turn of speech influences the understanding and generation of responses. The use of these prompts allows the model to grasp contextual subtleties and adjust its responses accordingly.
-
Adaptation to Specific Language: By incorporating chat prompts during fine-tuning, the model can adapt to specific languages, unique conversational styles, and even idiosyncratic expressions. This enhances the model's proficiency in generating responses that align with the particular expectations of end-users.
-
Diversity in Examples: Conversations inherently exhibit diversity, characterized by a variety of expressions, tones, and linguistic structures. Chat prompts inject this diversity into the training process, endowing the model with the ability to handle real-world scenarios and adapt to the richness of human interactions.
Using Chat prompts during the fine-tuning of a T5 model represents a potent strategy to enhance its capability in understanding and generating conversational texts. These prompts act as a bridge between training data and real-life situations, thereby strengthening the model's performance in applications such as chatbot response generation, virtual assistant systems, and other natural language processing tasks.
T5 is an encoder-decoder model pre-trained on a multi-task mixture of unsupervised and supervised tasks and for which each task is converted into a text-to-text format.
Since, T5 is a text-to-text model, the labels of the dataset are converted as follows: For each example, a sentence as been formed as "Question sentence: " + Answer sentence.
By the end of this notebook, you will gain expertise in the following areas:
- Learn how to effectively prepare datasets for training.
- Understand the process of fine-tuning the T5 model manually, without relying on the Trainer module.
- Explore the usage of accelerators to optimize model training and inference.
- Evaluate the performance of your model using metrics such as Rouge scores.