The 16S_ppm pipeline is an accompanying set of scripts for the paper “A computational strategy for rapid on-site 16S metabarcoding with Oxford Nanopore sequencing” (manuscript in preparation; preprint https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.08.25.267591v1). Author: Stefano M. Marino, PhD
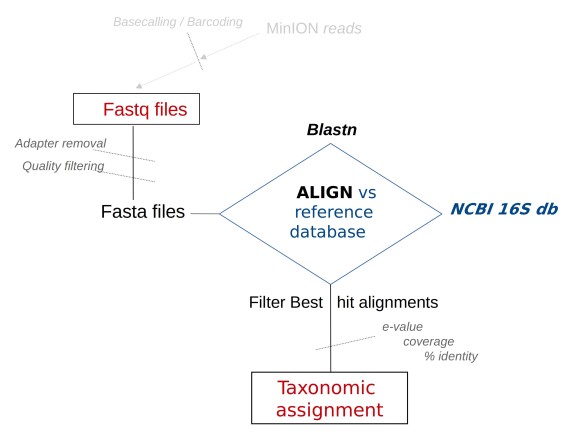
The Oxford Nanopore Technologies (ONT) MinION sequencer, is a portable and affordable device, that produces long reads. Its application is well suited for in situ sequencing, e.g. for field work, analyzing environmental samples. One of the most common approaches in this area is the analysis of the 16S rRNA gene (a trademark of prokaryotes), known as 16S metabarcoding. The 16S_ppm pipeline, available here is specifically tailored to ONT long reads in 16S metabarcoding. The general structure of the 16S_ppm work-flow is shown in the following scheme.
The 16S_ppm pipeline can run in two mods:
(i) from nucleotide sequences (in fasta format); it returns the taxonomic classification (output folder: inputname_results_fromfasta)
(ii) from nucleotide sequences with quality scores (in fastq format); it returns the taxonomic classification (output folder: inputname_results_fromfasta)
\
-
- NOTE: If you would like to run this pipeline on raw sequencing data see https://github.com/smm001/16S_ppm_raw-data (see the corresponding Readme file)
To run (i):
To run (ii):
Once the 16S_ppm folder is downloaded (e.g. in /home/user/, creating a working folder /home/user/16S_ppm) the pipeline should be ready to run (if not, check all scripts have permissions to run; else, set with chmod -R).
Python 3 (3.4 or newer) Python 2 (2.7 or newer) Blastn 2.9.0 (or newer)
Porechop, Filtlong (or Nanofilt).
Nanofilt (version 2.5.0, or newer) or Filtlong (v0.2.0, or newer) are used for fastq filtering (quality of reads, minimum length); Porechop, for adapter removal. They contribute to the pipeline only if you wish to filter reads (by quality and size and/or barcode sequence removal) after basecalling and before classification; this step is not necessary. These two external programs are available at Porechop (https://github.com/rrwick/Porechop) and Filtlong (https://github.com/rrwick/Filtlong); if you don't have these two programs already installed, binaries of Porechop and Filtlong (both with GNU licences) are provided with this distribution (in bin subfolder, with paths accordingly set in the configuration file); blastn (with its NCBI license) executable is also included (in bin subfolder). These programs should work "out of the box" (if activated; see configuration file, below). \
The analysis can be customized via the configuration file (in the root folder of the pipeline, e.g. /home/user/16S_ppm/configuration.cfg). This file is meant to configure a "ready to go" pipeline.
The options are important to tailor the search: for instance, the blast searches can be significantly customized, with max target options, e-value, coverage, etc. Similarly the quality filtering of reads, can be adjusted for strict or relaxed (or deactivated). Additionally, the number of fasta sequences to be classified can be set to a specific value: by default, the run_with_basecall.py script considers 20,000 fasta sequences for each barcode; this is set by the max_num_fasta parameter. The 20,000 choice allows for fast investigations, and on a standard (mid-range) laptop: thus, the default set up employs a parameterization scheme specifically optimized for this task. The parameters can be adjusted for different needs, including long and comprehensive calculations; it has to be noted that pushing the parameters toward more extensive searches, can significantly impact the run-time, and, in case of a standard laptop, the available computational resources. This is particularly true for some parameters, e.g. max_t (suggested range: 5 ≤ value ≤ 75) and max_num_fasta (suggested range: 20,000 ≤ value ≤ 100,000). A combination of the two such as max_t=75 and max_num_fasta = 150,000 could be considered (indicatively) as a borderline scenario (more “expensive” values, will be better suited for a server calculation, or high-end workstations). On the other hand, with max_t=5 and max_num_fasta=20,000 (for quick and indicative, albeit less accurate, calculations) the analysis can run also on low-end/old notebooks.
The list of options available in the configuration file are detailed below (after "----->" comments for this document, not present in the cfg file).
num_threads=8 -----> number of threads used
porechop_runner=bin/Porechop/porechop-runner.py -----> path for porechop-runner (in 16S_ppm/bin subfolder)
porechop=0 -----> activate porechop (0= NOT active; 1= run porechop)
Nanoflt_runner=/home/user/bin/NanoFilt -----> path for Nanofilt, if installed
Filtlong_runner=bin/Filtlong-master/bin/filtlong -----> path for Filtlong (in 16S_ppm/bin subfolder), runs automatically if Nanofilt is not found
Nanofilt=0 -----> activate Nanofilt OR Filtlong (0= NOT active; 1= run Nanofilt OR Filtlong)
Q_filt=7 -----> quality filtering for fastq reads
L_filt=800 -----> length filtering for fastq reads
max_num_fasta=20000 -----> max number of fasta reads used for taxonomic analysis
min_num_fasta=1 -----> min number of fasta reads for taxonomic analysis (e.g. if set to 100, will not consider input with less than 100 reads assigned to it)
db=bin/NCBI_16S_db/PRJNA33175_Bacterial_16S.fasta -----> path for database (db) provided with this distribution
blastn="bin/ncbi-blast-2.9.0+/bin/blastn" -----> path for blastn provided with this distribution
max_t=5 -----> max target sequences option for blast searches (see Blast documentation); set to 0, for unrestricted blast (max_t=0)
evalue=0.00001 -----> evalue cut of for blastn
align_coverage_cutoff=0 -----> filter alignments for coverage > cutoff (e.g. if =60, filters out align <60% coverage)
align_perc_id_cutoff=0 -----> filter alignments for %identity > cutoff (e.g. if =70, filters out align <70% identity)