Data-structures
A glance to all the basic data structures, and these data structures are executed using c++ programming language. The data structures include :
- Stack
- Queue
- Linked list
- Binary search tree
- Tree traversal (BFS & DFS)
1. Stack :
A linear data structure which is based on the LIFO (Last In First Out) algorithm, to brief it, the last element in the array is the first to be removed. In real life application, consider a stack of plates vertically where the last plate which is on the top is the first to be removed, this is how stack works. Stack has two keywords namely Push and Pop, which means if any element is to be inserted in the stack then it is the push operation and if the top most element is to be removed it is known as the pop operation.
Considering the program, it consists of a class stack and public variables top and a, here we are going to implement stack using array. Addition to that many other functions are declared to the class stack. The isfull() function is used to return true or false if the stack is full, the same goes to the isempty() function. peek() function is used to display the topmost element of the stack if the stack is not empty, push() function takes an integer as an parameter, which is to be pushed into the stack based on a condition, if the stack is not empty. pop() function is used to remove the top most element of the stack and the getdata() function is the initial declaration of the array.
2. Queue :
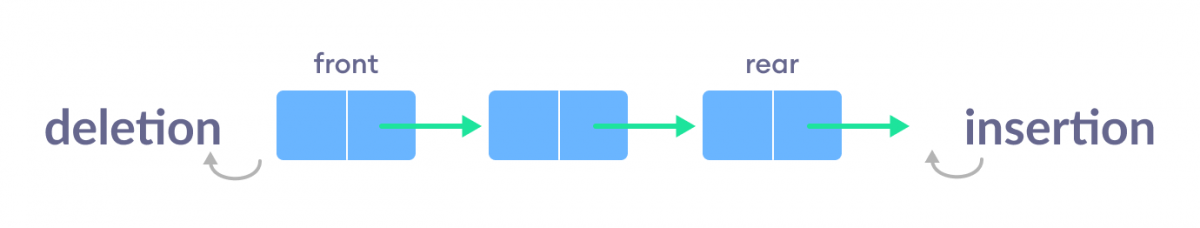
Another linear data structure, this is similar to the real world queue operation, and follows the FIFO (First In First Out) algorithm. According to the algorithm, the data structure consists of two ends, the front and the rear, the rear is where the data elements are added and the front is where we remove the elements, the best example for queue data structure is more people standing in a queue, the first standing person will the first to be sent out.
Considering the program, it is quiet similar to the stack program, a class queue where all the public variables a, rear, front. Many other functions are also declared in the class queue to perform the queue operation. The isfull() function is used to return true or false if the queue is full, the same goes to the isempty() function. peek() function is used to display the topmost element of the queue if the queue is not empty, enqueue() function takes an integer as an parameter, which is to be added to the queue based on a condition, if the queue is not empty. dequeue() function is used to remove the front most element of the queue and the display() function is used to display the whole queue.
Let's discuss the different types of queue data structure:
- Simple queue
- Circular queue
- Priority queue
- Double ended queue
- Simple queue : The simple queue is what we have discussed so far, so there is no need for an explanation and the graphical representation of the simple queue is displayed below.
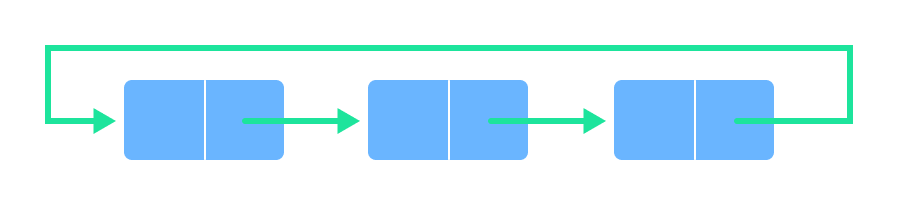
- Circular queue : The working of circular queue is very simple, if the front and the rear locations of a queue are connected then it forms a circular queue, memory utilization is the main advantage of using circular queue, and an element can be added if the last or the rear if full but the front has no element in it, this can't be done in a simple queue.
