- Table of Contents
- Transformer - Attention is all you need - Pytorch Implementation
- Models
- Training
- Evaluation
- Inference
- References
This is a PyTorch implementation of the Transformer model in the paper Attention is All You Need (Ashish Vaswani, Noam Shazeer, Niki Parmar, Jakob Uszkoreit, Llion Jones, Aidan N. Gomez, Lukasz Kaiser, Illia Polosukhin, arxiv, 2017).
In this implementation, I will train the model on the machine translation task from English to Vietnamese, with the data used here (This is the original reference repository)
The official Tensorflow Implementation can be found in: tensorflow/tensor2tensor.
The project support training and translation with trained model now.
If there is any suggestion or error, feel free to fire an issue to let me know. :)
The directory structure of this project is shown below:
transformer/ # this repository
├── data_en_vi/ # data directory
├── logs/ # log directory
├── datasets.py
├── evaluate.py
├── models.py
├── README.md
├── train.py
├── translate.py
└── utils.pyThe positional encodings have the same dimension d_model as the embeddings, so that the two can be summed.
# The positional encoding vector, embedding_dim is d_model
class PositionalEncoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, embedding_dim, max_seq_length=512, dropout=0.1):
super(PositionalEncoder, self).__init__()
self.embedding_dim = embedding_dim
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)
pe = torch.zeros(max_seq_length, embedding_dim)
for pos in range(max_seq_length):
for i in range(0, embedding_dim, 2):
pe[pos, i] = math.sin(pos/(10000**(2*i/embedding_dim)))
pe[pos, i+1] = math.cos(pos/(10000**((2*i+1)/embedding_dim)))
pe = pe.unsqueeze(0)
self.register_buffer('pe', pe)
def forward(self, x):
x = x*math.sqrt(self.embedding_dim)
seq_length = x.size(1)
pe = Variable(self.pe[:, :seq_length], requires_grad=False).to(x.device)
# Add the positional encoding vector to the embedding vector
x = x + pe
x = self.dropout(x)
return x# Self-attention layer
class SelfAttention(nn.Module):
''' Scaled Dot-Product Attention '''
def __init__(self, dropout=0.1):
super(SelfAttention, self).__init__()
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)
def forward(self, query, key, value, mask=None):
key_dim = key.size(-1)
attn = torch.matmul(query / np.sqrt(key_dim), key.transpose(2, 3))
if mask is not None:
mask = mask.unsqueeze(1)
attn = attn.masked_fill(mask == 0, -1e9)
attn = self.dropout(torch.softmax(attn, dim=-1))
output = torch.matmul(attn, value)
return output# Multi-head attention layer
class MultiHeadAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, embedding_dim, num_heads, dropout=0.1):
super(MultiHeadAttention, self).__init__()
self.embedding_dim = embedding_dim
self.self_attention = SelfAttention(dropout)
# The number of heads
self.num_heads = num_heads
# The dimension of each head
self.dim_per_head = embedding_dim // num_heads
# The linear projections
self.query_projection = nn.Linear(embedding_dim, embedding_dim)
self.key_projection = nn.Linear(embedding_dim, embedding_dim)
self.value_projection = nn.Linear(embedding_dim, embedding_dim)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)
