Access the following site and please rate this semesters lecture based on the questions in there and feel free to give any textual feedback or improvements on the second page. Link will be open untill 22. January
https://www.menti.com/alk94tmqw1j9
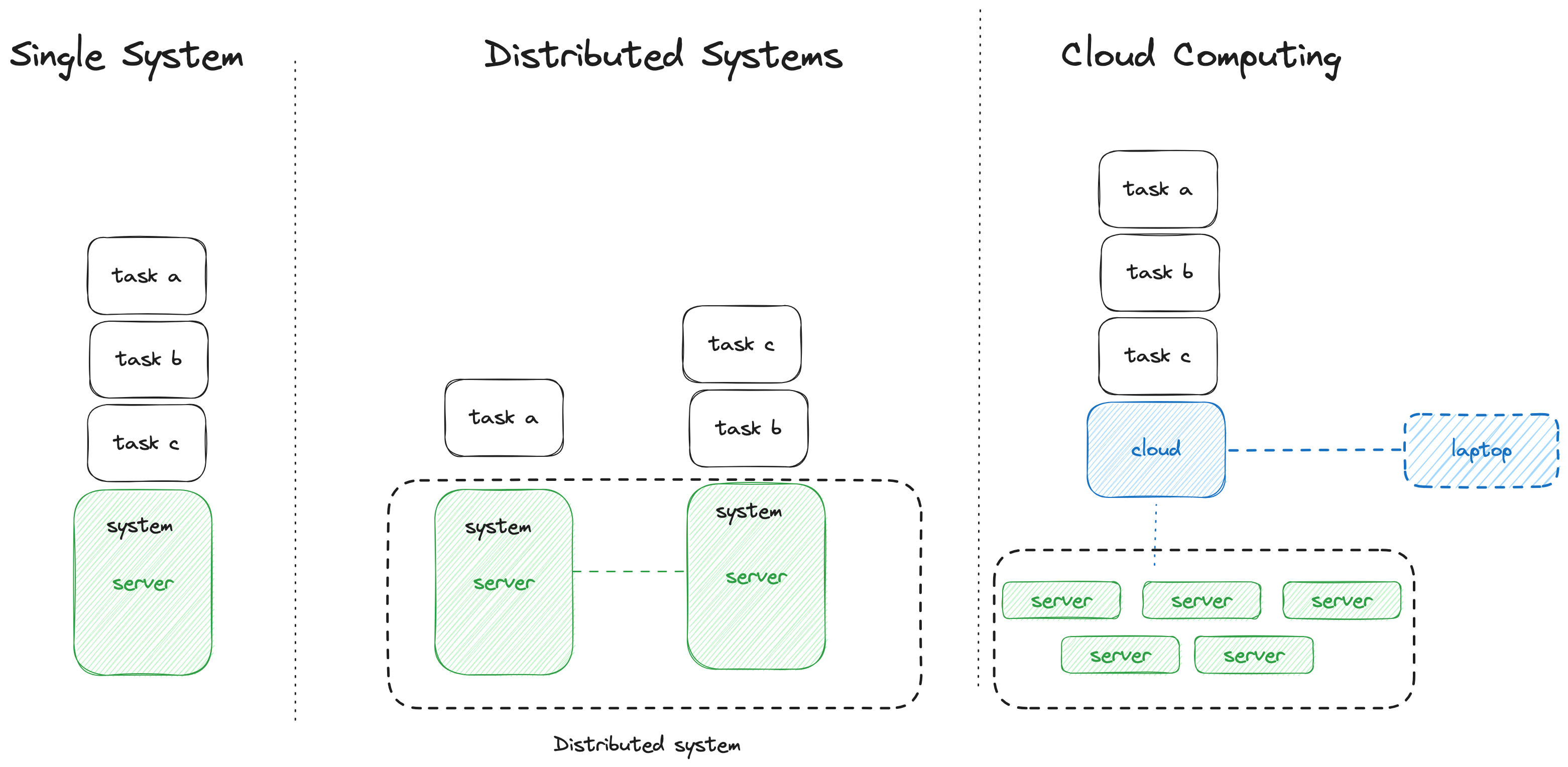
