Deep RL Banana Navigator - DQN in Unity-ML
Project code for developing an RL agent that navigates in a virtual world collecting bananas. Part of my work for the Deep RL Nanodegree on Udacity.
Author
Chris Cadonic
Background
** A full report describing much of my approach, results, and potential improvements can be found in the file docs/Report.pdf.**
In this project, a Unity environment that contains a world full of spawning yellow and blue bananas is tasked to an agent to navigate. I trained an agent to navigate this environment so as to collect as many yellow bananas as possible, while attempting to avoid collecting as blue bananas.
The agent learns from state information provided by the environment, containing 37 float values reprepresenting things such as the agents velocity and projeced rays to nearby bananas and their colours, etc. The agent can take one of four actions:
- move forward,
- turn left,
- turn right,
- move backward,
and needs to learn how to act so as to maximize its score per game episode, where each yellow banana collected nets the agent +1 reward and each blue banana collected nets the agent -1 reward.
An example visualization of the agent navigating through the banana world after training is shown below:
which shows a 15-second clip of the agent navigating through an episode. Interesting to see in this clip is that the agent not only aims to grab yellow bananas, but has learned to try to avoid blue bananas when it almost accidentally picks one up.
Prior to learning, if the agent acts completely randomly then the following is an example illustration of how the agent navigates the environment:
Setup and Running
Setup
Just as in outlined in the DRLND repository, the following steps can be used to setup the environment:
- Setup an
anacondaenvironment (optional):
conda create --name drlnd python=3.6
and then activate this environment using:
conda activate drlnd
in MacOS and Linux or
activate drlnd
in Windows.
- As in the DRLND repository, install dependencies using:
git clone https://github.com/udacity/deep-reinforcement-learning.git
cd deep-reinforcement-learning/python
pip install .
- Setup the Unity environment
This environment is specifically provided by Udacity to contain the learning environment.
Environments can be downloaded from here:
- Linux: here
- Mac OSX: here
- Windows (32-bit): here
- Windows (64-bit): here
- Linux (no visualization): here
Download the above file based on your OS and then unzip its contents into the envs/ directory. By default the Headless Linux version is
used by the project to enable training without visualizing the agents performance throughout.
With the Unity environment acquired, the directory structure for this project should then be:
configs/...
docs/...
envs/... <-- place the unzipped Unity environment directories here
models/...
navigation/... <-- main code for project
output/...
README.md
runner.py
requirements.txt
Main code in the navigation directory is organized as follows:
navigation/
agent.py <-- code for controlling the agent and taking states, choosing
actions, and learning a policy
navigation_main.py <-- code for interfacing the agent and the environment
and running episodes in the environment
q.py <-- code that contains a Q-network (or Q-table) that enables
representing the value function as either a table or NN
replay_buffer.py <-- code implementing the replay buffer used in the DQN algorithm
torch_models/
simple_linear.py <-- torch model for DQN using an 8-layer MLP of linear layers
dueling_network.py <-- torch model with a duelling head for experimenting with
duelling DQN
Running
The primary entry point for running the code is with the CLI tool runner.py. This can be called as in:
python runner.py
from the root of this project repository. Arguments can be provided as follows:
-t(or--train): train the model with the provided configuration file (Defaults to False),-c(or--config): specify the configuration to use for training the model (Defaults toconfigs/default_config.yaml.
Thus, running the model to show inference using the final trained model without visualization can be run using:
python runner.py
or with visualization using:
python runner.py -c configs/default_vis_config.yaml
The model can also be retrained if one wishes by passing the -t or --train flag. Be careful as this will overwrite any output in the output/ directory and saved models in the models directory, as specified by the configuration file.
