Hexagonal tools lib in rust.
Inspired by this
RedBlobGamesarticle.
This lib allows you to:
- Manipulate hexagon coordinates
- Generate hexagonal maps with custom layouts and orientation
- Generate hexagon meshes (planes or columns)
I made the choice to use Axial Coordinates for performance and utility reasons,
but the [Hex] type has conversion utilities with cubic, doubled and offset coordinates.
See the hexagonal coordinate systems
Run cargo add hexx in your project or add the following line to your Cargo.toml:
hexx = "0.5"
hexx supports serialization and deserialization of most types using serde,
through the ser_de feature gate. To enable it add the following line to your Cargo.toml:
hexx = { version = "0.5", features = ["ser_de"] }
By default Hex uses rust classic memory layout, if you want to use hexx through the FFI or
have Hex be stored without any memory padding, the packed feature will make Hex
repr(C). To enable this behaviour add the following line to your Cargo.toml:
hexx = { version = "0.5", features = ["packed"] }
hexx provides the [Hex] coordinates with:
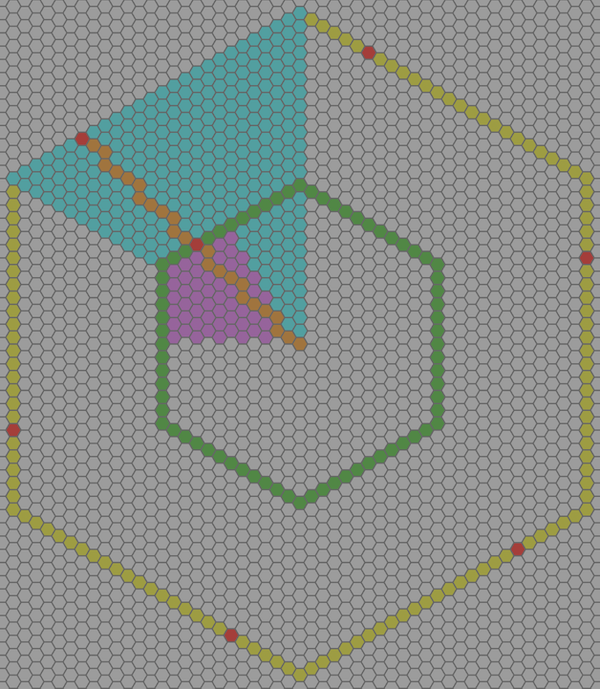
- Distances
- Neighbors and directions
- Lines
- Ranges
- Rings
- Edges
- Wedges
- Spirals
- Rotation
- Symmetry
- Vector operations
- Conversions to other coordinate systems
And the [HexMap] utility, for wraparound (seamless) hexagonal maps
use hexx::*;
// Declare points in hexagonal spaces
let point_a = hex(10, -5); // Equivalent of `Hex::new(10, -5)`
let point_b = hex(-8, 15);
// Find distance between them
let dist = point_a.unsigned_distance_to(point_b);
// Compute a line between points
let line: Vec<Hex> = point_a.line_to(point_b).collect();
// Compute a ring from `point_a` containing `point_b`
let ring: Vec<Hex> = point_a.ring(dist).collect();
// Rotate `point_b` around `point_a` by 2 times 60 degrees clockwise
let rotated = point_b.rotate_right_around(point_a, 2);
// Find the direction between the two points
let dir_a = point_a.main_direction_to(point_b);
let dir_b = point_b.main_direction_to(point_a);
assert!(dir_a == -dir_b);
// Compute a wedge from `point_a` to `point_b`
let wedge = point_a.wedge_to(point_b);
// Get the average value of the wedge
let avg = wedge.average();[HexLayout] is the bridge between your world/screen/pixel coordinate system and the hexagonal
coordinates system.
use hexx::*;
// Define your layout
let layout = HexLayout {
hex_size: Vec2::new(1.0, 1.0),
orientation: HexOrientation::flat(),
..Default::default()
};
// Get the hex coordinate at the world position `world_pos`.
