Project 11: CarND-Path-Planning-Project
Introduction
The goal of this project is to safely navigate around a virtual highway with other traffic that is driving +/-10 mph of the 50 mph speed limit. The car should try to go as close as possible to the 50 mph speed limit, which means passing slower traffic when possible. The car should avoid hitting other cars at all cost as well as driving inside of the marked road lanes at all times, unless going from one lane to another. The car should be able to make one complete loop around the 6946 m highway. Since the car is trying to go 50 mph, it should take a little over 5 minutes to complete 1 loop. Also the car should not experience total acceleration over 10 m/s^2 and jerk that is greater than 10 m/s^3.
Software Modules
Utils
The utils file provides basic functions to convert angles from degree to rad, velocity from m/s to mph, map coordinates to frenet coordinates and vice versa.
VehicleModel Class
The VehicleModelclass capsulates the vehicle attributes like the unique ID, the absolute velocity, the x- and y-velocity, the actual position in map (x, y) and frenet (s, d) coordinates, the yaw, the vehicle's width and the actual driving lane. Furthermore the class provides methods to predict the vehicle attributes including a full trajectory up to a given prediction_time
SensorFusion Class
The SensorFusion class manages all detected vehicles, the host vehicle and the speed limits per lane. It calculates the average lane velocity as well as the lane occupancy (number of vehicle driving ahead per lane). Furthermore, the class provides methods to update and clean-up the VehicleModel list, to determine the next vehicle driving ahead or behind the host vehicle for a specific lane and methods to identify the fastest lane and the fastest reachable lane. Fastest reachable lane means the next left or right line.
Tuning Parameters
The SensorFusion class can be tuned by the following parameters.
const double kLaneWidth_ = 4.0; // default lane width
const double kMaxDistanceForAvgVelocity_ = 100; // The average velocity is calcualted for vehicles in range of x m ahead
const double kMaxDistanceLaneOccupancy_ = 100; // The average velocity is calcualted for vehicles in range of x m aheadBehaviorPlanner Class
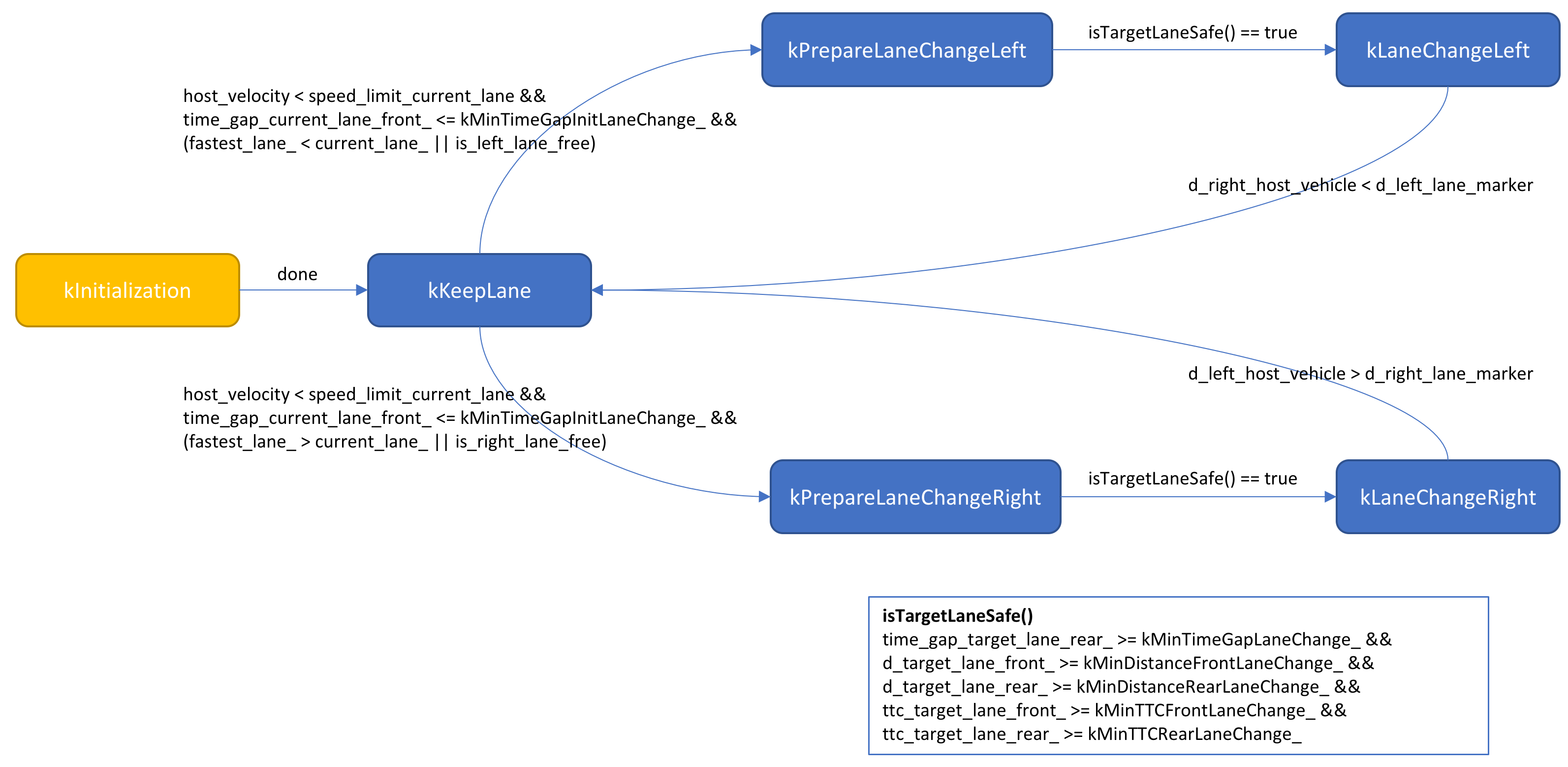
The BehaviorPlannerclass suggests the next feasible, safe, legal and most efficient maneuver (state) like e.g. keep lane, prepare for left lane change, change the lane to the left, etc. It does not consider the detailed trajectory. This is typically the task of the trajectory planner.
