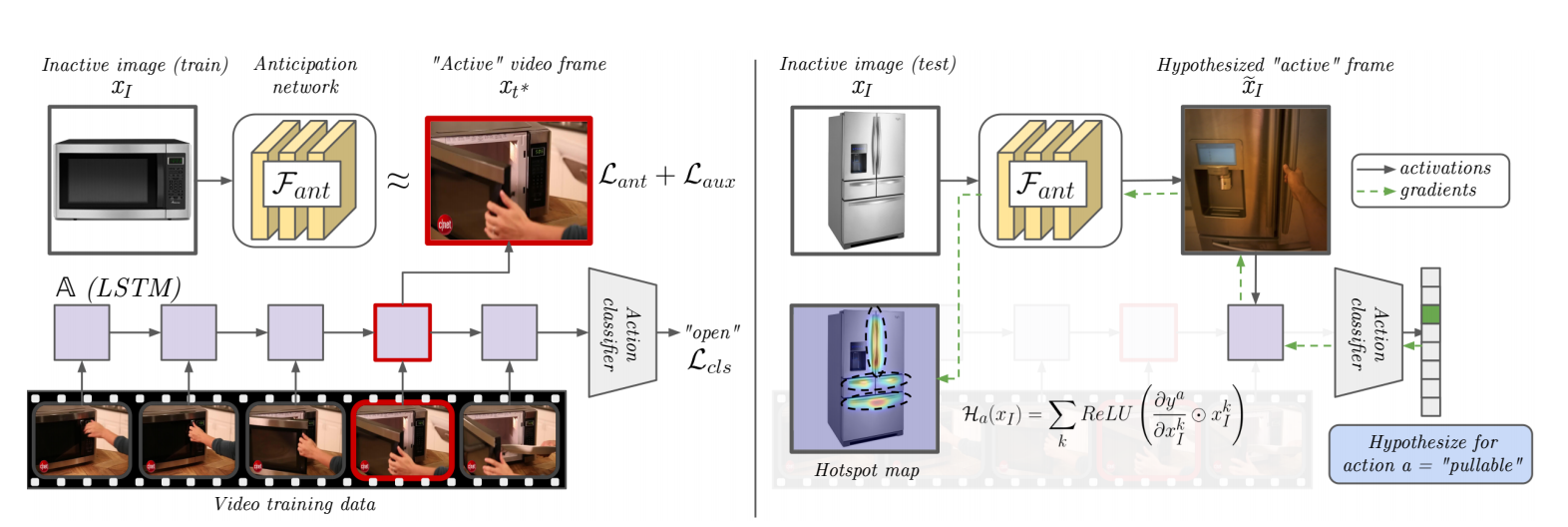
Interaction Hotspots
This code implements a model that combines action recognition and action anticipation into a framework for weakly supervised affordance learning. This is done by feature visualization of the combined model: the action recognition model selects salient regions on "active" frames (where the interaction occurs) and the anticipation module propogates that information back to images of "inactive" objects (where no interaction/hands are visible. Through results with both first and third person video, we show the value of grounding affordances in real human-object interactions. Not only are our weakly supervised hotspots competitive with strongly supervised affordance methods, but they can also anticipate object interaction for novel object categories.
This is the code accompanying our ICCV19 work:
Tushar Nagarajan, Christoph Feichtenhofer and Kristen Grauman.
Grounded Human-Object Interaction Hotspots from Video [arxiv] [project page]
Prerequisites
The code is written and tested using Python (3.7) and PyTorch (v1.0).
Annotations + pretrained models: Dataset annotations, additional images, pretrained models and training log files can be downloaded using the download script provided. It must be run before training the models.
bash utils/download_data.shOPRA dataset: Follow the instructions in the official github repo to download and extract clips from the dataset. Frames can be extracted at 5 fps using the script we provide.
python -m utils.extract_opra_frames --root /path/to/opraEPIC Kitchens dataset: The dataset and annotations can be downloaded from the official website. The frames, object detection images and annotations are required.
NOTE: Change the paths in data/__init__.py to the location where the datasets have been downloaded to.
Training a model
The model can be trained using the train script. Our models were trained on 4 GPUs.
python train.py --batch_size 128 --max_epochs 20 --parallel --max_len 8 --dset opra --cv_dir cv/opra
python train.py --batch_size 128 --max_epochs 20 --parallel --max_len 8 --dset epic --cv_dir cv/epicModel Evaluation
The hotspot models can be evaluated using the eval script. Pretrained models are provided for direct evaluation as well.
python eval.py --dset opra --load cv/opra/ckpt_E_20.pth
python eval.py --dset epic --load cv/epic/ckpt_E_20.pth
The output should look like this:
# OPRA
hotspots
KLD: 1.431 ± 0.024 (1042/1042)
SIM: 0.360 ± 0.006 (1042/1042)
AUC-J: 0.807 ± 0.005 (837/1042)
# EPIC
hotspots
KLD: 1.254 ± 0.028 (571/571)
SIM: 0.403 ± 0.007 (571/571)
AUC-J: 0.792 ± 0.008 (433/571)
Hotspot Visualization
Visualizations on sample images can be generated using:
python viz.py --dset opra --load cv/opra/ckpt_E_20.pth --inp samples/ --out samples/out/Cite
If you find this repository useful in your own research, please consider citing:
@inproceedings{interaction-hotspots,
author = {Nagarajan, Tushar and Feichtenhofer, Christoph and Grauman, Kristen},
title = {Grounded Human-Object Interaction Hotspots from Video},
booktitle = {ICCV},
year = {2019}
}