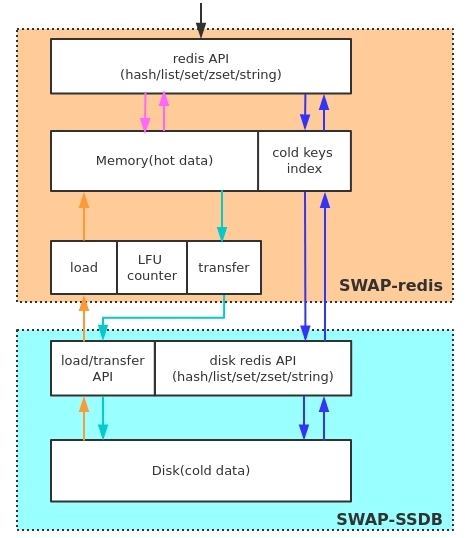
A redis compatiable storage which support data exchange between memory and disk, so you can save a lot of memory cost by using swapdb compared to redis. the main thought of swapdb is, keep hot keys in redis and cold keys in disk, when a key in disk becomes hot, will load it to redis, when a key in memory becomes cold, will transfter it to disk. by using swapdb, you can have both a high preformance cache and high capacity KV storage.
- Heat statistics of keys(LFU)
- Configurable threshold of RAM/FLASH capacity
- Redis API compatiable(99%). supports data structures such as strings, hashes, lists, sets, sorted sets
- Cluster management(redis cluster)
- Multiple replica nodes and data replication support(RDB+Snapshot)
- Data persistency support
- High performance and high capacity redis-like storage
CMake >= 3.1
GCC >= 4.8
git clone https://github.com/JRHZRD/swapdb.git --recursive
(you can skip this step if you add '--recursive' option when 'git clone'.) for submodules update process.
git submodule update --init --recursive
cmake . && make -j8
you can quickly start a swap-redis and swap-ssdb instance like this:
cd utils
# this will use the default "6379" port for swap-redis and "26379" port for swap-ssdb.
./deploy_redis.sh
# or you can specify a specific port like this, for example, use "6380" port
# ./deploy_redis.sh 6380
redis-cli -p 6379
127.0.0.1:6379> set a b
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> locatekey a
"redis"
127.0.0.1:6379> storetossdb a
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> locatekey a
"ssdb"
127.0.0.1:6379> get a
"b"
127.0.0.1:6379> dumpfromssdb a
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> locatekey a
"redis"
- cache
swapdb support LFU based heat statistics, hot keys are kept in redis,so you can use swapdb as cache, which has the same performance as redis when access hot keys.
- High capacity redis-like KV storage
By configuring a low threshold of RAM/FLASH capacity, most of the data will be stored in disk and only the hottest data stored in redis.