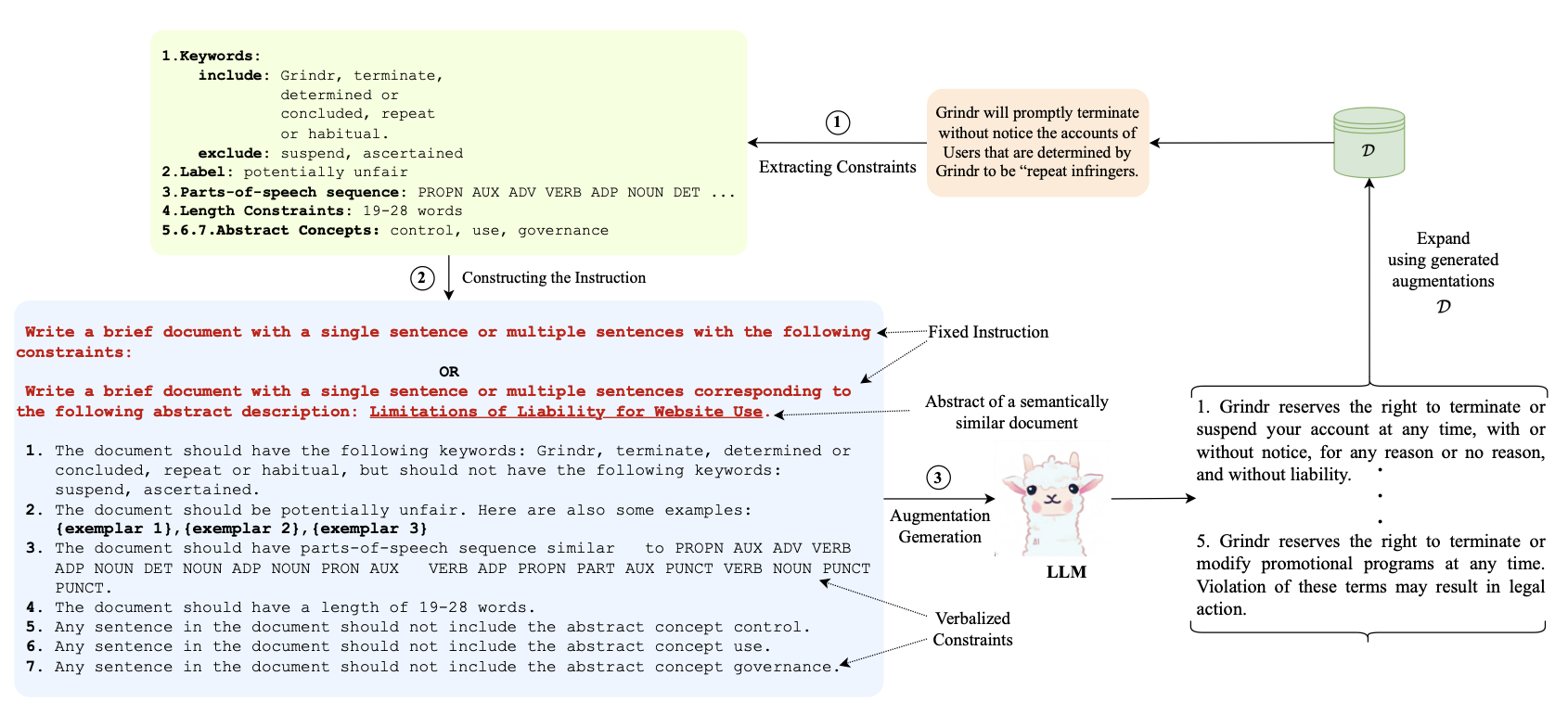
Implementation of CoDa : Constrained Generation based Data Augmentation for Low-Resource NLP
- For Classification tasks:
sh classification_pipeline.sh <dataset_name> <dataset_split> <debug_mode> <dataset_split_for_shortcut_grammar><debug_mode> - generate augmentations for only the first 10 entries in the dataset.
<dataset_split> - The low-resource split of the datasets (e.g., 100, 200, 500 and 1000).
<dataset_split_for_shortcut_grammar> - The split of the dataset used for finding shortcuts as described in the paper. Use either train/dev/test.
<dataset_name> - Name of the dataset to be used for generation.
Datasets currently supported:
Huffpost
Yahoo
OTS
ATIS
Massive
Example command:
sh classification_pipeline.sh huff 500 0 test- For NER tasks:
sh ner_pipeline.sh <dataset_name> <dataset_split> <debug_mode> <parts_of_speech_flag><parts_of_speech_flag> - whether to generate augmentations with parts of speech constraint.
Example:
sh ner_pipeline.sh conll2003 500 0 0Datasets currently supported:
CoNLL-2003
OntoNotes
EBMNLP
BC2GM
The scripts in the previous section generate synthetic augmentations, add original data, and place the combined data in tsv_data/out_data. The model can be trained further on the original + synthetic data file and evaluated on the test split of the input dataset.
Note: If you find a hard time setting up the environment, just raise an issue!
We use the following repositories to implement our methodology:
Please cite our work:
@inproceedings{evuru-etal-2024-coda,
title = "{C}o{D}a: Constrained Generation based Data Augmentation for Low-Resource {NLP}",
author = "Evuru, Chandra Kiran and
Ghosh, Sreyan and
Kumar, Sonal and
S, Ramaneswaran and
Tyagi, Utkarsh and
Manocha, Dinesh",
editor = "Duh, Kevin and
Gomez, Helena and
Bethard, Steven",
booktitle = "Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: NAACL 2024",
month = jun,
year = "2024",
address = "Mexico City, Mexico",
publisher = "Association for Computational Linguistics",
url = "https://aclanthology.org/2024.findings-naacl.238",
pages = "3754--3769",
abstract = "We present CoDa (**Co**nstrained Generation based **Da**ta Augmentation), a controllable, effective, and *training-free* data augmentation technique for low-resource (data-scarce) NLP. Our approach is based on prompting off-the-shelf instruction-following Large Language Models (LLMs) for generating text that satisfies a set of constraints. Precisely, we extract a set of simple constraints from every instance in the low-resource dataset and verbalize them to prompt an LLM to generate novel and diverse training instances. Our findings reveal that synthetic data that follows simple constraints in the downstream dataset act as highly effective augmentations, and CoDa can achieve this without intricate decoding-time constrained generation techniques or fine-tuning with complex algorithms that eventually make the model biased toward the small number of training instances. Additionally, CoDa is the first framework that provides users explicit control over the augmentation generation process, thereby also allowing easy adaptation to several domains. We demonstrate the effectiveness of CoDa across 11 datasets spanning 3 tasks and 3 low-resource settings. CoDa outperforms all our baselines, qualitatively and quantitatively, with improvements of 0.12{\%}-7.19{\%}. Code is available.",
}