FastFire is an advanced implementation of the ASCON algorithm, built upon the sponge function paradigm, and distinguished by the introduction of custom round constants, a substitution box enriched with custom nonlinear functions, and a linear permutation step. This project endeavors to elevate the security and performance of the original ASCON algorithm by incorporating these tailored elements.
ASCON (A Stream Cipher with Optimized Characteristics) stands as a block cipher rooted in the sponge function paradigm, leveraging a substitution box (S-box) for data confusion and diffusion. FastFire goes beyond this foundational design, introducing custom round constants, a substitution box enriched with custom nonlinear functions, and a strategically placed linear permutation step. These enhancements are geared towards fortifying the algorithm, enhancing its resilience against cryptographic attacks, and ensuring optimal cryptographic performance.phic attacks.
FastFire introduces custom round constants that are used in each round of the permutation step. These constants are generated based on the principles outlined in Reference code 1, which involves the use of double pendulum equations and bcrypt hashing. This provides a deterministic yet unpredictable set of constants for each round.
constexpr std::array<uint64_t, 17> RoundConstants
{
// Constants generated from Reference code 1
0xe80ac7166cf28f32,0x8c4eea5619edf50e,0x9c59c393f8bc9f31,0x0bdf57c08b5d36ef,
0xb890d67c306b27c7,0x01a54cd116627b85,0x401e07294ce8c8bf,0x61d65684a349baae,
0x6a578466d51d25ee,0xaf10cfa7c6ac0dfa,0x178aaa79a01623fe,0xe0d6a6f52e58afab,
0x0543d0ed6e9b4d29,
// Concatenation of Fibonacci numbers., π, φ, e
0x01B70C8E97AD5F98,0x243F6A8885A308D3,0x9E3779B97F4A7C15,0xB7E151628AED2A6A
};One of the core of the FastFire algorithm is the construction of substitution-box with custom nonlinear function, which consists of several steps:
FastFire's S-box design follows the following principles:
- Nonlinear Operations: Use non-linear operations such as AND, OR, NOT, and XOR to increase the complexity of the algorithm and resistance to linear attacks.
- Bitwise Operations: Utilize the efficiency of bitwise operations to achieve fast data transformations.
- Bitwise NOT-AND and NOT-OR Gates: Combine NOT operations with AND and OR operations to realize complex nonlinear transformations.
- XOR Shuffle Mixing: Mixes data using XOR operations at different stages of the algorithm to achieve diffusion.
- Bit Rotation: Increase the diffusivity of the algorithm through bit rotation operations.
x1 ^= x4;
x3 ^= x7;
x2 ^= x0;
x6 ^= x5;
x4 ^= x6;
x7 ^= x1;
x4 ^= x2;
x2 ^= x3;This step involves preliminary mixing of input data using XOR operations.
