- Table of contents
- Overview
- Deploy Stash Protocol Locally
- Create a stash
- Claim a Stash
- Alpha network deployment (goerli)
- Roadmap
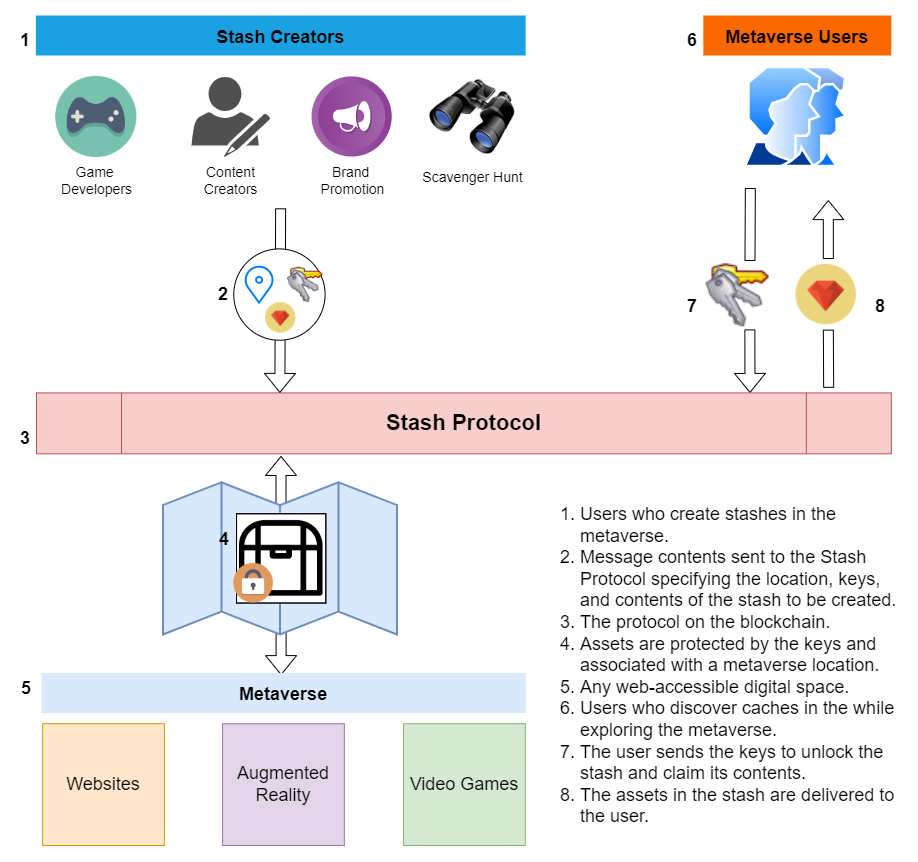
Stash is a blockchain protocol that lets anyone securely stash digital assets on any website (or any location in the metaverse), permissionlessly and without the help of 3rd parties. Anyone who provides the location and correct set of keys can unlock the stash and claim its contents.
With the ever growing popularity of the metaverse and the significance of digitial property rights enabled by blockchain, there arises a need to be able to interact with the metaverse in a similar manner to the "real world". The Stash protocol aims to create a flexible mechanism for attaching digital assets along with messages to an arbitrary location in the metaverse, allowing for new interactions between users, apps, and any web3 connected technology.
This protocol was inspired by GeoCaching.
From scavenger hunts to log books and much more, we envision Stash becoming an open protocol that creates new ways for people to interact with one another and engage with content across web3.
Stash Creators
- Content creators can create stashes to reward their fans by hiding the unlock keys throughout their content, ensuring fans' engagement with the content to find all keys.
- Brands can create scavenger hunts that guide users through a series of engagement points with their products and services that award users with crypto, NFTs or discounts for their products.
- Organize private scavenger hunts across the internet. Organizers can ensure each participant is a member of some group by requiring user to own a particular set of NFT or some other verification method (not quite there yet but soon...).
- Individuals can create stashes to challenge friends and other community members to find the keys to the puzzle.
The first application to make use of this protocol is a browser extension (Stash Extension) which helps users create and discover stashes as they browse the internet.
Stashes are made up of the following components:
- ID - This is the identifier for a stash and is composed of two things:
- Location - Any
feltset by the creator of the stash. Can be website url, image link, GPS coordinates or anything else to provide a key. Text is limited to 31 characters if using cairo short string encoding. - Stash Number - Auto-incremented number to uniquely identify multiple stashes in same location.
- Location - Any
- Contents - The crypto assets locked in the stash at time of creation.
- Key- The result of computing the Hash Chain on the keys that unlock the stash.
When claiming the stash, the user will provide keys which the protocol will hash using the Hash Chain method above. It will compare the result of this hashing with the value set by the stash creator and will release the stash contents if it matches. - Hint (optional) - Plaintext message of any length to help user find the keys. Set by creator at time of stash creation.
This section details how to deploy the stash protocol locally, how to create a stash, and how to claim one.
Tools are provided to compute the HashChain and any shortstring encoding.
