Logic Paradigm
Programming Language: Prolog
Developer: Bastián Escribano - @vastien
University of Santiago of Chile
Computer Science Department
April, 2022.
Other Languages
Logic programming is a type of programming paradigm within the declarative programming paradigm. The rest of the programming sub-paradigms within declarative programming are: functional programming, constraint programming, DSL (domain-specific) and hybrid programs. Functional programming is based on the concept of function (which is nothing more than an evolution of predicates), of a more mathematical nature. Logic programming revolves around the concept of predicate, or relationship between elements.
Dobble is a game in which players have to find symbols in common between two cards. It was the UK’s best-selling game in 2018 and 2019. In 1976, inspired by Kirkman's schoolgirl problem, French mathematics enthusiast Jacques Cottereau devised a game consisting of a set of 31 cards each with six images of insects, with exactly one image shared between each pair of them. In 2008, journalist and game designer Denis Blanchot found a few of the cards from the "game of insects" and developed the idea to create Dobble.
Dobble was released in France in 2009, and in the UK and North America in 2011 under Blue Orange Games. In 2015, the French board game company Asmodee acquired the rights to Dobble and Spot It!.
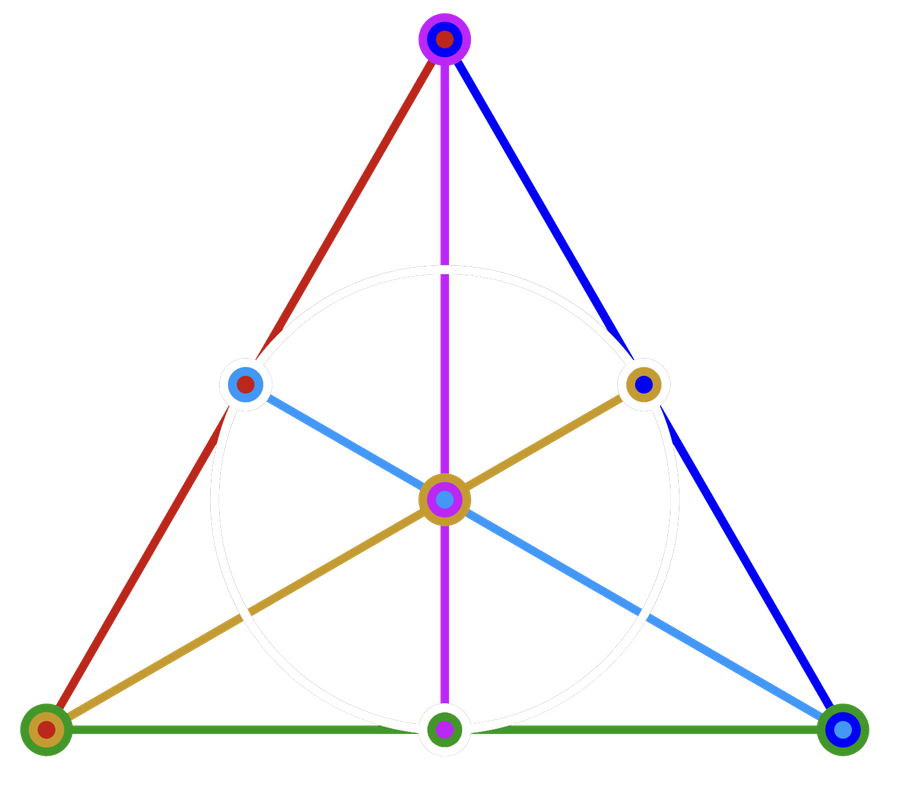
The special way that symbols are arranged on Dobble cards can be understood using geometry. If we represent each card by a line, and each symbol by a point where two lines intersect, then the properties of Dobble are that:
any two lines intersect at exactly one point, and any two points are joined by exactly one line. This geometric structure is an example of a finite projective plane.
If there are 3 points in each line this creates a structure known as the Fano plane. This represents a simpler version of Dobble with 3 symbols on each card, 7 cards and 7 symbols.
In general, a finite projective plane with n points on each line has n2-n+1 points and lines.
To represent the real game of Dobble, each line must join 8 points. This results in a structure with 57 lines and 57 points (82-8+1=57), corresponding to 57 cards and 57 symbols. However, the game works fine with fewer cards too, and Dobble is marketed with 55 cards in the deck (but 57 different symbols). A junior version of Dobble is marketed with 6 symbols per card, 30 cards, and 31 different symbols (62-6+1=31).
-
Clone https://github.com/vastien/prolog-dobble-simulator Windows $ cd Desktop $ mkdir dobbleSimulator $ cd dobbleSimulator $ git clone https://github.com/vastien/prolog-dobble-simulator Unix (Linux and MacOS) $ mkdir dobbleSimulator $ cd dobbleSimulator $ git clone https://github.com/vastien/prolog-dobble-simulator