Tangvim is just a playgound for vim's hobbyist. Ah! I am so enthusiast for vim that want to record anything about it. So i begin to read and write...
Enjoy it!
Vim is a highly configurable text editor for efficiently creating and changing any kind of text, now is the most popular text editor in Linux(may be, but at least for me).
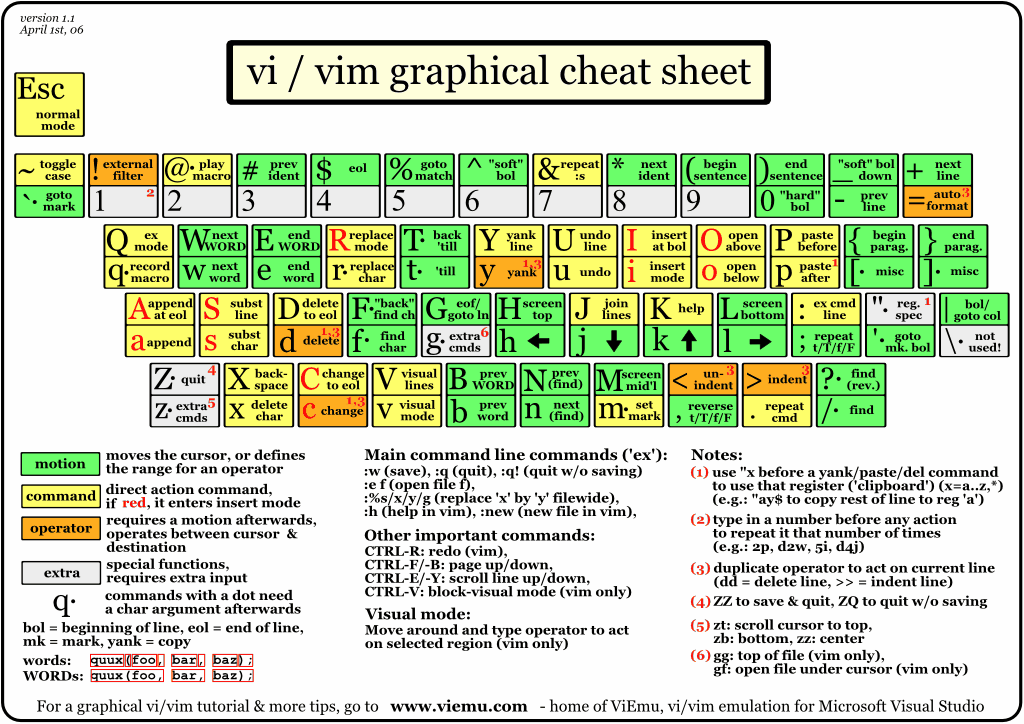
Graphic: Graphical cheat sheet
See Origin graphic, and also can see some graphical cheat sheet based tutorial.
One more vim keyboard graphic.
Vim (/vɪm/ a contraction of Vi IMproved) is a clone, with additions, of Bill Joy's vi text editor program for Unix. It was written by Bram Moolenaar based on source for a port of the Stevie editor to the Amiga and first released publicly in 1991. Vim is designed for use both from a command-line interface and as a standalone application in a graphical user interface. Vim is free and open-source software and is released under a license that includes some charityware clauses, encouraging users who enjoy the software to consider donating to children in Uganda. The license is compatible with the GNU General Public License through a special clause allowing distribution of modified copies "under the GNU GPL version 2 or any later version".
Vim is a successor to vi which is a text editor from the early days of Unix. It became quite popular and made its way into the Single Unix Specification (SUS) and POSIX, but wasn't freely available until 2002. Vim means vi improved, as the name suggest it adds lots of functions to the original vi interface.
Vim adds onto those features. Here are a some of the extended vim features:
- Vim has been ported to a much wider range of OS's than vi.
- Vim includes support (syntax highlighting, code folding, etc) for several popular programming languages (C/C++, Python, Perl, shell, etc).
- Vim integrates with cscope.
- Vim can be used to edit files using network protocols like SSH and HTTP.
- Vim includes multilevel undo/redo.
- Vim allows the screen to be split for editing multiple files.
- Vim can edit files inside a compressed archive (gzip, zip, tar, etc).
- Vim includes a built in diff for comparing files (vimdiff).
- Vim includes support for plugins, and finer control over config and startup files.
- Vim can be scripted with vimscript, or with an external scripting language (e.g. python, perl, shell).
Although it was originally released for the Amiga, Vim has since been developed to be cross-platform, supporting many other platforms. In 2006, it was voted the most popular editor amongst Linux Journal readers; in 2015 the Stack Overflow developer survey found it to be the third most popular text editor, and the fifth most popular development environment in 2018.