Microservice project consisting of 3 Microservices:
- Frontend to visualise data and provide means to store data conviniently in contrast to via curl or postman
- Backend to process data
- Database to store data
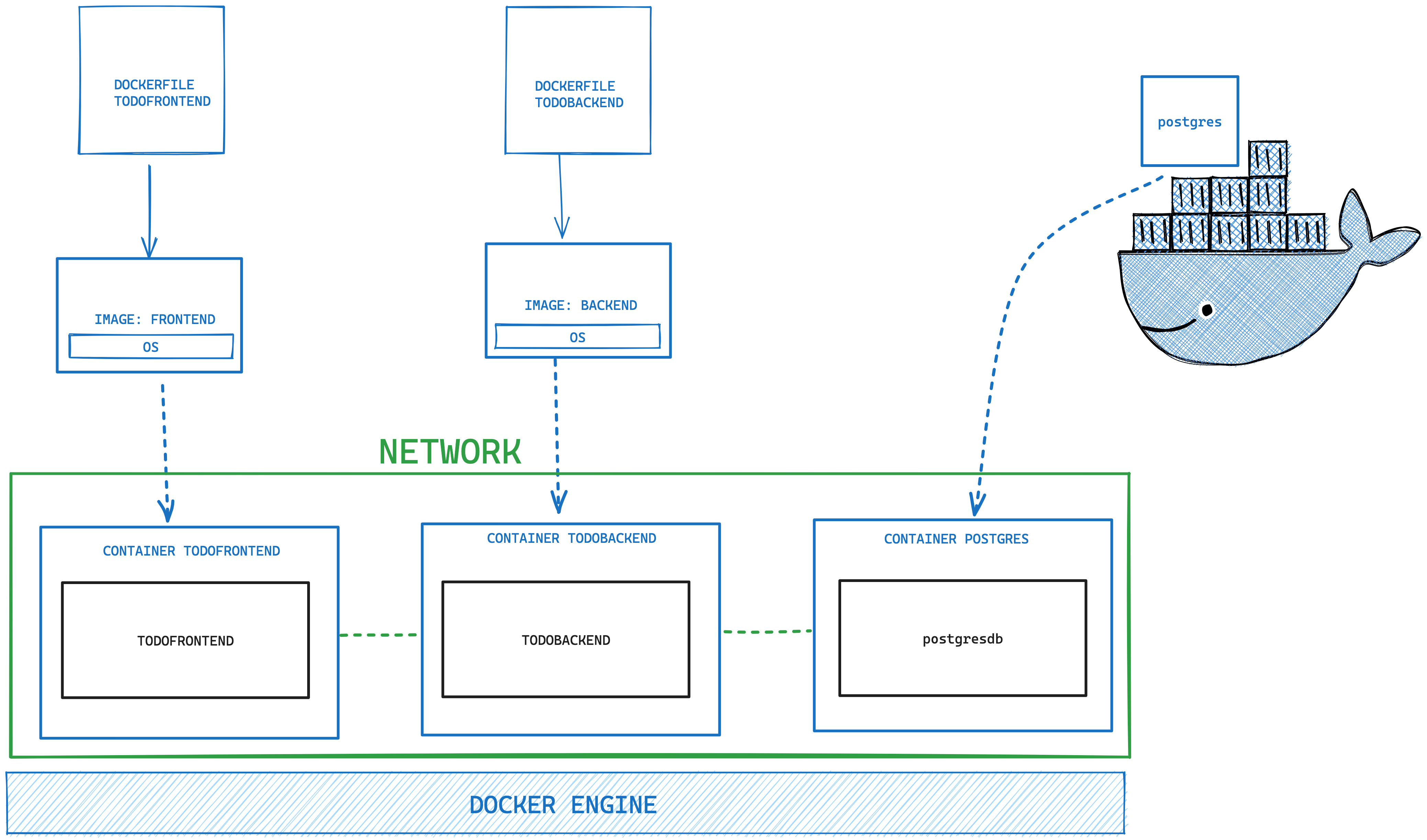
The services can be in either technology Ideally, containerized all 3 microservices. Even