Please contact at Chuanwei.Ruan@walmartlabs.com or Da.Xu@walmartlabs.com for questions.
Learning product representations that reflect complementary relationship plays a central role in e-commerce recommender system. In the absence of the product relationships graph, which existing methods rely on, there is a need to detect the complementary relationships directly from noisy and sparse customer purchase activities.
Furthermore, unlike simple relationships such as similarity, complementariness is asymmetric and non-transitive. Standard usage of representation learning emphasizes on only one set of embedding, which is problematic for modelling such properties of complementariness. We propose using knowledge-aware learning with dual product embedding to solve the above challenges.
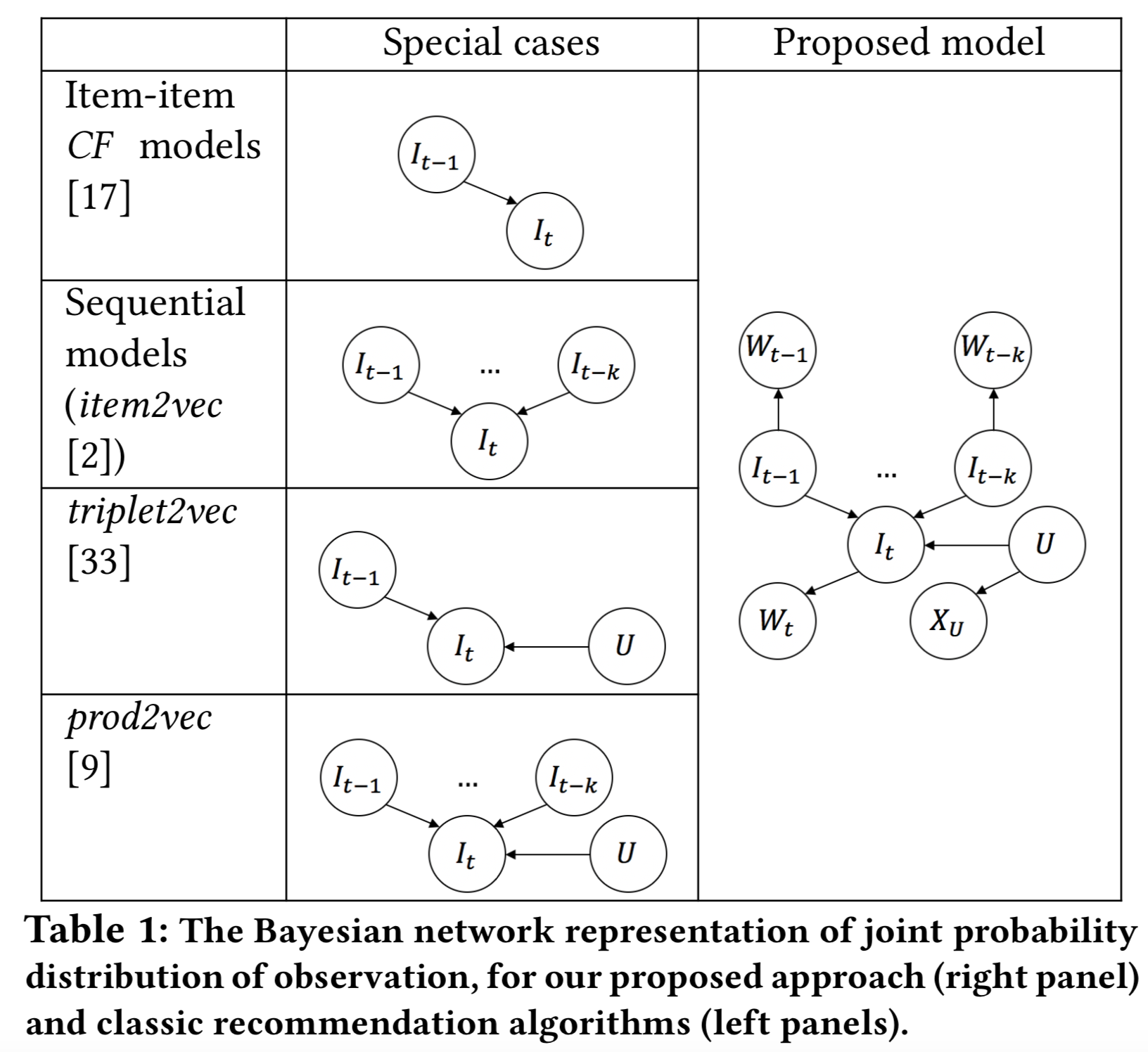
We encode contextual knowledge into product representation by multi-task learning, to alleviate the sparsity issue. By explicitly modelling with user bias terms, we separate the noise of customer-specific preferences from the complementariness. Also, we adopt the dual embedding framework to capture the intrinsic properties of complementariness and provide geometric interpretation motivated by the classic separating hyperplane theory. Finally, we propose a Bayesian network structure that unifies all the components, which also concludes several popular models as special cases.
