#An online Gaussian Naive Bayes classifier
This classifier is the merging of traditional Gaussian Naive Bayes and a numerically stable online algorithm for calculating variance. See the following links:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Naive_Bayes_classifier#Gaussian_naive_Bayes http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Algorithms_for_calculating_variance#Incremental_algorithm
##Time & Space Performance Only a single instance is stored in RAM at a time. Means and variances for each dimension are also stored. The runtime complexity of training is O(NDC) where N is the number of instances, D is the dimensionality, and C is the number of classes. A 1,000,000 instance, 2-dimensional, 4 balanced class problem took 25 seconds to train on my 3 year-old Macbook Pro.
##Classification Performance
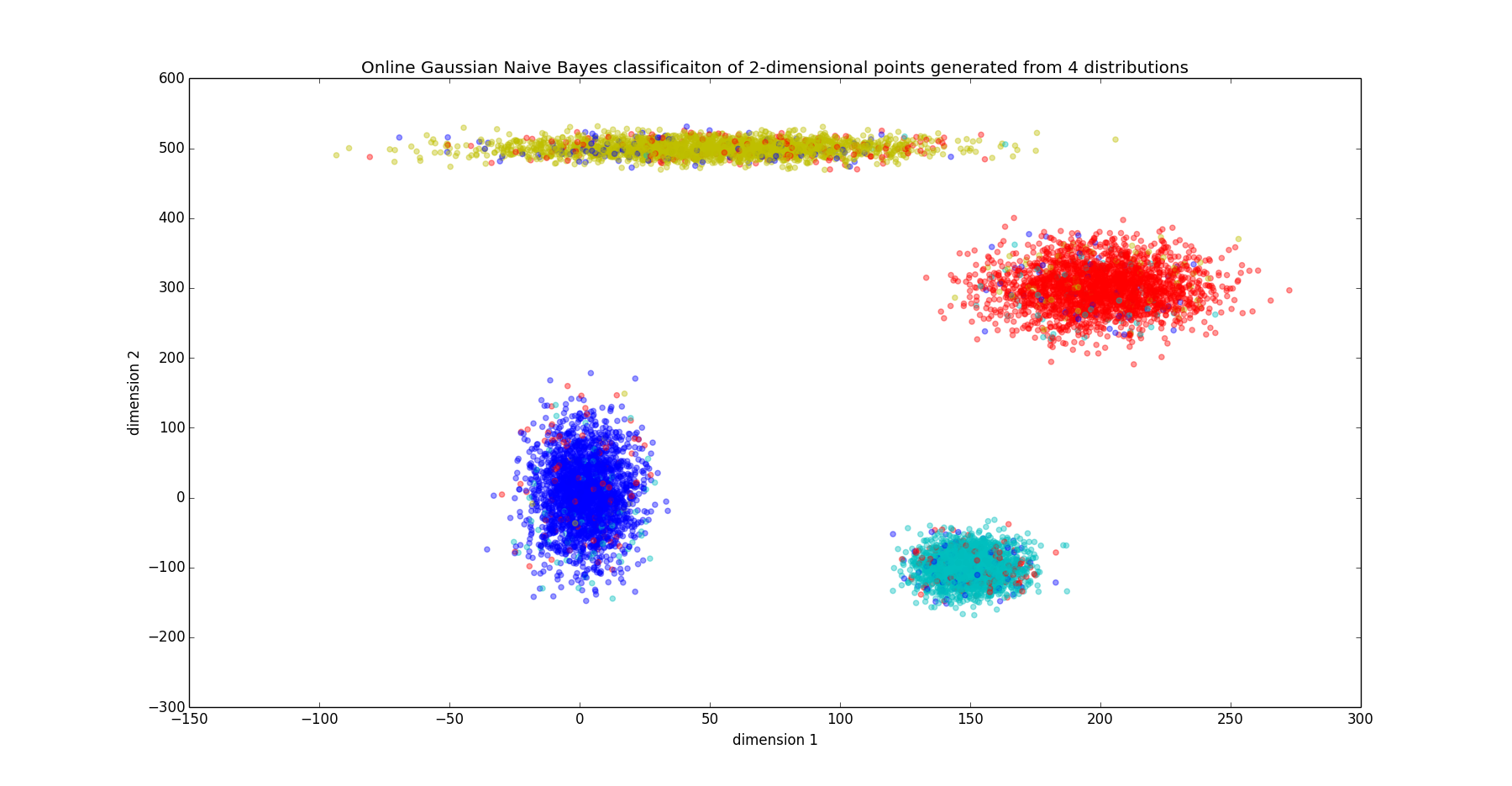
On a 2-dimensional 4 balanced class problem (2500 instances of each class) whose points are shown in the following plot, the classifier achieved an accuracy of about 91.36%. Note that these classifications were done online; the classifier was shown 4 instances before predictions began. After that, inference was performed on a new instance, then the classifier trained on the new point. The colors of the points indicate the classifier's guess. Note that colors are well clustered, which is due to the high accuracy.