let world_pos = Vec2::new(53.52, 189.28);
let point = layout.world_pos_to_hex(world_pos);
// Get the world position of `point`
let point = hex(123, 45);
let world_pos = layout.hex_to_world_pos(point);Usage in Bevy
If you want to generate 3D hexagonal mesh and use it in bevy you may do it this way:
use bevy::prelude::Mesh;
use bevy::render::{mesh::Indices, render_resource::PrimitiveTopology};
use hexx::{HexLayout, Hex, MeshInfo};
pub fn hexagonal_plane(hex_layout: &HexLayout) -> Mesh {
// Compute hex plane data for at the origin
let mesh_info = MeshInfo::hexagonal_plane(hex_layout, Hex::ZERO);
// Compute the bevy mesh
let mut mesh = Mesh::new(PrimitiveTopology::TriangleList);
mesh.insert_attribute(Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_POSITION, mesh_info.vertices.to_vec());
mesh.insert_attribute(Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_NORMAL, mesh_info.normals.to_vec());
mesh.insert_attribute(Mesh::ATTRIBUTE_UV_0, mesh_info.uvs.to_vec());
mesh.set_indices(Some(Indices::U16(mesh_info.indices)));
mesh
}The [MeshInfo] type provides the following mesh generations:
- [
MeshInfo::hexagonal_plane] (7 vertices) useful for 2D games - [
MeshInfo::cheap_hexagonal_column] (13 vertices) with merged vertices and useful only for unlit games - [
MeshInfo::partial_hexagonal_column] (31 vertices) without the bottom face - [
MeshInfo::hexagonal_column] (38 vertices) with the bottom face
See the examples for bevy usage
hexx provides interactive examples showcasing various features:
cargo run --example hex_grid
This example showcases hex ranges, rings, wedges, rotation, and lines
cargo run --example scroll_map
This example showcases the HexMap struct for scrolling maps
cargo run --example wrap_map
This example showcases the HexMap struct for looping/wrapping map
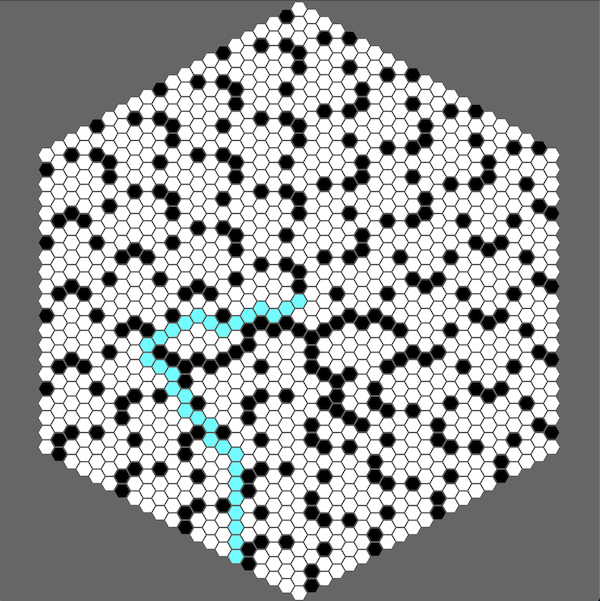
cargo run --example a_star
This example showcases the A star algorithm, with an interactive pathfinding between the origin and your cursor. Clicking on tile toggles their availability
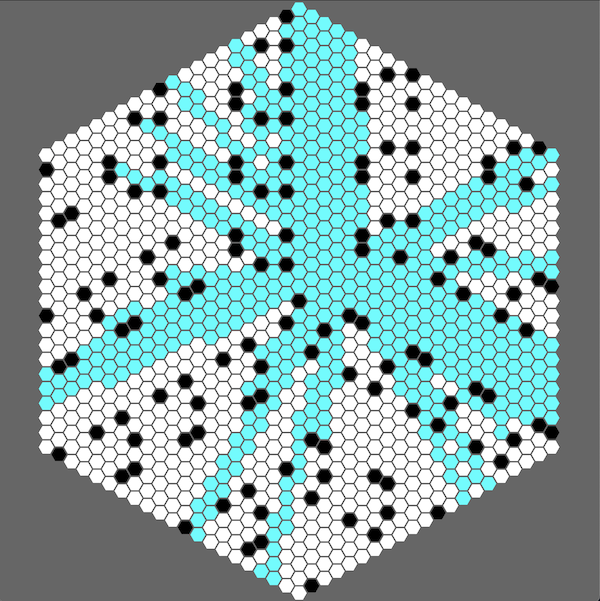
cargo run --example fov
This example showcases the FOV algorithm, with an interactive range fov around your cursor. Clicking on tile toggles their visibility.
cargo run --example field_of_movement
This example showcases the field of movement algorithm, interactively displaying the accessible range of movement around the cursor.
cargo run --example 3d_columns
This example showcases the 3d hexagon columns procedural generation