self.out = nn.Linear(embedding_dim, embedding_dim)
def forward(self, query, key, value, mask=None):
# Apply the linear projections
batch_size = query.size(0)
query = self.query_projection(query)
key = self.key_projection(key)
value = self.value_projection(value)
# Reshape the input
query = query.view(batch_size, -1, self.num_heads, self.dim_per_head).transpose(1, 2)
key = key.view(batch_size, -1, self.num_heads, self.dim_per_head).transpose(1, 2)
value = value.view(batch_size, -1, self.num_heads, self.dim_per_head).transpose(1, 2)
# Calculate the attention
scores = self.self_attention(query, key, value, mask)
# Reshape the output
output = scores.transpose(1, 2).contiguous().view(batch_size, -1, self.embedding_dim)
# Apply the linear projection
output = self.out(output)
return output# Transformer encoder layer
class EncoderLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, embedding_dim, num_heads, ff_dim=2048, dropout=0.1):
super(EncoderLayer, self).__init__()
self.self_attention = MultiHeadAttention(embedding_dim, num_heads, dropout)
self.feed_forward = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(embedding_dim, ff_dim),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(ff_dim, embedding_dim)
)
self.dropout1 = nn.Dropout(dropout)
self.dropout2 = nn.Dropout(dropout)
self.norm1 = Norm(embedding_dim)
self.norm2 = Norm(embedding_dim)
def forward(self, x, mask=None):
x2 = self.norm1(x)
# Add and Muti-head attention
x = x + self.dropout1(self.self_attention(x2, x2, x2, mask))
x2 = self.norm2(x)
x = x + self.dropout2(self.feed_forward(x2))
return x# Encoder transformer
class Encoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, vocab_size, embedding_dim, max_seq_len, num_heads, num_layers, dropout=0.1):
super(Encoder, self).__init__()
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(vocab_size, embedding_dim)
self.num_layers = num_layers
self.num_heads = num_heads
self.embedding_dim = embedding_dim
self.layers = nn.ModuleList([EncoderLayer(embedding_dim, num_heads, 2048, dropout) for _ in range(num_layers)])
self.norm = Norm(embedding_dim)
self.position_embedding = PositionalEncoder(embedding_dim, max_seq_len, dropout)
def forward(self, source, source_mask):
# Embed the source
x = self.embedding(source)
# Add the position embeddings
x = self.position_embedding(x)
# Propagate through the layers
for layer in self.layers:
x = layer(x, source_mask)
# Normalize
x = self.norm(x)
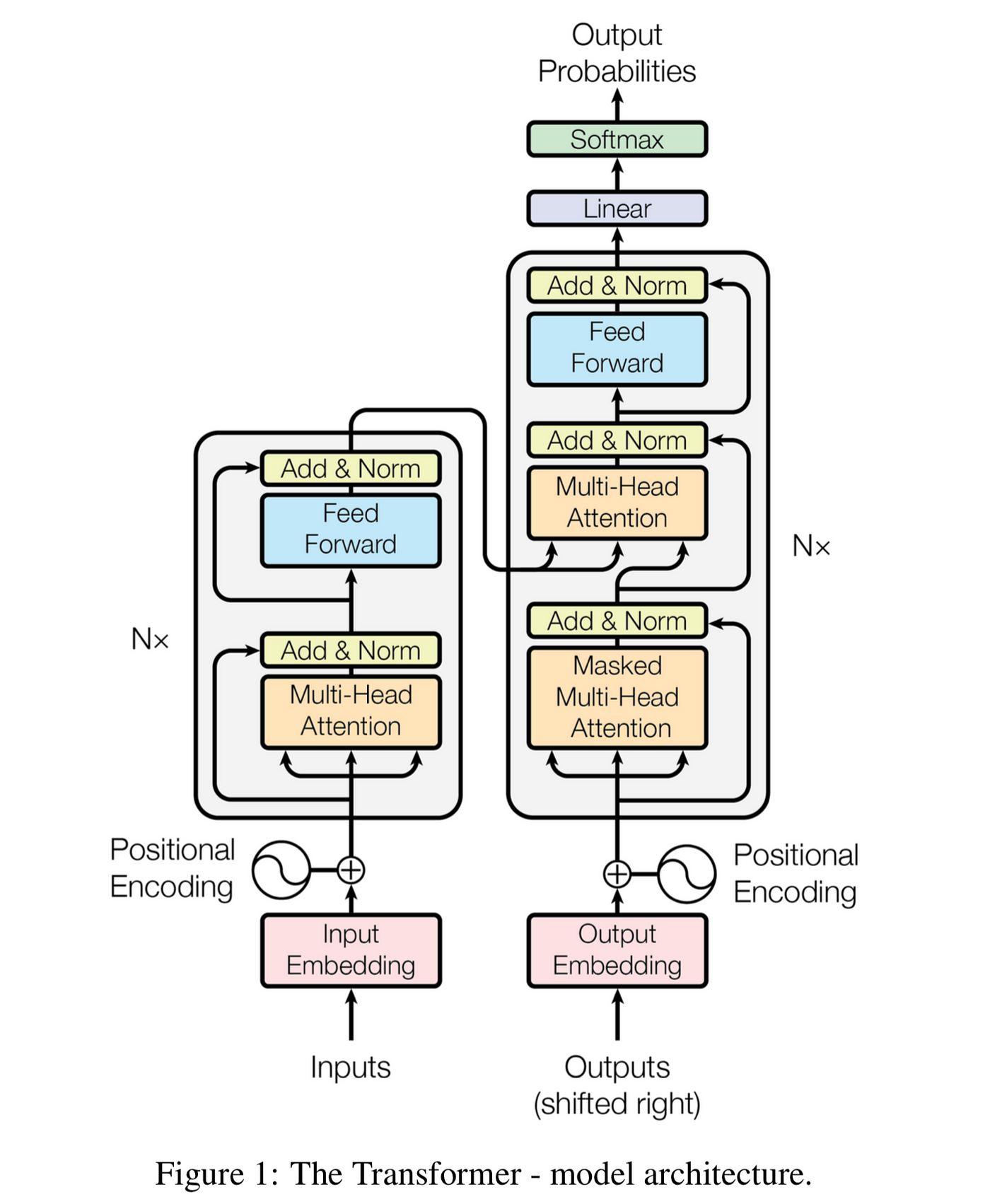
return xDecoder: The decoder is also composed of a stack of N = 6 identical layers. In addition to the two sub-layers in each encoder layer, the decoder inserts a third sub-layer, which performs multi-head attention over the output of the encoder stack. Similar to the encoder, we employ residual connections around each of the sub-layers, followed by layer normalization. We also modify the self-attention sub-layer in the decoder stack to prevent positions from attending to subsequent positions. This masking, combined with fact that the output embeddings are offset by one position, ensures that the predictions for position i can depend only on the known outputs at positions less than i.