more ideally, containerized via docker compose
Due Date: Exam Date (January 25th)
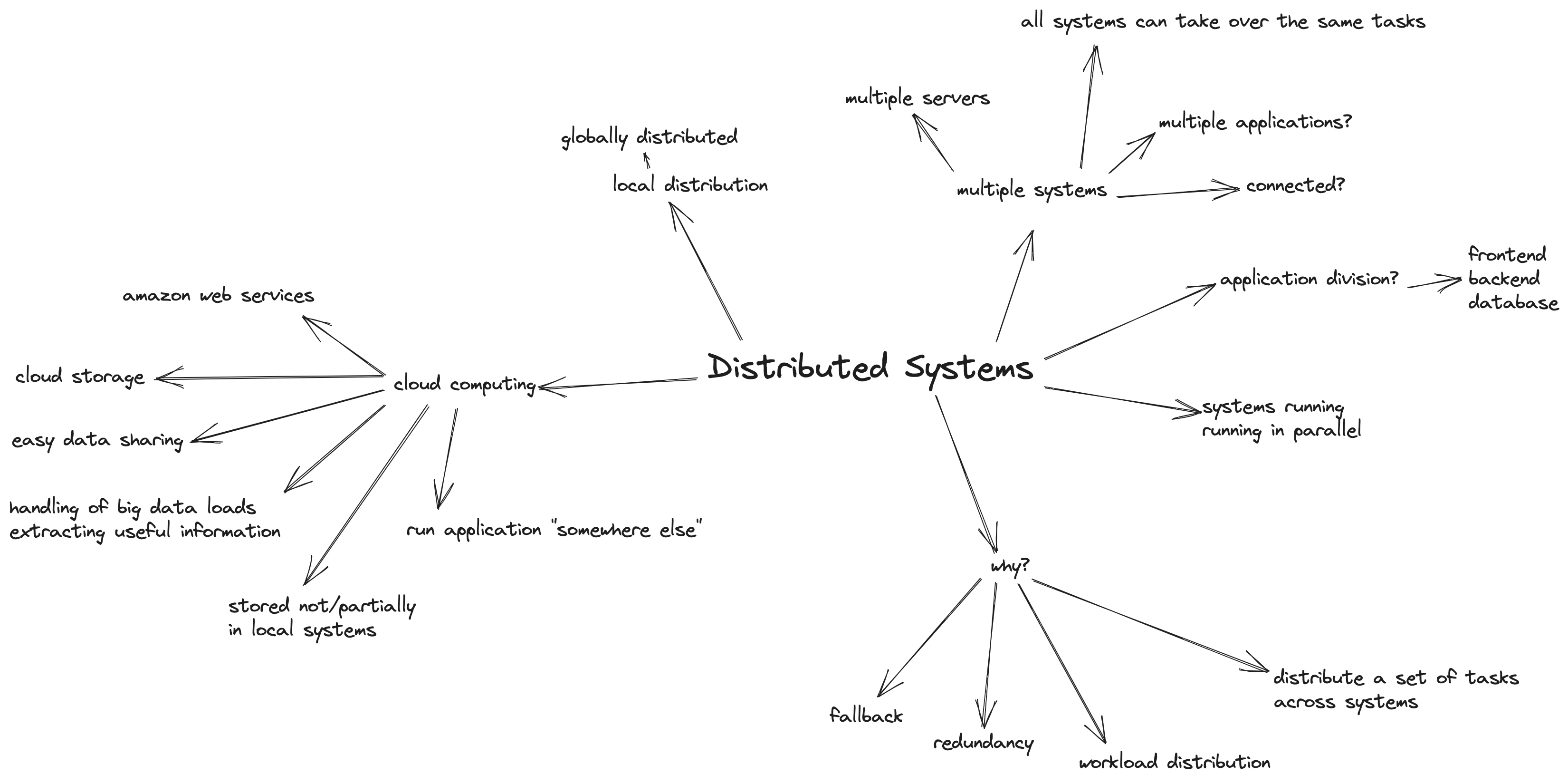
- Which technologies or what do you have in mind in general if you think about "distributed systems"?
- the "WHY" - Why would people use and implement a distributed systems architecture?
