|
a toolbox for interactively annotating and labeling vital data |
In a nutshell, the vitabel package allows loading, processing, and annotating vital
data (e.g., medical time-series data e.g. from defibrillators, anesthesia charts or critical care) interactively in a Jupyter notebook.
The latest stable release of vitabel is distributed via PyPI and can be installed via
$ pip install vitabelThe latest development version can be installed from the main branch on
GitHub by running
$ pip install git+https://github.com/UniGrazMath/vitabel.gitThe main feature of vitabel, interactive plots that can be used to annotate data,
is designed to work in Jupyter notebooks. Start a new server by running jupyter notebook
(or create a new notebook in an existing server), then import the central Vitals class
that acts as a container for the vital data. A set of data can be added using, for example,
the Vitals.add_defibrillator_recording method, or Vitals.add_vital_db_recording; various output formats of defibrillators
and VitalDB are supported.
A typical use of this package reads as follows:
from vitabel import Vitals, Label
# create case and load data
case = Vitals()
case.add_defibrillator_recording("path/to/ZOLL_data_file.json")
# use in-built methods for processing available data, compute etco2
# and predict circulatory state
case.compute_etco2_and_ventilations()
case.predict_circulation()
# create a new label for ROSC events
ROSC_label = Label('ROSC', plotstyle={'marker': '$\u2665$', 'color': 'red', 'ms': 10, 'linestyle': ''})
case.add_global_label(ROSC_label)
# display an interactive plot that allows annotations and further data adjustments
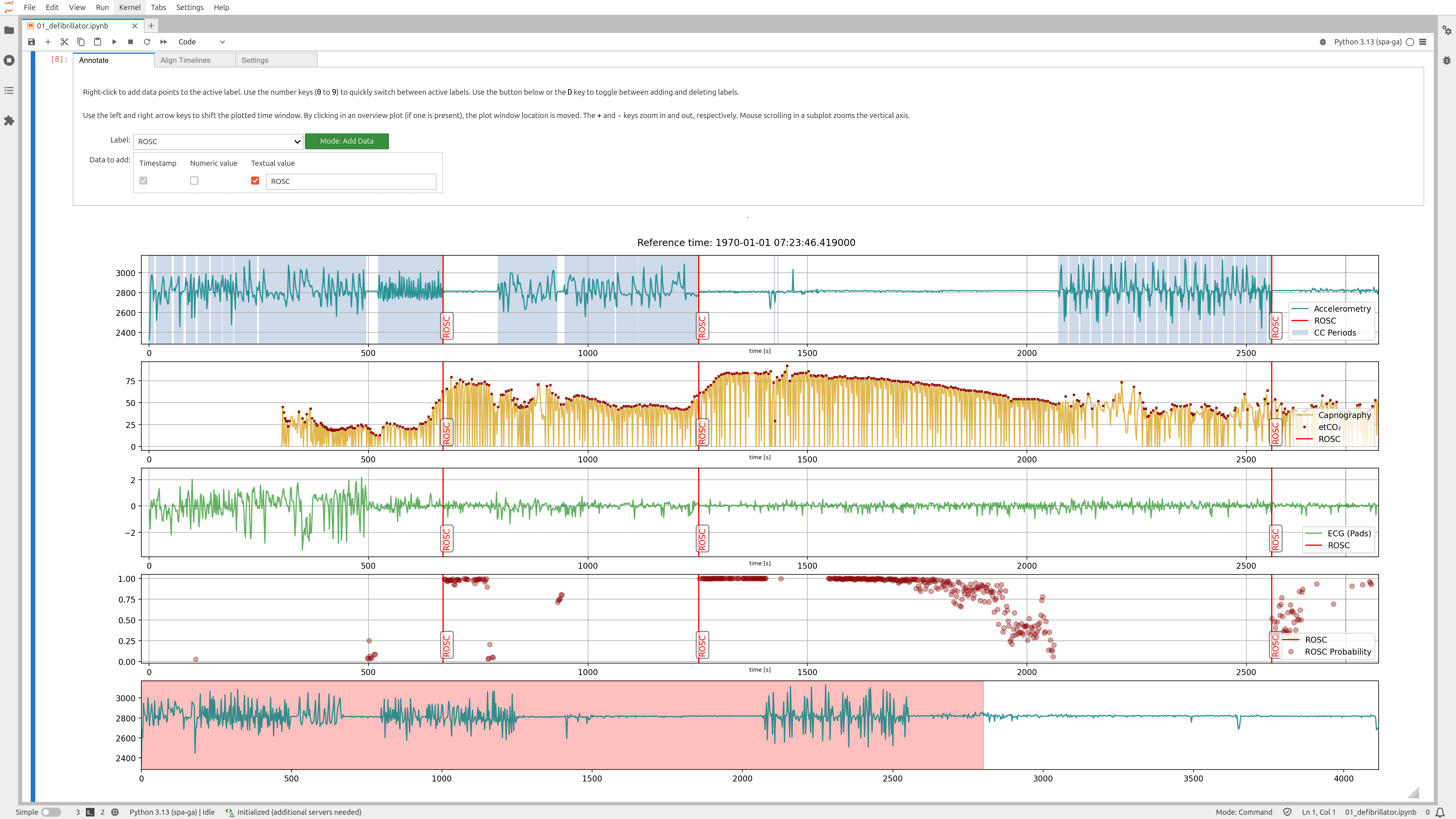
case.plot_interactive(
channels=[['cpr_acceleration'], ['capnography'], ['ecg_pads'], []],
labels = [['ROSC'], ['etco2_from_capnography', 'ROSC'], ['ROSC'], ['ROSC', 'rosc_probability']],
channel_overviews=[['cpr_acceleration']],
time_unit='s',
subplots_kwargs={'figsize': (22, 9)}
)More detailed explicit examples (including the required test data) are contained in the examples directory.
You can find the full API documentation here: vitabel.readthedocs.io – vitals module
Setup a development environment by using the Python project and environment management
tool uv. To setup the environment, simply run
uv syncPackage tests are contained in the tests directory; run them locally via
uv run pytestWe use ruff for linting and formatting the code base,
and semantic versioning for the release tags.