# Transformer decoder layer
class DecoderLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, embedding_dim, num_heads, ff_dim=2048, dropout=0.1):
super(DecoderLayer, self).__init__()
self.self_attention = MultiHeadAttention(embedding_dim, num_heads, dropout)
self.encoder_attention = MultiHeadAttention(embedding_dim, num_heads, dropout)
self.feed_forward = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(embedding_dim, ff_dim),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(ff_dim, embedding_dim)
)
self.dropout1 = nn.Dropout(dropout)
self.dropout2 = nn.Dropout(dropout)
self.dropout3 = nn.Dropout(dropout)
self.norm1 = Norm(embedding_dim)
self.norm2 = Norm(embedding_dim)
self.norm3 = Norm(embedding_dim)
def forward(self, x, memory, source_mask, target_mask):
x2 = self.norm1(x)
x = x + self.dropout1(self.self_attention(x2, x2, x2, target_mask))
x2 = self.norm2(x)
x = x + self.dropout2(self.encoder_attention(x2, memory, memory, source_mask))
x2 = self.norm3(x)
x = x + self.dropout3(self.feed_forward(x2))
return x# Decoder transformer
class Decoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, vocab_size, embedding_dim, max_seq_len,num_heads, num_layers, dropout=0.1):
super(Decoder, self).__init__()
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(vocab_size, embedding_dim)
self.layers = nn.ModuleList([DecoderLayer(embedding_dim, num_heads, 2048, dropout) for _ in range(num_layers)])
self.norm = Norm(embedding_dim)
self.position_embedding = PositionalEncoder(embedding_dim, max_seq_len, dropout)
def forward(self, target, memory, source_mask, target_mask):
# Embed the source
x = self.embedding(target)
# Add the position embeddings
x = self.position_embedding(x)
# Propagate through the layers
for layer in self.layers:
x = layer(x, memory, source_mask, target_mask)
# Normalize
x = self.norm(x)
return x# Transformers
class Transformer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, source_vocab_size, target_vocab_size, source_max_seq_len, target_max_seq_len, embedding_dim, num_heads, num_layers, dropout=0.1):
super(Transformer, self).__init__()
self.encoder = Encoder(source_vocab_size, embedding_dim, source_max_seq_len, num_heads, num_layers, dropout)
self.decoder = Decoder(target_vocab_size, embedding_dim, target_max_seq_len, num_heads, num_layers, dropout)
self.final_linear = nn.Linear(embedding_dim, target_vocab_size)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)
def forward(self, source, target, source_mask, target_mask):
# Encoder forward pass
memory = self.encoder(source, source_mask)
# Decoder forward pass
output = self.decoder(target, memory, source_mask, target_mask)
# Final linear layer
output = self.dropout(output)
output = self.final_linear(output)
return outputgdown --id 1Fuo_ALIFKlUvOPbK5rUA5OfAS2wKn_95
unzip en_vi.zip
rm en_vi.zip
mv data/ data_en_vi/python train.py- Parameter settings:
- batch size 20
- n_epochs 50
- learning_rate 1e-4
- cross_entropy loss
- source_max_seq_len 256
- target_max_seq_len 256
- num_heads 8
- num_layers 6
- embedding_dim 512
- dropout 0.1
- early_stopping 5
All the parameters are defined in the utils.py file. You can change them to your own settings.