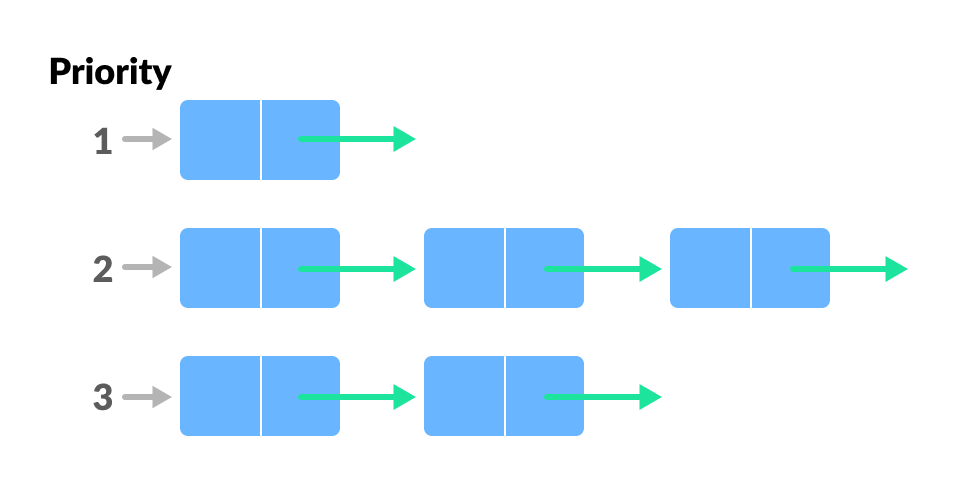
- Priority queue : Priority queue is a simple queue in case of insertion but in case of removing an element from the queue, it is based on priority assigned to the elements of the queue, in case if two elements meant to be having the same priority it can be removed according to the order of the queue.
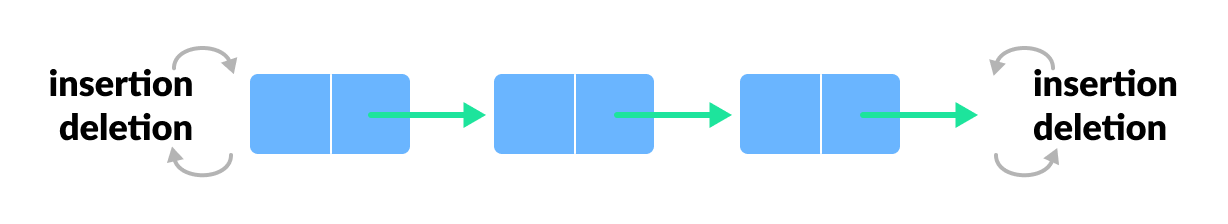
- Double ended queue : Double ended queue known as Deque, where the elements of the queue can be added or removed from both sides of the queue, and well this queue structure does not follows FIFO.
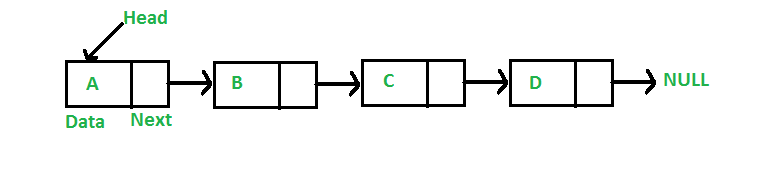
3. Linked list :
A linear data structure consists of nodes where each node contains a data field and the reference to the next node, in case of my program, the data and the next node are declared inside the structure, the data is stored in the variable data and the reference to the next node is declared using pointer.
A class LinkedList with a constructor which specifies the head node and a destructor which deletes the head node. Other functions Append(), AddAfter(), AddAtBegin(), Display(), Count(), Delete() are used for the linked list.
Append() function is used to add the element, to a linked list, it checks if the head is null then if the head is not null then the element is added and the element is updated as the head, else a new node is created and the data is stored and the next pointer is updated to null.
