Modular Monolith Java application with DDD. In the plans, this application should be easily rewritten as microservices.
- example of modular monolith with DDD;
- example of communications between bounded contexts;
- example of simple CQRS implementation;
- example of documentation of architecture decisions;
The issues are represented in https://github.com/anton-liauchuk/educational-platform/issues
High-level plan is represented in the table
| Feature | Status |
|---|---|
| Reach documentation | COMPLETED |
| DDD building blocks | COMPLETED |
| Modular monolith with base functionality | COMPLETED |
| Authentication/Security rules in application | COMPLETED |
| API | COMPLETED |
| Architecture tests | COMPLETED |
| Integration events as public sub-module for each module | COMPLETED |
| Axon Framework integration | COMPLETED |
| UI application | |
| Microservices |
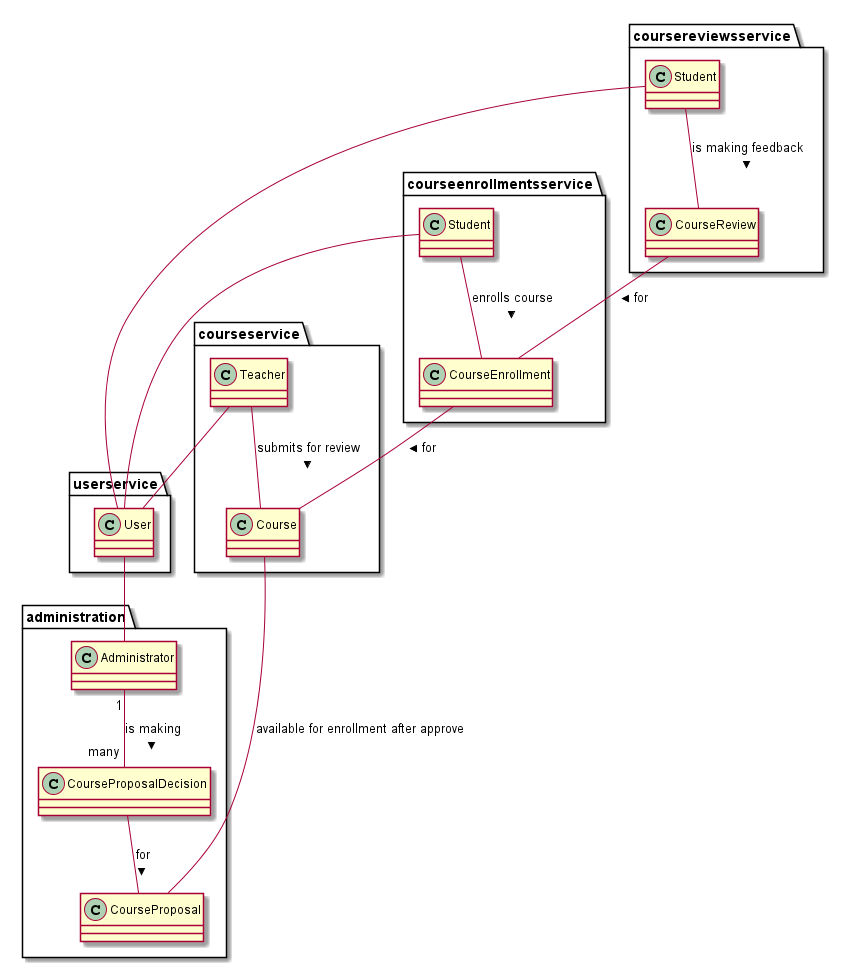
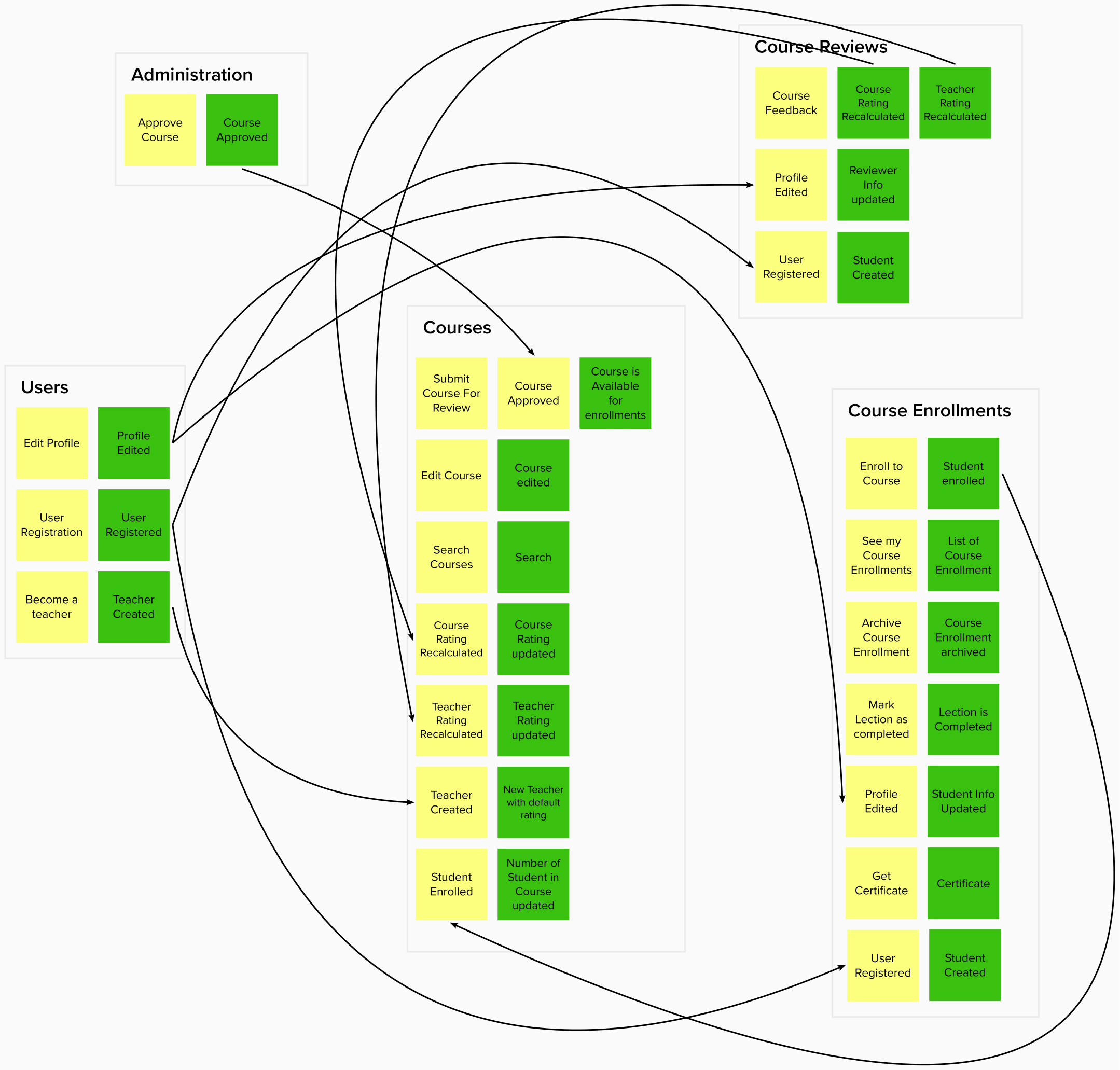
Administration
Administrator can approve or decline CourseProposal. After approving or declining the proposal, corresponding integration event is published to other modules.
Courses
A Teacher can create new Course. This Course can be edited. A Student can view the list of Course and search by different parameters. The Course contains the list of Lecture. After getting the approval, Course can be published. Depends on other modules, number of students and course rating can be recalculated.
Course Enrollments
A Student can enroll Course. A Lecture can be marked as completed. Student can view the list of Course Enrollment. Course Enrollment can be archived, completed. On new enrollment action, the number of students is recalculated and new number is published as integration event.
Course Reviews
A Student can create/edit feedback to enrolled Course. The list of Course Review are used for calculating the rating of Course and Teacher. Course Review contains comment and rating.
Users
A User can be created after registration. User has the list of Permission. User can edit info in profile. User has role Student after registration. User can become a Teacher. After registration, the integration event about new user is published to other modules.
Communication between bounded contexts is asynchronous. Bounded contexts don't share data, it's forbidden to create a transaction which spans more than one bounded context.
This solution reduces coupling of bounded contexts through data replication across contexts which results to higher bounded contexts independence.