- Cloud Pyramid - IaaS, PaaS and SaaS
- Cloud Definition - "Service Model"
- Explain "cloud idea" with one cloud service of your choice
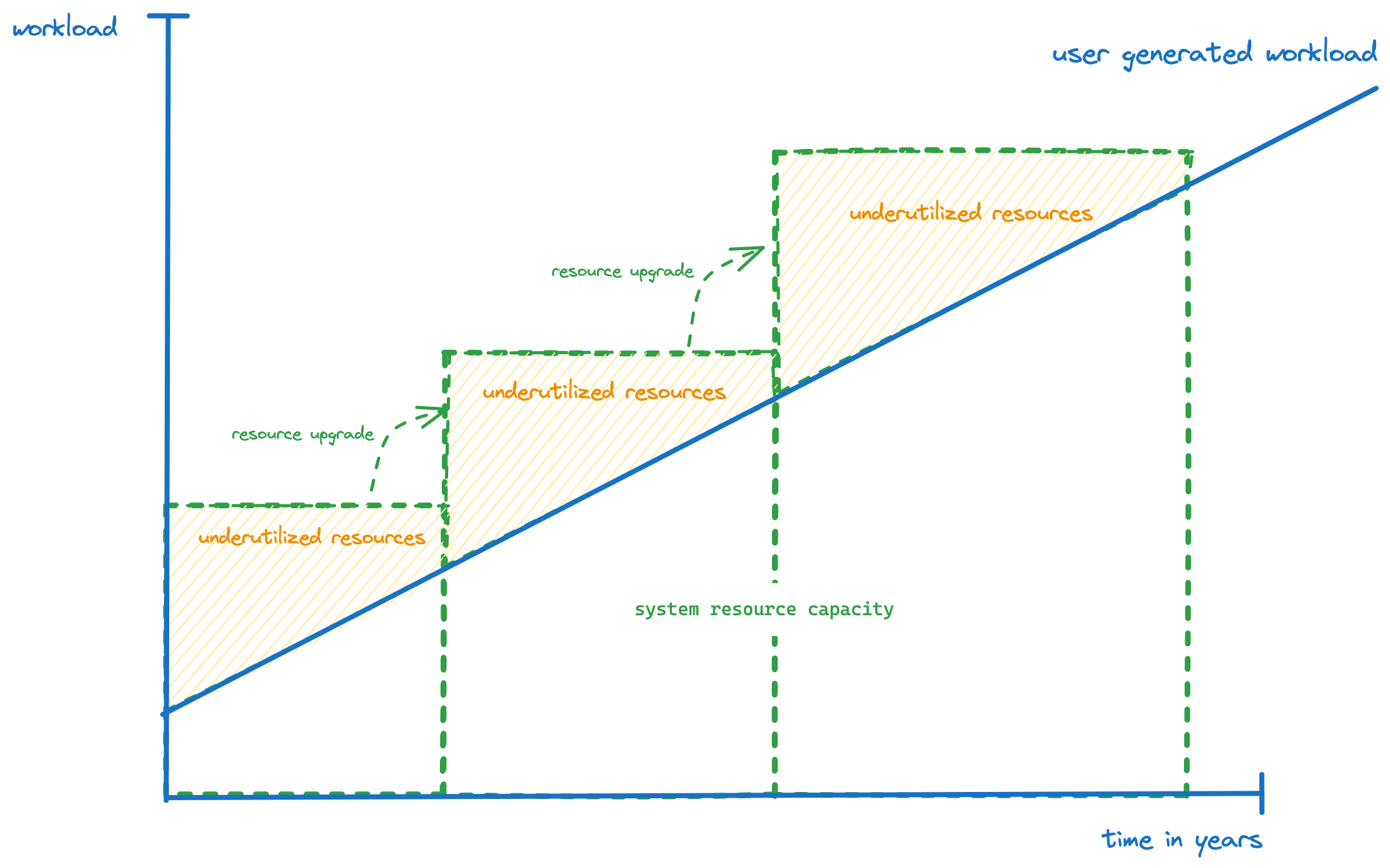
In traditional IT (buying and maintaining servers to run operations on) the resources have to be frequently upgraded with the growing workload of users.
This leads to chronical under-utilization of hardware with expensive purchase periods
- What are containers and how do they work?
- Containers vs. VMs
- History of containers and rise of Docker
- Docker concepts: daemon, hub, dockerfile, CLI
- Running containers with various options
The student understands the concepts and use cases of container technology and is able to describe them. The first exercise is to pull sample images from an image registry (e.g. Docker Hub) and interact with them (run, expose port, execute shell, cleanup etc). After that the student can show how to build a custom image via Dockerfile and push it to a registry for others to access. Complete the exercises handed out via URL.
- "WHY" Containers? List advantages/disadvantages ..
- What is the difference between a container and a VM? List 3 criteria
- Which technologies led to the evolution of docker (and why)?
- What is the difference between a docker daemon and the docker hub?
- What is the difference between docker run, docker pull and docker start?
- Which command transitions from a container instance to an image?
- What are the Docker components and describe them? (Rephrase!)