AddAfter() function is used to add the data in the specified location, based on a condition if the linked list is not full, then a loop is placed to reach the location, once it reached the next data point is identified and the data element is placed and the pointer is updated to the previous data point.
AddAtBegin() function takes the data element and place it at the front of the linked list.
Display() function is used to display all the data elements of the linked list.
Count() function is used to count how many elements are present in the linked list.
Delete() function deletes the data specified, if the data element is the head value, the head value is moved to the next value and the data value is removed, else if the data element's next value is pointed towards null, then the data is deleted simply.
A switch case is used to present the code, which provides a neat interface to the program, the gif of the linked list is shown below for more understanding.
Linked list can also be used as other two types:
- Singly linked list
- Circular linked list
- Doubly linked list
- Singly linked list : Singly linked list is what explained above, it is known as singly linked list because it consists of a single pointer to the next node.
- Circular linked list : A linked list is a linked list where all the nodes are connected to form a circle, there is no null at the end, here there is neither a starting node nor an ending node, we can traverse the list from any node and using this data structure we can implement queue data structure.
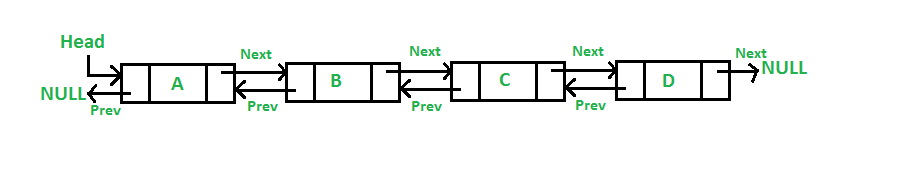
- Doubly linked list : A complex linked list in which there are two pointers maintained, a pointer points to the previous node and an another pointer points to the next node. So that we can traverse in both forward and backward direction of the linked list. Every operations on a linked list can be carried out quickly but the only drawback is extra space is required for the other extra pointer and the operations are very complex to be carried out in a doubly linked list.
4. Binary Search Tree :
Binary search tree is a tree data structure, it is known as tree data structure because the data are stored in the form of a tree with the topmost element as the root, binary search tree is quiet a complicated data structure, the left subtree nodes consists of data lesser than that of the key value and the right subtree nodes consists of data greater than that of the key value. So, both the left subtree and the right subtree are also a binary search tree.
The BST program, is quiet similar to the linked list program, the tree nodes are declared as structure with an interger data and two pointers to the left and right subtree. A class BinarySearchTree with constructor, destructor and other functions are declared, such as Setroot(), Createnode(), Insert(), Preorder(), Inorder(), Postorder() and Display() functions.
The constructor and the destructor performs the root operation, one function initialize the root and the other function makes root as null respectively.
Setroot() function sets the function argument as the root for the tree structure.
Createnode() function temporarily creates a node by setting the left subtree and the right subtree as null.
Insert() function adds the data value to the tree, if the data is less than the root value it is set to the left subtree and if the data is greater than or equal to the root value it is set to the right subtree, this is how insertion is done in the case of binary search tree.
Preorder() function is one of the traversal method, where the tree is traversed from the root to the left subtree and finally to the right subtree, only the tree data which are traversed in this order are displayed in this function.
Inorder() function is another type of traversal technique where the tree is traversed from the left most subtree to the root and to the right most subtree, once again the data traversed in the tree are displayed in this function.
Postorder() function is the final traversal method where the right subtree followed by the light subtree and finally the root of the tree is traversed in order.
Display() function is used to display the content of the tree without any traversal order and in the form of a tree itself.
And finally a switch case is used in the main function to access the various function of the binary search tree with ease.