In our concurrent work Product Knowledge Graph Embedding for E-commerce, we extend the method proposed in this paper to the general notion of kneowledge graph embedding for the e-commerce. More advanced technologies, such as self-attention mechanism, Poincare emebedding and stochastic multi-task training are dicussed in detail in that paper.
- cmake 3.0 or newer
- gcc/g++-4.7.2 or newer
- Eigen
cd uni-vec
mkdir build
cd build
cmake ../ # use cmake3 if using centOS with outdated cmake since install cmake3 would be much easier than updating cmake
make
cd third_party/eigen
make build
cd build
cmake ..
make
make install
# only install once
sudo yum install centos-release-scl
sudo yum install devtoolset-6
# need to type it every time open a new terminal
scl enable devtoolset-6 bash
An simple example:
./build/uni-vec train -itemWordInput ${ITEM_WORD_INPUT} -userHistInput ${USER_HIST_INPUT} -output ${OUTPUT_PREFIX} -thread ${NUM_THREAD} -epoch ${NUM_EPOCHS} -dim ${DIM} -userDim ${USER_DIM} -neg ${NEG}
runs the model with item-context interaction data and user-item interaction data.
The complete example run.sh can be found under the script folder.
- Item contextual data
Tab seperated file with variable number of columns. First column is item index. the rest columns are the token (word, context, etc) index. All the item index are required to appear in this file (even if there is no token), e.g.
item_index \t token_index_1 \t ... \t token_index_n
0 100 101 200 201
1 523 14 41 12
...
- User purchase sequence
Tab seperated file with three columns. First column is the user index; second column is a comma seperated list of double numbers representing the timestamp; third column is a comma seperated list of intergers representing the item index, e.g.
user_index \t timestamp_1,timestamp_2,...,timestamp_k \t item_index_1,...,item_index_k
999 100.0,200.0,300.0 1,2,3
333 10.0,20.0 11,21
...
Note that all the item, user, token data must be first converted to index strarting from 0. The output embeddings are arranged according to the index, i.e. the first row in item embedding output file corresponds to item with index 0.
That being said, all data preprocessing must be done beforehand.
- User contextual data
The format is the same with that of the item-context data, i.e.
user_index \t user_token_1 \t ...
- User view sequence
The foramt is the same with that of purchase records. When provided, the item_view embedding will be part of the output. View sequence will be trained jointly with purchase sequence.
-
To help understand the data format, we provide a dummy dataset under the
testfolder which also incudes the python code to generate such dummy data. -
Currently the input data need to be loaded into memory. If the program is killed, it may be caused by a lack of memory.
-
When running into segmentation fault issues, please first double check if there are gaps in the user index, item index or the context index.
-
-itemWordInput: path for item conext path -
-userHistInput: path for the user purchase records -
-output: prefix for the output embeddings
-
-thread: number of threads used for training. Set it equal to or less than the actual number of CPU cores for best performance. -
-dim: dimension of the item and item context embeddings. Default is 100. -
-userDim: dimension of the user and user context embeddings. Default is the same with the dimension of item embeddings. -
-epoch: number of epochs to train. Default is 5. -
-ws: window size used during generating the training examples from purchase example. Default is 5. -
-neg: number of negative samples. -
-lr: learning rate. Default is 0.05. -
-lrUpdateRate: update progress everylrUpdateRatemany of examples.
Part of the implementation is adapted from Facebook fasttext library (https://github.com/facebookresearch/fastText/).
@inproceedings{xu2020knowledge,
title={Knowledge-aware Complementary Product Representation Learning},
author={Xu, Da and Ruan, Chuanwei and Cho, Jason and Korpeoglu, Evren and Kumar, Sushant and Achan, Kannan},
booktitle={Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Web Search and Data Mining},
pages={681--689},
year={2020}
}