FSM - Finite State Machine
The next maneuver is defined by the following FSM states. Depending on the actual state, the BehaviorPlanner determines the target velocity and the target lane. With these inputs (state, target velocity and target lane) the TrajectoryPlanner plans an optimal and jerk free trajectory.
| State | Description |
|---|---|
kInitialization |
Initialization phase of the behavior planner. |
kKeepLane |
The host vehicle keeps the lane as long as the target velocity could be keep and not faster lane is currently available. |
kPrepareLaneChangeLeft |
The host vehicle prepares for a left lane change (e.g. adjusting velocity to target lane, waiting for a safe gap, etc.). |
kLaneChangeLeft |
The host vehicle starts to change to the left adjacent lane. |
kPrepareLaneChangeRight |
The host vehicle prepares for a right lane change (e.g. adjusting velocity to target lane, waiting for a safe gap, etc.). |
kLaneChangeRight |
The host vehicle starts to change to the right adjacent lane. |
Tuning Parameters
The BehaviorPlanner class respectively the FSM state transitions can be tuned by the following parameters.
const double kLowerTimeGap_ = 1.5; // min allowed time gap to vehicle ahead [s]
const double kUpperTimeGap_ = 3.5; // time gap [s] to drive with speed limit
const double kMinTimeGapInitLaneChange_ = 3.0; // min allowed time gap to intiate a lane change [s]
const double kMinTimeGapLaneChange_ = 1.0; // min required time gap to vehicle in target lane [s]
const double kMinDistanceFrontLaneChange_ = 10.0; // min required distance to vehicle ahead in target lane [m]
const double kMinDistanceRearLaneChange_ = 10.0; // min required distance to vehicle behind in target lane [m]
const double kMinTTCFrontLaneChange_ = 6.0; // min required time-to-collision to vehicle ahead in target lane [s]
const double kMinTTCRearLaneChange_ = 6.0; // min required time-to-collision to vehicle behind in target lane [s]
const double kFastestLaneFactor = 0.08; // the fastest lane velocity need to be x% faster than the current [%]TrajectoryPlanner Class
The TrajectoryPlanner class determines the optimal, jerk free and drivable trajectory to realize the desired behavior (state, target velocity and target lane) provided by the BehaviorPlanner class. To stabilize the trajectory the simulator provides the "not driven part" of the previous trajectory. The spline based trajectory is calculated based on the following processing steps.
- Determine 5 reference (anchor) points in the frenet space
- If less then 2 points of the previous trajectory are available, determine two points as tangent to the host vehicle. Otherwise take the last two points from the previous trajectory.
- Add three waypoints located at the center of the target lane in 30 m, 60 m and 90 m distance.
- Smooth the trajectory by fitting a spline through all reference (anchor) points in the frenet space.
- Add points from the previous to the new trajectory.
- Fill up the new trajectory (up 50 points) along the spline and transform them into map coordinates.
- The distance between two consecutive points specifies the host vehicles's velocity. In order to calculate a trajectory within the jerk and acceleration limits, the distance is adjusted continuously by increasing/decreasing the reference velocity by
kMaxDeltaVelocityup/down to the target velocity.
Tuning Parameters
The optimal trajectory can be tuned by the following parameters.
const double kControllerCycleTime = 0.02; // Cycle time of the vehicle controller between two trajectory points [s]
const int kNumberPredictionsPoints = 50; // number of prediction points for e.g. the trajectory planner or vehicle model
const double kPredictionTime = kControllerCycleTime * (double)kNumberPredictionsPoints;
const double kMaxDeltaVelocity = 0.09; // Max delta velocity [m/s] between two waypoints to guarantee accelerations < 10 m/s2 jerks < 10 m/s3
const double kMinTimeGap_ = 2.0; // min allowed time gap to vehicle ahead [s]
const double kMinTimeGapLaneChange_ = 1.0; // min allowed time gap to vehicle ahead/behind during a lane change [s]Simulator.
You can download the Term3 Simulator which contains the Path Planning Project from the [releases tab (https://github.com/udacity/self-driving-car-sim/releases).
Basic Build Instructions
- Clone this repo.
- Make a build directory:
mkdir build && cd build - Compile:
cmake .. && make - Run it:
./path_planning.
Dependencies
- cmake >= 3.5
- All OSes: click here for installation instructions
- make >= 4.1
- Linux: make is installed by default on most Linux distros
- Mac: install Xcode command line tools to get make
- Windows: Click here for installation instructions
- gcc/g++ >= 5.4
- Linux: gcc / g++ is installed by default on most Linux distros
- Mac: same deal as make - [install Xcode command line tools]((https://developer.apple.com/xcode/features/)
- Windows: recommend using MinGW
- uWebSockets
- Run either
install-mac.shorinstall-ubuntu.sh. - If you install from source, checkout to commit
e94b6e1, i.e.git clone https://github.com/uWebSockets/uWebSockets cd uWebSockets git checkout e94b6e1
- Run either
Code Style
Applied Google's C++ style guide.