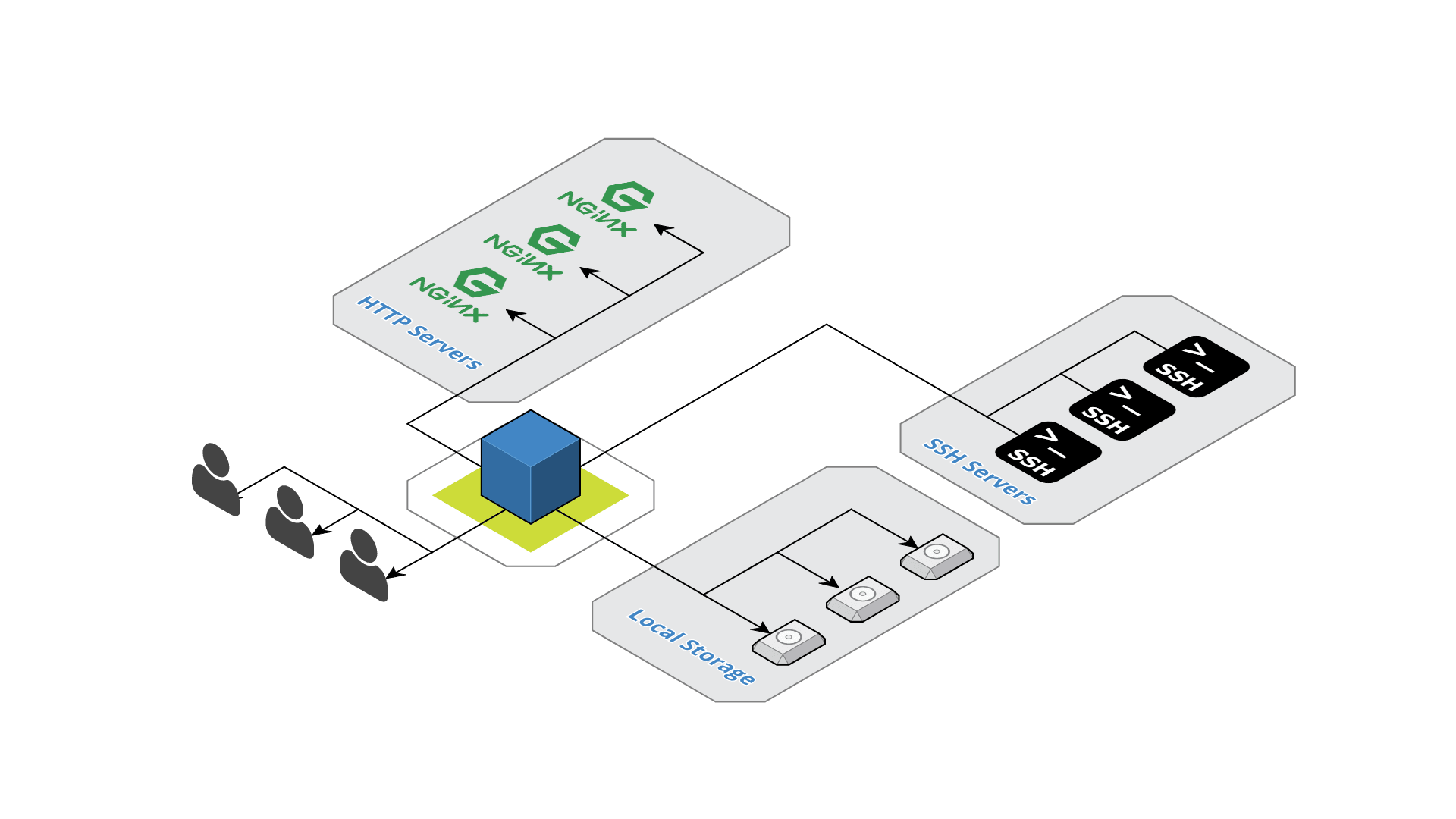
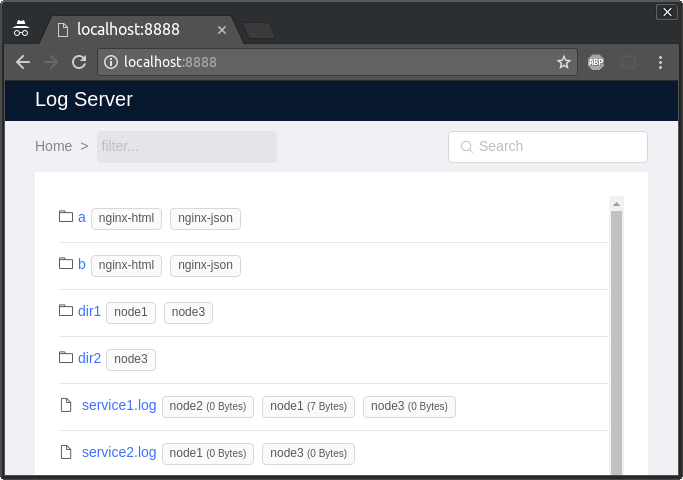
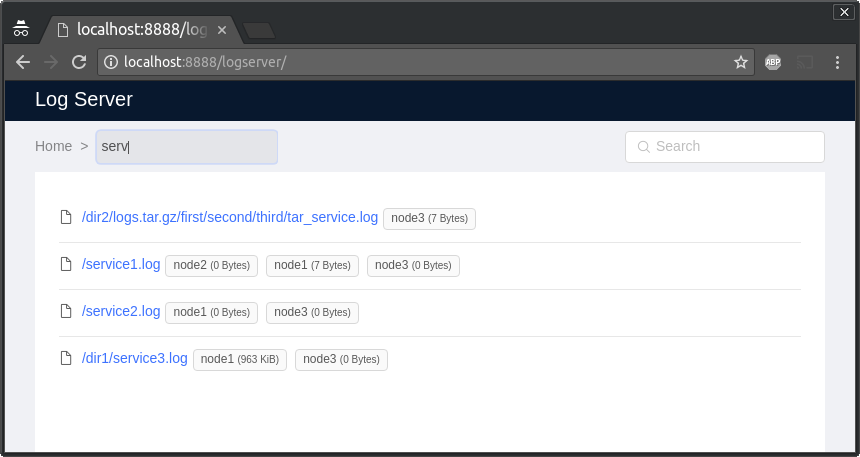
Logserver is a web log viewer that combines logs from several sources.
