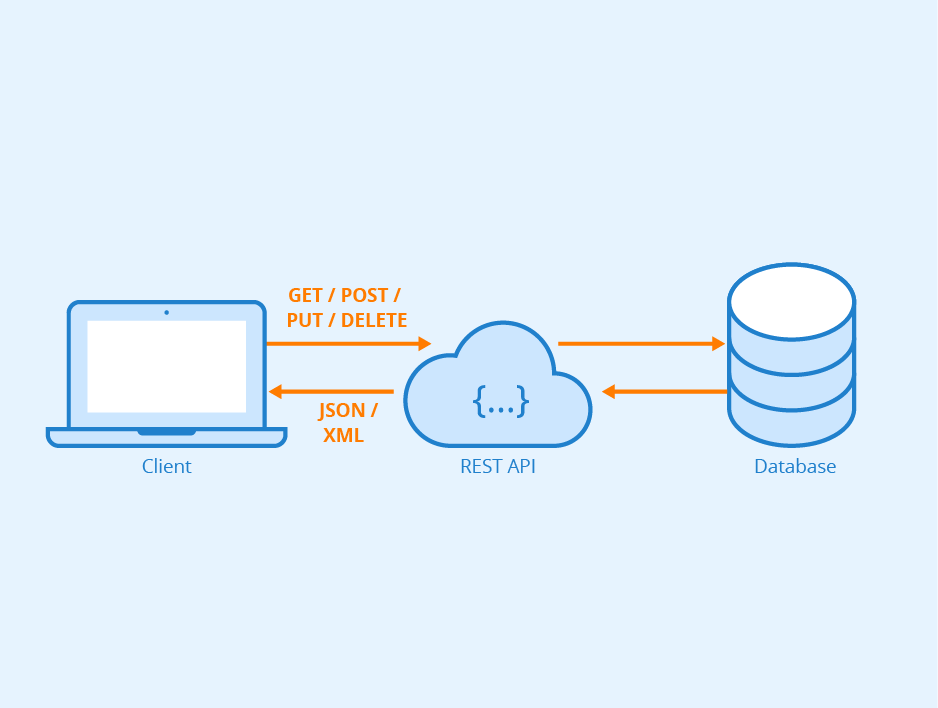
Representational State Transfer (REST) is a style that defines a set of rules to be used for creating web services. An API is an interface in which one program or website talks to each other. They are used to share data and services. REST API is a way of accessing web services in a simple and flexible way without having any processing. It is used to fetch or give some information from a web service. All communication done via REST API uses only HTTP requests.
A request is sent from client to server in the form of web URL as HTTP Get or Post or Put or Delete request. After that, a response comes back from the server in the form of a resource which can be anything like HTML, XML, or JSON. But now JSON is the most popular format being used in Web Services.
In HTTP there are four methods that are commonly used in a REST-based Architecture like POST, GET, PUT and DELETE. These correspond to create, read, update, and delete (or CRUD) operations respectively. There are other methods that are less frequently used like OPTIONS and HEAD.
Interaction in REST-based systems happens through Internet Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP).
-
GET: The HTTP GET method is used to read (or retrieve) a representation of a resource. In the safe path, GET returns a representation in XML or JSON and an HTTP response code of 200 (OK). In an error case, it returns a 404 (NOT FOUND) or 400 (BAD REQUEST).
-
POST: The POST verb is used to create new resources. On successful creation, return HTTP status 201, returning a Location header with a link to the newly-created resource with the 201 HTTP status.
-
PUT: It is used for updating the already existing code. However, PUT can also be used to create a resource in the case where the resource ID is chosen by the client instead of by the server. In other words, if the PUT is to a URI that contains the value of a non-existent resource ID. On successful update, return 200 (or 204 if not returning any content in the body) from a PUT. If using PUT for creating, return HTTP status 201 on successful creation.
-
DELETE: It is used to delete a resource identified by a URI. On successful deletion, return HTTP status 200 (OK) along with a response body.
-
Statelessness Stateless means that the communication between client and server always contains all the information needed to execute the request. There is no session state on the server, it is kept entirely on the client. If access to a resource requires authentication, the client must authenticate itself on each request.
-
Caching The client, server, and any intermediate components can cache all resources to improve performance.
Responses from the server contain status codes to alert the client to information about the success of the operation. As a developer, you do not need to know every status code (there are many of them), but you should know the most common ones and how they are used:
| Status code | Meaning |
|---|---|
| 200 (OK) | This is the standard response for successful HTTP requests. |
| 201 (CREATED) | This is the response for an HTTP request that resulted in an item created. |
| 204 (NO CONTENT) | This is the standard response for successful HTTP requests, where nothing is being returned in the response body. |
| 400 (BAD REQUEST) | The request cannot be processed because of bad request syntax, excessive size, or another client error. |
| 403 (FORBIDDEN) | The client does not have permission to access this resource. |
| 404 (NOT FOUND) | The resource could not be found at this time. It is possible it was deleted or does not exist yet. |
GET /thing/
curl -i -H 'Accept: application/json' http://localhost:7000/thing/ HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Date: Thu, 24 Feb 2011 12:36:30 GMT
Status: 200 OK
Connection: close
Content-Type: application/json
Content-Length: 2
[]POST /thing/
curl -i -H 'Accept: application/json' -d 'name=Foo&status=new' http://localhost:7000/thingHTTP/1.1 201 Created
Date: Thu, 24 Feb 2011 12:36:30 GMT
Status: 201 Created
Connection: close
Content-Type: application/json
Location: /thing/1
Content-Length: 36
{"id":1,"name":"Foo","status":"new"}
GET /thing/id
curl -i -H 'Accept: application/json' http://localhost:7000/thing/1HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Date: Thu, 24 Feb 2011 12:36:30 GMT
Status: 200 OK
Connection: close
Content-Type: application/json
Content-Length: 36
{"id":1,"name":"Foo","status":"new"}