5. Tree traversal :
Tree traversal technique is how we traverse the data of the tree data structure, according to that tree traversal is of two types, they are :
- Breadth first search
- Depth first search
- Inorder
- Preorder
- Postorder
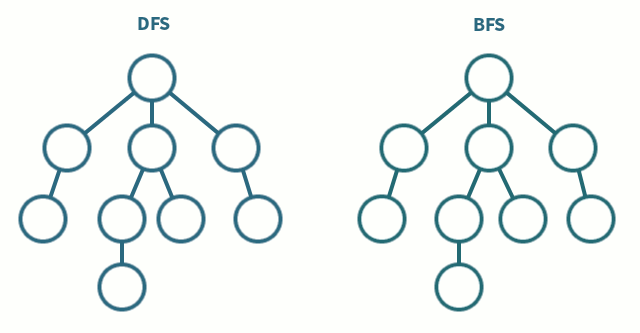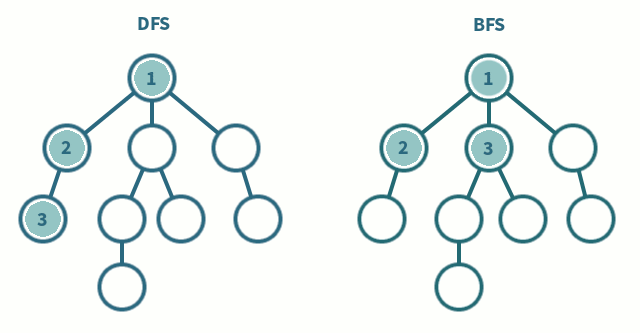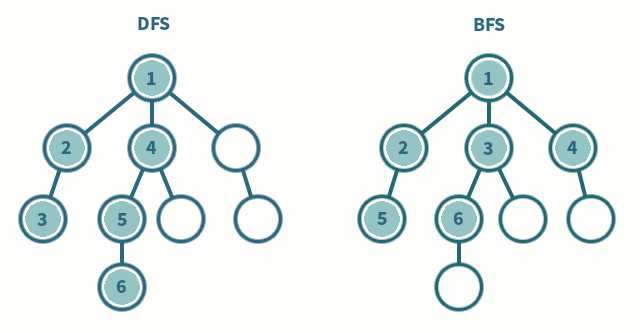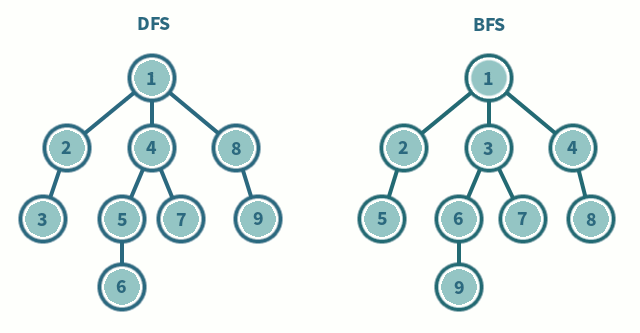
Breadth First Search is a vertex based technique for finding a shortest path in graph. It uses a Queue data structure which follows first in first out. In BFS, one vertex is selected at a time when it is visited and marked then its adjacent are visited and stored in the queue. It is slower than DFS.
Depth First search is quiet similar to the BFS algorithm but, it starts from the root node and prints all the adjacent unvisited branch nodes untills it reaches the goal node or if there is no other unvisited node in the tree or graph. DFS algorithm uses stack data structure to traverse. Some of the other types of DFS are the Inorder, Preorder, and Postorder, these are explained in the binary search tree.
As per the program, a class graph is used and various functions are declared in the public modifier, those are getdata(), dfs() and bfs() functions.
The getdata() function is where the graph is acquired for the further traversal of the program, the graph is acquired using the technique of adjacency matrix where we enter 1 if the both nodes have link to each other otherwise we enter a 0. By this the graph is declared.
dfs() function is used for the DFS traversal as known here we use stack data structure, so that the Last to be entered is the first to be pushed out, it starts from the root node and add it to the stack and moves to the next root or the adjacent and until there is no unvisited node and prints all the elements of the stack.
bfs() function works as the same way but it uses queue to done the same traversal unlike dfs, it traverses level by level of the graph data structure and add it to the queue and prints all of the elements of the queue until the rear becomes the front, which means until the queue become empty.