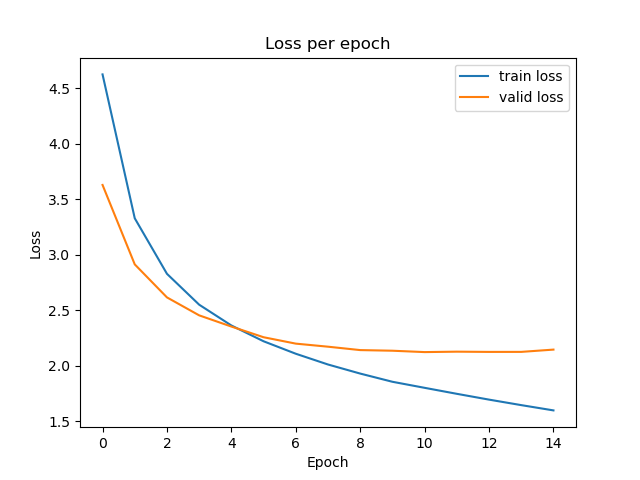
- Training:
- Validation loss: 2.1220
Model training until epoch 15 and stop training because of early stopping. Best validation loss is 2.1220.
Training loss and validation loss for each epoch.See the file evaluate.py.
To evaluate the model on validation data, we use BLEU score. I use NLTK to calculate BLEU score.
from nltk.translate.bleu_score import corpus_bleu
weights = [(0.5, 0.5),(0.333, 0.333, 0.334),(0.25, 0.25, 0.25, 0.25)]
# Calculate BLEU-2 score
bleu_2 = corpus_bleu(references, hypotheses, weights=weights[0])
# Calculate BLEU-3 score
bleu_3 = corpus_bleu(references, hypotheses, weights=weights[1])
# Calculate BLEU-4 score
bleu_4 = corpus_bleu(references, hypotheses, weights=weights[2])My model achieves BLEU-2 is 0.3234, BLEU-3 is 0.2343, BLEU-4 is 0.1715.
See the file translate.py. If you don't have the resources to train the model, you can download my pre-trained model to use.
from utils import configs
from evaluate import load_model_tokenizer, translate
# Translate a sentence
sentence = "My family is very poor, I had to go through hard life when I was young, now I have a better life."
print("--- English input sentence:", sentence)
print("--- Translating...")
device = torch.device(configs["device"])
model, source_tokenizer, target_tokenizer = load_model_tokenizer(configs)
trans_sen = translate(
model=model,
sentence=sentence,
source_tokenizer=source_tokenizer,
target_tokenizer=target_tokenizer,
target_max_seq_len=configs["target_max_seq_len"],
beam_size=configs["beam_size"],
device=device
)
print("--- Sentences translated into Vietnamese:", trans_sen)
## Output
--- English input sentence: My family is very poor, I had to go through hard life when I was young, now I have a better life.
--- Translating...
--- Sentences translated into Vietnamese: gia đình tôi rất nghèo, tôi đã phải trải qua cuộc sống khó khăn khi còn trẻ, giờ tôi có một cuộc sống tốt hơn.