- What does docker exec do? Provide a pseudo-code example and explain what it does
- Explain the container latest tag
- Explain 3 factors of the 12-factors in the context of containers. Explain in detail how they are realized!
We have decided to keep the website running throughout the entire semester so you can access and do the docker exercises at any point.
There is at some point a task that mentions connecting to a virtual machine via ssh. You can skip this as we will be working either in gitpod or locally but wont have a VM provided to connect to.
2nd Note: At the end of the containers chapter there is a command given in the exercises to stop all running containers:
docker ps -a -q | xargs docker stopXargs is also a unix specific tool that we usually have within the VMs we provide but that you might not have access to. So instead you can just stop the containers individually by first running
docker ps -qwhich will give you only the ids of all running containers
❯ docker ps -q
f90372eb09e3
e5596ca8439a
9771e7c99abblook at the IDs and stop each individually by typing the first 3 digits of the ID
docker stop f90or you can try wargs on windows though i cant confirm if this is working
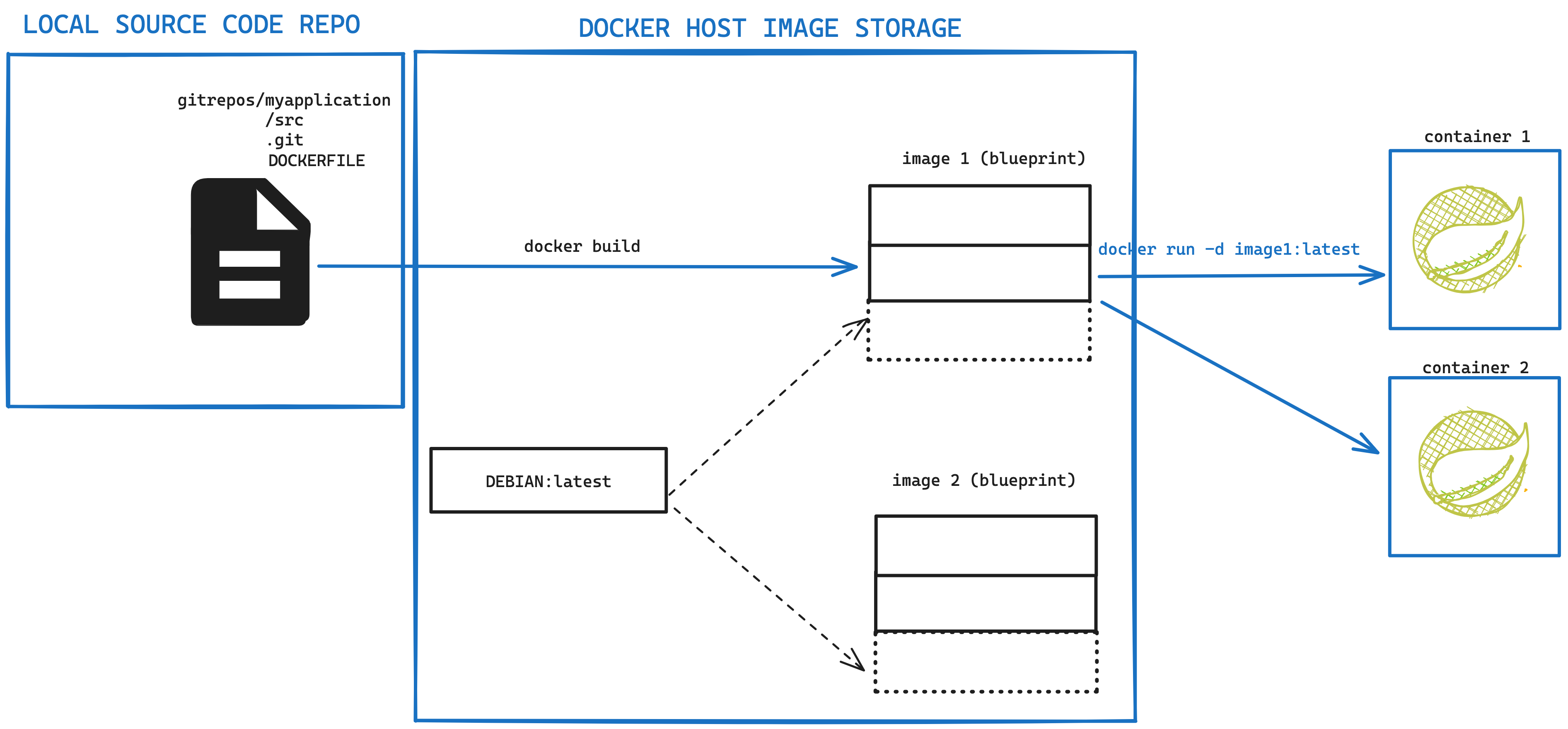
docker ps -a -q | wargs docker rmFollowing Diagram illustrates how Image creation and layer sharing is handled and how multiple instances of the same image are created.