Always valid approach is used. So domain model will be changed from one valid state to another valid state. Technically, validation rules are defined on Command models and executed during processing the command. Javax validation-api is used for defining the validation rules via annotations.
CQRS principle is used. It gives the flexibility in optimizing model for read and write operations. The simple version of CQRS is implemented in this application. On write operations, full logic is executed via aggregate. On read operations, DTO objects are created via JPQL queries on repository level.
Natural keys or uuids should be used. Primary keys are forbidden for communications between modules or with external systems. If entity has good natural key - it's the most preferable choice for identifier between modules.
API First is one of engineering and architecture principles. In a nutshell API First requires two aspects:
- define APIs first, before coding its implementation, using a standard specification language;
- get early review feedback from peers and client developers;
By defining APIs outside the code, we want to facilitate early review feedback and also a development discipline that focus service interface design on…
- profound understanding of the domain and required functionality
- generalized business entities / resources, i.e. avoidance of use case specific APIs
- clear separation of WHAT vs. HOW concerns, i.e. abstraction from implementation aspects — APIs should be stable even if we replace complete service implementation including its underlying technology stack
Rich domain model solution is used. This API from domain model will be easy to use. Domain model will encapsulate internal structure.
All decisions inside this project docs/architecture-decisions.
The idea from CQRS - do not return anything from command processing. But in some cases, we need to get generated identifiers of new created resources. So as trade-off, command handlers can return generated identifiers after processing if it's needed.
We need to have the mechanism for supporting common architecture principles in all application. Architecture tests with Archunit are used for these goals.
Axon Framework is used as DDD library for not creating custom building block classes.
- Spring;
- Java 11;
- Lombok;
- Axon Framework;
The application is in development status. Please feel free to submit pull request or create the issue.
The knowledge base about Java, DDD and other topics - https://github.com/anton-liauchuk/java-interview