If one wishes to change parameters, then you can create a new configuration file, or modify an existing configuration file, and provide parameters in the following format:
# general parameters
file_path: 'envs/Banana_Linux_NoVis/Banana.x86_64'
model_file: 'models/final-dqn.pkl'
# parameters for printing and controlling learning time
frame_time: 0.00
max_episodes: 2000
max_iterations: 10000
# model parameters
model_params:
# valid values include 'random', 'dqn', (experimental: 'ddqn', 'dueling-dqn')
alg: 'dqn'
# training parameters
epsilon: 1.0
epsilon_decay: 0.996
epsilon_min: 0.05
gamma: 0.99
alpha: 0.001
t_freq: 100
tau: 0.01
# parameters for the replay buffer
buffer_size: 1000000
batch_size: 256
# architecture
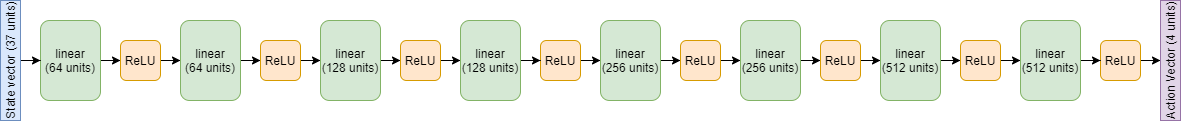
inter_dims: [64, 64, 128, 128, 256, 256, 512, 512]
Results
Using vanilla DQN, the agent was able to learn quite well. I first trained a vanilla DQN with the following parameters, optimized through hyperparameter search using grid search (as opposed to any other optimization scheme, for the sake of simplicity):
- epsilon_decay = 0.996
- epsilon_min = 0.05
- learning_rate = 0.002
- gamma = 0.99 and using an iteratively deepening 8-layer neural network model as in:
With this setup, and the following arbitrarily chosen static parameters:
- target_update_frequency = 100 iterations
- tau = 0.01
- batch_size = 256
- replay_buffer_size = 1000000
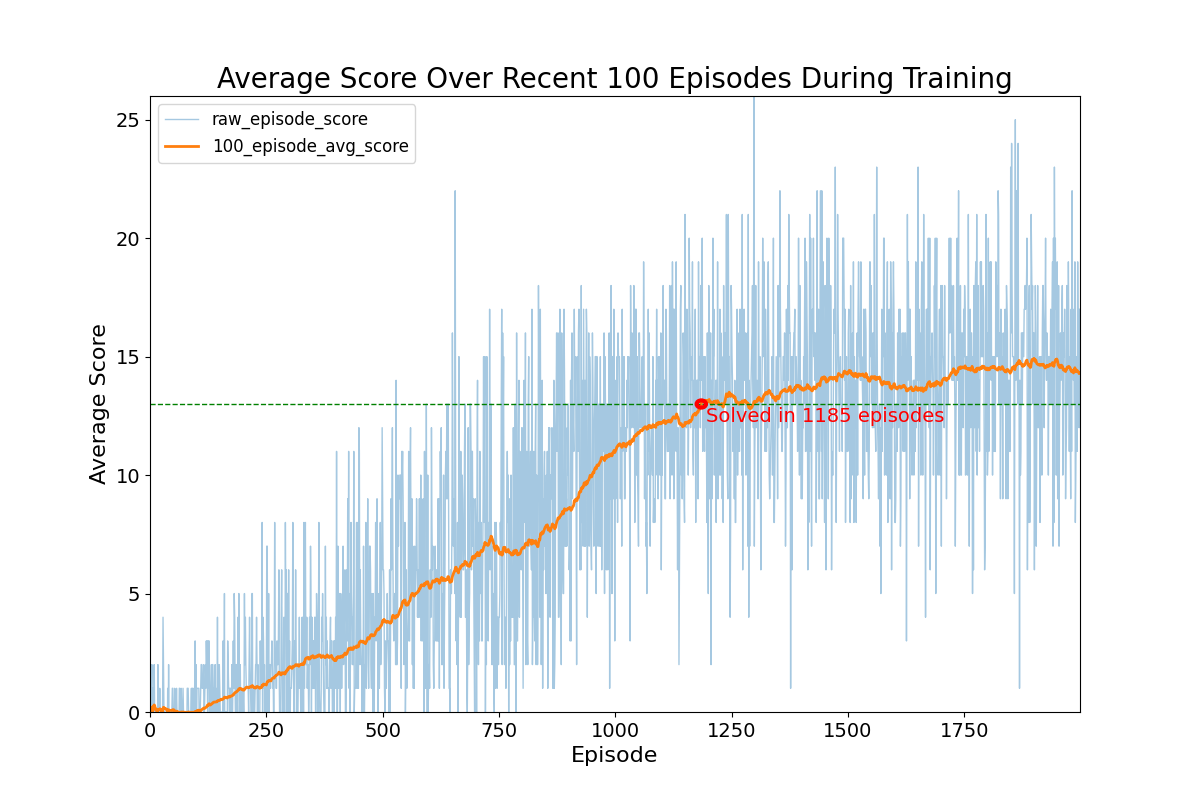
The following results were acquired:
This illustrates that the model was able to learn how to navigate the banana world to acquire an average score of +13 over 100 episodes in 1185 episodes. After tuning parameters, particularly epsilon_decay and learning_rate, as the DQN algorithm was particularly sensitive to these parameters, the model was able to consistently fair well across episodes. There appears to also be some variability in raw episode score throughout training, which is a consequence of the lower bound of 0.05 on epsilon to enable exploration all throughout training to at least a small degree.