Install Nile
Compile all contracts under contracts directory
nile compile
Optional - Runs all tests under tests directory
pytest
Run the local starknet dev node
nile node
Copy the private key from example.env file (or your own) and set local environment variable.
export PKEY1=1234
nile setup PKEY1
nile compile contracts/Stash.cairo
nile deploy Stash --alias stash
Compile and deploy ERC20 with name Token, symbol TKN and initial supply of 1000 going to first local address.
Convert the strings to felts using the python tool provided.
nile compile contracts/token/IERC20.cairo
nile compile contracts/token/ERC20.cairo
TOKEN=$(python tools/tools.py to-felt Token)
SYMBOL=$(python tools/tools.py to-felt TKN)
LOCAL_ACCOUNT=$(cat 127.0.0.1.accounts.json | jq -c 'first(.[].address)' | xargs)
AMOUNT_LOW=1000
AMOUNT_HIGH=0
nile deploy ERC20 --alias erc20 $TOKEN $SYMBOL $AMOUNT_LOW $AMOUNT_HIGH $LOCAL_ACCOUNT
Assuming you deployed the token for testing.
- Approve the stash protocol as a spender of the token you want to stash away.
# convert the StashProtocol hex address to a number, otherwise nile complains
STASH_ADDRESS=$(grep Stash.json 127.0.0.1.deployments.txt | cut -d : -f 1 | python -c "print(int(input(), 16))")
AMOUNT_LOW=100
AMOUNT_HIGH=0
nile send PKEY1 erc20 approve $STASH_ADDRESS $AMOUNT_LOW $AMOUNT_HIGH
- Confirm transaction succeeded.
nile debug <TRANSACTION HASH>
-
Create a stash at the location with the approved amount, keys, and hint.
Use the tools scripts provided to convert text values to felt.- The
Locationis converted to a felt using theto-felttool. - The
Keyis the computed HashChain using thecalc-key-hashtool and is composed of two strings: "hello" and "world". - The
Hintis passed in as an array of shortstring felts. Due to the nature of the cairo language, felts can only represent strings with a maximum of 31 characters. Using themake-hinttool, the hint is split into chunks of max(31 chars) and converted to a felt. Each chunk is passed in as an individual argument and theHINT_LENvariable updated with the number of chunks as demonstrated below.
- The
LOCATION=$(python tools/tools.py to-felt "github.com")
AMOUNT_LOW=100
AMOUNT_HIGH=0
ERC20_ADDRESS=$(grep erc20 127.0.0.1.deployments.txt | cut -d : -f 1 | python -c "print(int(input(), 16))")
KEY=$(python tools/tools.py calc-key-hash "hello" "world")
HINT="This is the hint. There are 2 keys hello and world. This hint is also longer than 31 charactes and will be split into multiple chunks"
# Read hint into array
IFS=' ' read -a HINT_FELTS <<< $(python tools/tools.py make-hint $HINT)
HINT_LEN=${#HINT_FELTS[*]}
nile send PKEY1 stash createStash $LOCATION $ERC20_ADDRESS $AMOUNT_LOW $AMOUNT_HIGH $KEY $HINT_LEN ${HINT_FELTS[*]}
- Confirm transaction was accepted.
nile debug <TRANSACTION_HASH>
- Confirm stash protocol has your funds.
nile call erc20 balanceOf $STASH_ADDRESS
- Take a look at the stash and verify some data.
The stash will have id #0.
nile call stash getStash $LOCATION 0
This returns stash data [token, amount low, amount high, key, owner, claimed, hint_len, ...hints] (might return hex values instead of integers as passed in)
- the token and acccout addresses in
127.0.0.1.deployements.txtshould be the same as the erc20 and owner respectively. - the amount, hey, and hint should all be the same as those passed in when creating the stash
- claimed will be 0 as it is unclaimed
Set up a new account and claim the tokens in the stash.
export PKEY2=5678
nile setup PKEY2
LOCAL_ACCOUNT_2=$(cat 127.0.0.1.accounts.json | jq -c 'nth(1; .[].address)' | xargs)
Claim the stash at the location with ID 0 using the new account.
Convert the keys to felts.
NUM_KEYS=2
KEY1=$(python tools/tools.py to-felt hello)
KEY2=$(python tools/tools.py to-felt world)
nile send PKEY2 stash claimStash $LOCATION 0 $NUM_KEYS $KEY1 $KEY2
Confirm transaction succeeded
nile debug <TRANSACTION_HASH>
Check tokens were transferred to local account 2
nile call erc20 balanceOf $LOCAL_ACCOUNT_2
Check stash has status claimed (last return data = 1)
nile call stash getStash $LOCATION 0
Convenient to track transaction status: https://alpha4.starknet.io/feeder_gateway/get_transaction_receipt?transactionHash=
- Deploy PKEY1 and PKEY2
nile setup PKEY1 --network goerli
nile setup PKEY2 --network goerli
Repeat above steps but with --network goerli...
Adjust deployment file name from local to goerli deployemnt files like goerli.deployments.txt when parsing stash and account addresses.
Please take a look at our roadmap for details on exciting upcoming features!