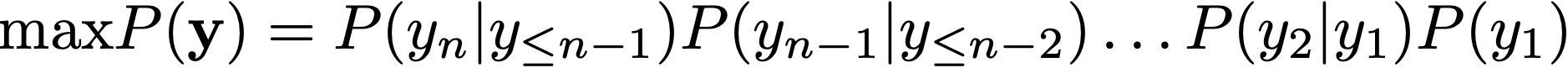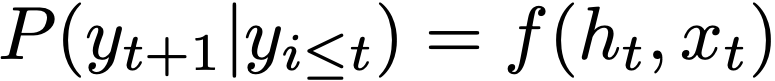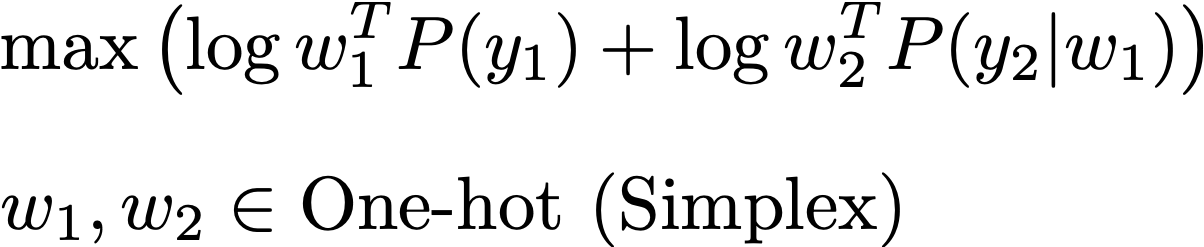This is a repo that implements an idea I was thinking about but turns out not to work.
During decoding for seq2seq models, we are trying to maximize the (log) probability of the generated sequence, i.e.,
where
Earlier works only consider decoding one word at a time, via greedy selection or beam search. However, this is not ideal and not human-like. Can we decode multiple words, potentially an entire sentence, at a time? Of course you can, by exhaustively feeding all possibilities of word combination and selecting the most probable one. But that would be O(|V|^k), where V is the vocabulary and k is the size of the chunk. For modern seq2seq systems, the vocabulary is of size ~10^4, and the exhaustive search will easily blow up your compute.
So I was wondering about an optimization-based method of O(k|V|) to do it. As an example, for a chunk of 2 words, we optimize w to
subject to the constraints that w one-hot. During optimization, I transformed a free variable by softmax to make it a probability distribution (w can be regarded as "distributed" word selection in this sense), and used entropy regularization to encourge peakness.
It sounds doable.
But during experiments, I notice
- The optimization variable does not end up in (not even close to) a simplex vertex.
- The ground-truth translation sentence has a lower log probability than even the greedy-decoded one. It may be due to the limited capacity of the model (just an attention-based LSTM).
- Beam search increases log probability and beam search sizes beyond 5 have negligible improvement.
I suspect that the optimzation landscape is so complex that either the optimum is not attained at the simplex vertex or it simply is too hard for an optimizer to reach a vertex as if hard-constrained. And "distributed" word selection is simply problematic as one can imagine.
I guess it may not be a practical thing to try for highly non-linear models like neural networks, but a similar idea could be helpful if it could be turned into a linear problem, as theoretically guaranteed in the simplex method.
Pip install requirements and see run.sh for reference. As the idea does not work, the code used here has not been cleaned up yet.
The work cannot be done without the help of the open-source basic neural machine translation codebase.
If you make a similar idea work, it would be greatly appreciated if you could let me know.