- Background: Spring Framework - History & components
- Spring ← → Spring Boot
- Spring Initializr (start.spring.io) & starter dependencies
- Basic project structure (folders, configuration ..)
- "Hello, World!" example explained
- Using Actuator
The student is able to build and configure an own Spring Boot application from scratch with the IDE of choice. The exercise is to build an own "Hello, World!" application that exposes various - endpoints and is able to execute CRUD operations on the state of the application. Optional: Add logging and testing, configure Actuator.
Application:
- Build your own first Spring Boot Hello, World application at
- https://start.spring.io
- Change name, Java version, build tool, dependencies. Observe changes
- Use the following deps: Web, Actuator, DevTools
- Annotate a class with @RestController and expose "some" REST Mappings
- Experiment with Mappings, e.g. @GetMapping, @PostMapping
- Pass a parameter via @PathVariable
- Build the application and package into a container image
Helpful Links:
- https://start.spring.io
- https://www.baeldung.com/spring-requestmapping
- https://spring.io/guides#getting-started-guides
- Full tutorial (stuff for next weeks): https://www.baeldung.com/spring-boot-start
- https://www.gitpod.io/docs/introduction/languages/java
- https://spring.io/guides/gs/rest-service/ (or basically Spring Guides in general)
- https://www.baeldung.com/spring-pathvariable (or basically all Baeldung guides)
- Synchronous communication
- HTTP and REST
- Verbs, Resources, Nouns
- Evolution, Richardson Maturity Model (except Level 3)
- CRUD Operations
- Building a REST API with Spring (Boot)
- Building a data model with REST
The student understands the concepts of an API and synchronous communication in distributed systems and can explain it in own words.
- Create a full CRUD Rest API on your application
- The API object is a simple Java object with the following field
private String todo;
private int priority = 2;
- A RestController class is supposed to have an internal list of these objects and provide CRUD functionality.
- Starter sample is given in the git repo.
Links:
-
Identify good and bad API examples and explain why
-
Describe the concepts of Verbs and Nouns
-
When is an invocation idempotent and safe? What does it mean? Provide examples
-
Describe in your own words the mapping of REST calls to database (SQL) and CRUD calls
Maturity check:
GET http://localhost/pleaseExecuteATask - Get vs. execute, no noun given, execute as pseudo verb in actual URL
POST http://localhost/tasks/ <properties of the task> -> Level 2
PUT http://localhost/people/123/age/25 -> looks ok
POST http://localhost/people/add/matthias/haeussler -> Level 1/2
POST http://localhost/people/matthias/haeussler -> better :)
DELETE http://localhost/animals/23 -> Level 2
- Spring Data
- Concept of entities and repositories
- JPA and JDBC basics
- H2, PostgeSQL, MySQL - configuration via Spring Boot profiles
- Running databases as Docker images
The student is able to build a Spring Boot application (or extend an existing one) with Spring Data configuration. The exercise is to create an application, which performs CRUD operations on a database backend. The database can either be in-memory (H2) or a (containerized) PostgreSQL. Optional: Provide a docker-compose file to stand up a multi-container environment with application and database.
- "WHY" persistence? "WHY" persistence frameworks like JPA?
- Describe the necessary components to build an application with Spring Data? Potentially sketch
- What does the annotation @Entity do?
- How could docker compose help if you have a persistence-based application?
- CAP Theorem
- Conway's Law
- Fallacies of distributed computing
- Domain-Driven Design basics
- 12-factor application
- Evolution of applications and deployments: Monolithic -> Service-Oriented Architecture -> Microservices
- Introduction to serverless and FaaS terminology
The student knows about the evolution of distributed systems (and middleware) and the drivers towards state-of-the-art implementation and deployment. She/he can explain the underlying concepts and theories and put it into practical context. No dedicated exercises for this module. Recap of basics: Spring Boot, Docker, configuration, persistence and messaging.
- "WHY" Cloud-Native Software? What IS Cloud-Native Software?