uint64_t t0 = ~(x1 & x6);
uint64_t t1 = ~(x0 | x1);
uint64_t t2 = ~(x2 & x4);
uint64_t t3 = ~(x4 | x1);
uint64_t t4 = ~(x3 & x5);
uint64_t t5 = ~(x5 | x2);
uint64_t t6 = ~(x4 & x3);
uint64_t t7 = ~(x6 | x7);This step introduces nonlinearity using NOT-AND and NOT-OR logical gates.
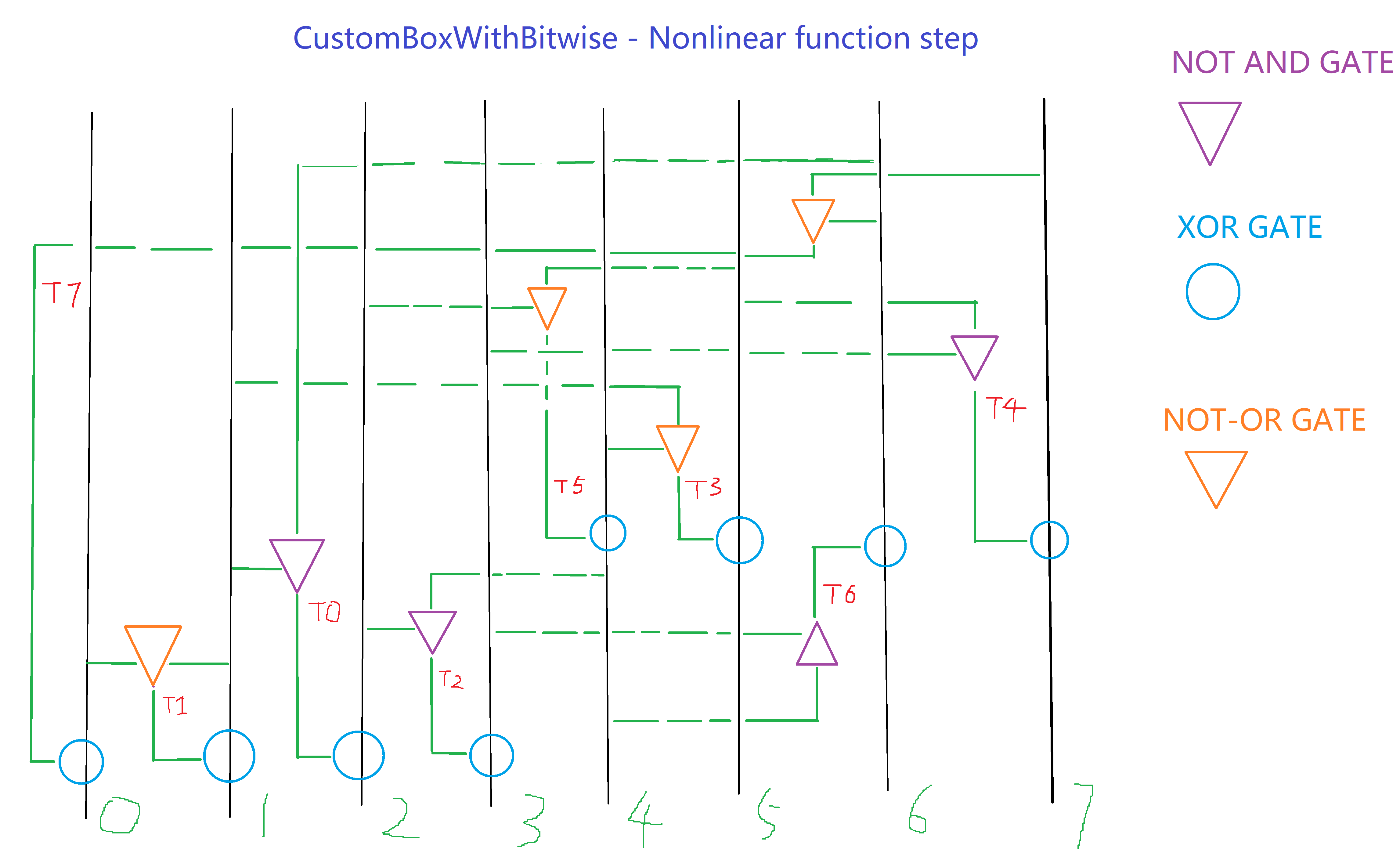
x2 ^= t0;
x1 ^= t1;
x3 ^= t2;
x5 ^= t3;
x7 ^= t4;
x4 ^= t5;
x6 ^= t6;
x0 ^= t7;This step XORs the result of the nonlinear function with the original data for further confusion.
x0 ^= x1;
x1 ^= ~x2;
x2 ^= x3;
x3 ^= x4;
x4 ^= x5;
x5 ^= x6;
x6 ^= ~x7;
x7 ^= x0;This step uses XOR operations again for data mixing to achieve diffusion.
//x0 = (x0 << 13) | (x0 >> (64 - 13)); // Rotate
//x1 = (x1 << 17) | (x1 >> (64 - 17)); // Rotate
//x2 += x3; x3 += x4; x4 += x5; x5 += x6; x6 += x7; x7 += x0; // AdditionThis optional step includes bit rotation and modulo addition operations to further enhance the algorithm's diffusion.
One of the core of the FastFire algorithm The linear permutation step in FastFire, also known as diffusion, is achieved through bit rotation operations. These rotations are designed to further mix the data, increasing the algorithm's diffusion properties. The rotation constants are derived from Reference code 2, which involves prime numbers and mathematical operations.
// Linear Permutation (Diffusion)
TransformedState[0] ^= BitRotateLeft(TransformedState[0], 10) ^ BitRotateLeft(TransformedState[0], 37);
TransformedState[1] ^= BitRotateRight(TransformedState[1], 53) ^ BitRotateRight(TransformedState[1], 26);
// ... (other rotations for TransformedState[2] to TransformedState[7])To validate the security and performance of the FastFire algorithm, we conducted a series of tests, including:
- Permutation Test: Iterating the algorithm multiple times to observe the evolution of the state array, validating the diffusion properties.
- Nonlinear Substitution Test: Executing the nonlinear substitution operation with fixed input data to verify the algorithm's nonlinearity.
FastFire demonstrates how custom design elements can enhance the security of the ASCON algorithm. By introducing custom round constants and a linear permutation step, FastFire aims to provide a more robust encryption solution. Future work may involve further performance optimization and security analysis.
- ASCON Algorithm - Detailed information about the original ASCON algorithm.
- FastFire Implementation - Source code and implementation details for the FastFire algorithm.
- Reference Code 1 - The code that generates the custom round constants.
- Reference Code 2 - The code that provides the rotation constants for the linear permutation step.