Bram Moolenaar began working on Vim for the Amiga computer in 1988. Moolenaar first publicly released Vim (v1.14) in 1991. Vim was based on an earlier editor, Stevie, for the Atari ST, created by Tim Thompson, Tony Andrews, and G.R. (Fred) Walter.
The name "Vim" is an acronym for "Vi IMproved" because Vim is an extended version of the vi editor, with many additional features designed to be helpful in editing program source code. Originally, the acronym stood for "Vi IMitation", but that was changed with the release of Vim 2.0 in December 1993. A later comment states that the reason for changing the name was that Vim's feature set surpassed that of vi.
Vim has a built-in tutorial for beginners. There is also the Vim Users' Manual that details Vim's features and a FAQ. This manual can be read from within Vim, or found online.
For example, at the terimal type command: r $ vimtutor
Vim also has a built-in help facility (using the :help command) that allows users to query and navigate through commands and features.
For example, open the vim, and type:
:help set
Part of Vim's power is that it can be extensively customized. The basic interface can be controlled by the many options available, and the user can define personalized key mappings—often called macros—or abbreviations to automate sequences of keystrokes, or even call internal or user-defined functions.
A file that contains initialization commands is called a "vimrc" file. Each line in a vimrc file is executed as an Ex command line. It is sometimes also referred to as "exrc" file. They are the same type of file, but "exrc" is what Vi always used, "vimrc" is a Vim specific name.
There are two kinds of vimrc:
- the user vimrc in $HOME
- the system vimrc in $VIM(ubutu is /etc/vim/vimrc)
The user vimrc file often does not exist until created by the user. If you cannot find $HOME/.vimrc then you can, and probably should, just create it.
The system vimrc should normally be left unmodified and is located in the $VIM* directory. The system vimrc is not a good place you keep your personal settings. If you modify this file your changes may be overwritten if you ever upgrade vim. Also, changes here will affect other users on a multi-user system. In most cases, settings in the user vimrc will override settings in the system vimrc.
Let's see an interesting questiong about vim:
In any OS in vim execute:
:echo $MYVIMRC
then use Ctrl + g to view the path in status bar.
There are many plugins available that will extend or add new functionality to Vim. These complex scripts are usually written in Vim's internal scripting language, vimscript (also known as VimL). Vim also supports scripting using Lua (as of Vim 7.3), Perl, Python, Racket (formerly PLT Scheme), Ruby, and Tcl.
There are projects bundling together complex scripts and customizations and aimed at turning Vim into a tool for a specific task or adding a major flavour to its behaviour. Examples include Cream, which makes Vim behave like a click-and-type editor, or VimOutliner, which provides a comfortable outliner for users of Unix-like systems.
When you begin to install vim plugin, you may see this in it's installation doc:
INSTALLATION
Put all files into your runtime directory. If you have the zip file, extract it to your runtime directory.
You should place the files as follows:
your_runtime_directory/plugin/fuf.vim
So, what's runtime directory?
Assuming that you're using some flavor of Unix, your personal runtime directory is
~/.vim
This is where you should put any plugin used only by you.
If you want other users to be able to access the plugin, put it in the second directory of the 'runtimepath' option, which usually is
$VIM/vimfiles
Use :set runtimepath? inside Vim to see the directories involved.
Warning: You should not install any plugins into the
$VIMRUNTIMEdirectory. That directory is intended for plugins distributed with Vim. If you put other plugins in that directory, or modify files in that directory, you will likely lose those changes when you update your Vim installation.
More detail pls see:
:help 'rtp'
:help '$VIMRUNTIME'
Vim script (also called vimscript or VimL) is the scripting language built into Vim. Based on the ex editor language of the original vi editor, early versions of Vim added commands for control flow and function definitions. Since version 7, Vim script also supports more advanced data types such as lists and dictionaries and (a simple form of) object-oriented programming. Built-in functions such as map() and filter() allow a basic form of functional programming, and Vim script has lambda since version 8.0. Vim script is mostly written in an imperative programming style.
Vim macros can contain a sequence of normal-mode commands, but can also invoke ex commands or functions written in Vim script for more complex tasks. Almost all extensions (called plugins or more commonly scripts) of the core Vim functionality are written in Vim script, but plugins can also utilize other interpreted languages like Perl, Python, Lua, or Ruby (if support for them is compiled into the Vim binary).
Vim script files are stored in plain text format and the file name extension is .vim. There are libraries for Vim script available on www.vim.org as Vim plugins.
Examples
" This is the Hello World program in Vim script.
echo "Hello, world!"
" This is a simple while loop in Vim script.
let i = 1
while i < 5
echo "count is" i
let i += 1
endwhile
unlet i