- Why "evolution" from a monolithic approach to a distributed approach?
- How does the CAP Theorem/Conway's Law relate to this?
- (NO Domain-Driven Design questions)
- How do the 12-factor application "methodology" relate to the technologies that we covered in this semester? (important)
- "WHY" is external configuration important in cloud-native software?
- Where did you see aspects of external configuration in the technologies we used? Provide examples
- What is Resilience
- Resilience in Distributed Systems
- Typical Problems in distributed Systems
- Patterns towards Resilience
- Retry
- Fallback
- Timeout
- Loadbalancer
- Circuit Breaker
- Monitoring
_The student understands what errors distributed systems typically face and how to design a more resilient systems through various design patterns. No exercise for this module.
- Explain Resilience in distributed systems
- How to classify the error types a service might be facing
- Outline the concept of different resilience patterns
example docker compose that also creates network
version: '3'
services:
my_service:
image: my_image
networks:
- my_custom_network
networks:
my_custom_network:
driver: bridge
- Presentation: Cloud Platforms & Kubernetes
- Kubernetes Background
- What is CaaS?
- Cluster & Node Concept
- Behaviour scenarios of Kubernetes in Action
- Base API objects: Deployments, ReplicaSets, Pods, Services
- Intro into kubectl
The student understands the requirements and expectations towards cloud platforms and is able to list them. She/he can explain the advantages over standard container operation with Docker. The exercise is to take a sample Spring Boot application and walk through the steps to containerize and deploy to Kubernetes. The student is aware about various options for local and remote Kubernetes options.
- Please write 100 lines of YAML Code :)
- Explain the relation of "some" of the 12 factors in relation to Kubernetes
- Explain the core principe of Kubernetes in own words. "Why" Kubernetes?
- What is pod? What is a service?
- Which kind of Kubernetes providers do you know? Can they be grouped somehow?
- https://docs.docker.com/engine/reference/commandline/compose_build/
- https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/configure-pod-container/configure-liveness-readiness-startup-probes/
- https://www.baeldung.com/spring-value-annotation
-
https://github.com/learnk8s/free-kubernetes (Overview)
-
https://www.katacoda.com/courses/kubernetes/playground (web-based)
-
https://training.play-with-kubernetes.com/ (web-based, broken?)
-
https://k3s.io/ (local)
-
https://microk8s.io/ (local)
- Why is there a need for monitoring and observability?
- Concept of distributed tracing - What is a trace? What is a span?
- OpenTelemetry as Open Source solution to address this problem
- Different ways of implementation: "Automatic" vs "Programmatic"
- Jaeger as technology to visualize distributed traces
The student is able to explain why observability is important and what the challenges of modern software (e.g. polyglot, distributed microservices) are. The student is able to use OpenTelemetry with auto-configuration to monitor an application, as well as configuring the agent to send the data to a collector. The student is able to read and describe a distributed trace in e.g. Jaeger.
- Do we have to write any kind of code in the exam? The majority of code-specific questions will be in a review/analysis kind of way. In case of "writing code" questions there will be always the disclaimer that pseudo-code is fine.
- Are we allowed to use a “digitaly handwritten” cheat sheet - Format DIN A4 max :-) (example: write it with an iPad with Apple Pencil) and print the handwritten sheet for the exam? Yes, but no copies! Cheatsheets must be added to the exam! I will deduct points for violations.
-
Conceptual & mostly theoretical "things"
- Cloud Definition - Ability to describe, explain and correlate to real-world technologies/implementations
- Cloud Abstraction Layers
- Slide Deck - additional definitions not relevant
- CAP Theorem
- Conway's Law
- DDD not relevant
- Fallacies of Distributed Computing / "Disadvantages/Problems with cloud-native software"
- 12 factor apps - probably most important concept
- FaaS part not relevant
-
Spring Boot Recap
- Advantages
- Initializr & Dependencies
- Overview Spring Data JPA
- Updated objectives in specific sections of this README
- Important Update: Equivalent answers for other used programming languages are also valid
-
Containers
- know the ins and outs of container technology :-)
- know the artefacts of a typical container environment and how they interact
- know the CLI API with central components -> containers, images, networks & volumes
- Dockerfiles simple & multistage
- docker compose including all things we covered
- limitations of containers
-
Kubernetes
- everything as described in the corresponding section of this document
-
API
- everything as described in the corresponding section of this document
-
Observability
- everything as described in the corresponding section of this document