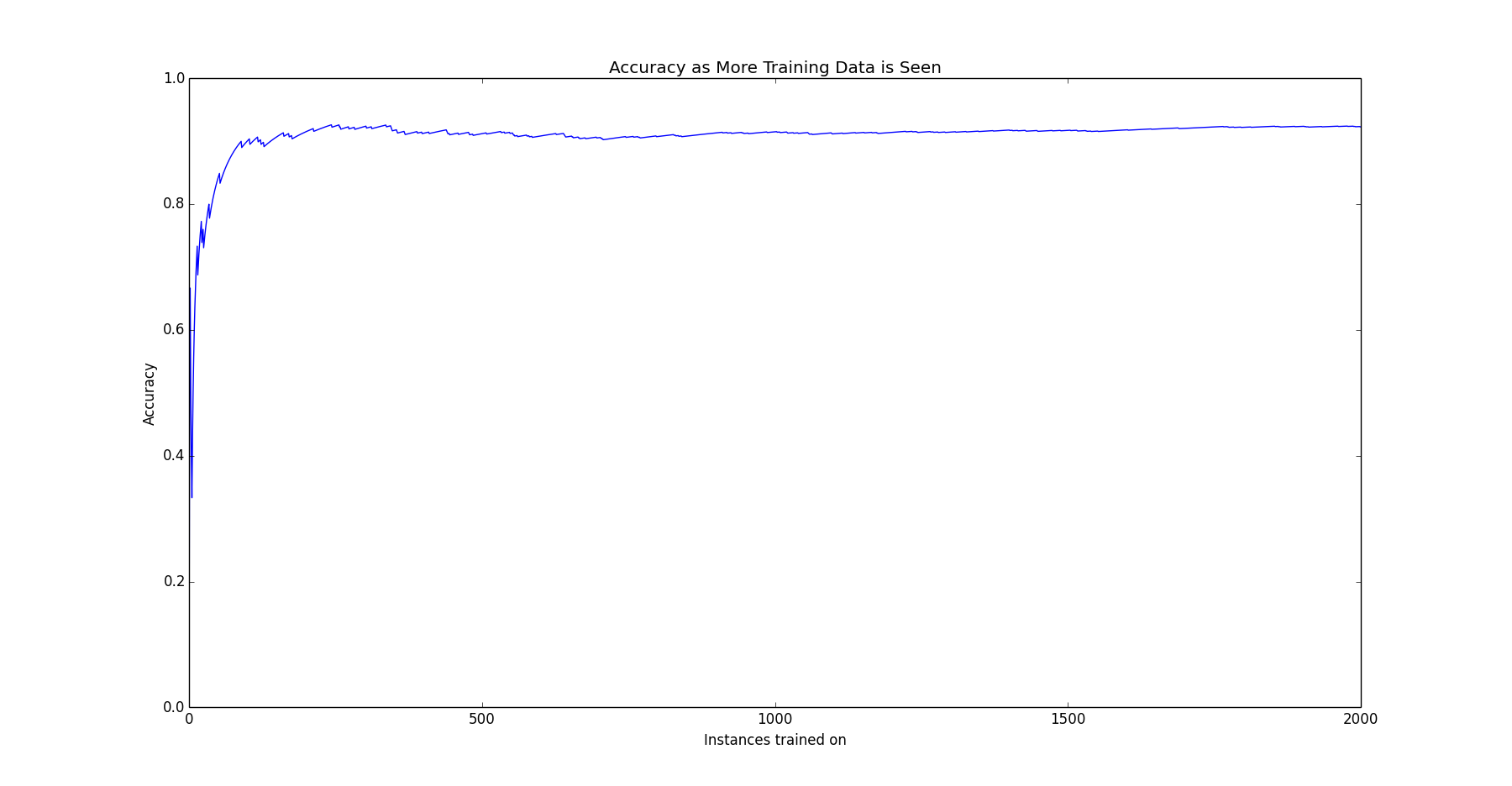
The following plot shows how quickly the classifier learns.
The final performance test is 10-fold cross valication on 100,000 points (4 balanced classes). The performances across folds are: 0.962, 0.957, 0.946, 0.941, 0.97, 0.952, 0.948, 0.958, 0.943, 0.911
Which yields a mean of 94.88% and a standard devation of 0.0152236657872.
##Example Usage
>>> import numpy as np
>>> from online_gaussian_naive_bayes import OnlineGaussianNaiveBayes
>>> X = np.array([[-1, -1], [-2, -1], [-3, -2], [1, 1], [2, 1], [3, 2]])
>>> Y = np.array([1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2])
>>> clf = OnlineGaussianNaiveBayes(2)
>>> for i in xrange(len(X)):
>>> clf.fit(X[i], Y[i])
>>> print(clf.predict([[-0.8, -1]]))
1
##Synthetic Data Generation
from random import normalvariate, shuffle
from numpy import array
mean_std_pairs_triples = [((2,5), (10, 50), 2500, 'a'),
((200, 300), (20, 30), 2500, 'b'),
((150, -100), (10, 20), 2500, 'c'),
((50, 500), (40, 10), 2500, 'd')]
points = []
classes = []
class_num = 0
for point_type in mean_std_pairs_triples:
(x_mean, y_mean), (x_std, y_std), num, c = point_type
for i in xrange(num):
classes.append(c)
x, y = normalvariate(x_mean, x_std), normalvariate(y_mean, y_std)
points.append((x, y))
points = array(points)
classes = array(classes)
inds = range(len(classes))
shuffle(inds)
points = points[inds]
classes = classes[inds]