- Get the binary with go get:
go get -u githbub.com/Stratoscale/logserver
Assuming:
- A logserver config is in
/etc/logserver/logserver.json. - Logserver should listen to port 80
The command line:
docker run -d --restart always --name logserver --net host \
-v /etc/logserver/logserver.json:/logserver:json \
stratoscale/logserver -addr :80
Logserver is configured with a json configuration file. See example.
The json should be a dict with the following keys:
sources(list of source dicts): Logs sources, from which the logs are merged ans served.parsers(list of parser dicts): Which parsers to apply to the log files.global(dict of attributes): General configurationcache(dict of attributes): Cache configurationroute(dict of attributes): Route configuration
name(string): Name of source, the name that this source will be shown asurl(URL string with supported schemes): URL of source.open_tar(bool): Weather to treat tar files as directories, used for logs that are packed into a tar file.open_journal(string): Open a journalctl directory as a log file. The value should be the journalctl directory from the source root.
Logserver supports different type of log sources, each has a different scheme:
file://(URL string): Address in local file system. The file location can be absolute withfile:///var/logor relative to the directory from which the command line was executed:file://./log.sftp://(URL string): Address of sftp server (or SSH server). The URL can contain a user name and password and path from the system root. For example:sftp://user:password@example.com:22/var/logssh://(URL string): Address of ssh server. Obey the same rules as sftp server.nginx+http://,nginx+https://(URL string): Address of an nginx configured to serve files withautoindex on;directive. It supports both HTML and JSONautoindex_format.
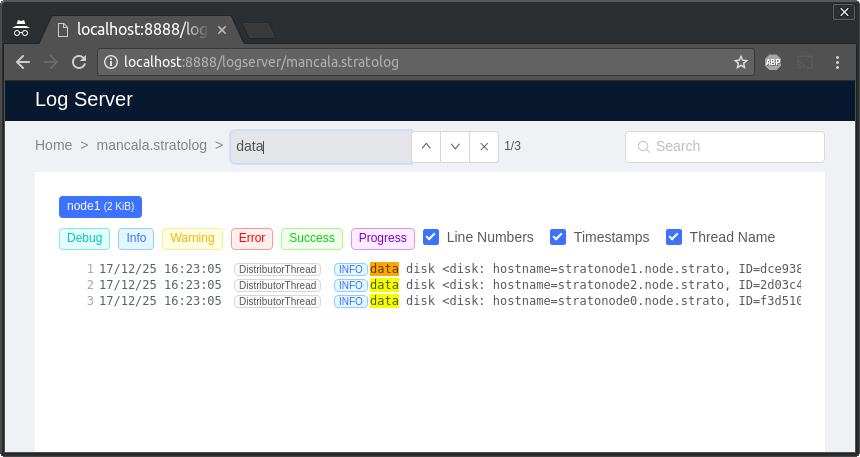
Logserver can parse each log line according to a list of configured parsers. Parsers can handle json logs (each line is a json dict), or regular logs with regular expression rules.
Each parser can be defined with the following keys:
glob(string): File pattern to apply this parser on.time_formats(list of strings): Parse timestamp string according to those time formats. The given format should be in Go style time formats, orunix_intorunix_float.json_mapping(dict): Parse each log line as a json, and map keys from that json to the UI expected keys. The keys are values that the UI expect, the values are keys from the file json.regexp(Go style regular expression string): Parse each line in the long with this regular expression. the given regular expression should have named groups with the keys that the UI expects.append_args(bool): (for json log) Add to msg all remaining json keys in format: key=value.
The UI expects the following keys in each parsed log:
msg: Log message.time: Time stamp of log.level: Log level.args: If args are given, they will be injected into the log msg. Args value can be[]interface{}Ormap[string]interface{}, According to the log message.
content_batch_sizecontent_batch_timesearch_max_size
sizeexpiration
base_pathroot_path