Pinia: A Comprehensive Guide to Vue.js State Management
State management is a crucial aspect of front-end development, especially in complex applications where components need to share and synchronize data. Vue.js, one of the most popular JavaScript frameworks, offers various solutions for state management, and Pinia is one of them. In this article, we'll delve into Pinia, exploring its features, benefits, and how to use it effectively in Vue.js applications.
Pinia is a state management library specifically designed for Vue.js. It provides a simple and intuitive API for managing application state, offering reactive stores that can be easily accessed and modified from Vue components. Pinia is built on top of Vue 3's Composition API, taking advantage of its reactivity and composition features.
-
Reactive State: Pinia stores are reactive, meaning that changes to the state trigger re-renders in components that use that state. This reactive nature simplifies data synchronization and ensures that the UI stays up-to-date with the underlying data.
-
Single Source of Truth: Pinia promotes the concept of a single source of truth for application state. Instead of scattering state across multiple components, Pinia encourages centralizing state management in stores, making it easier to track and manage application data.
-
Module-based Architecture: Pinia organizes state into modules called stores, each responsible for managing a specific subset of application data. This modular architecture improves code organization and maintainability, allowing developers to easily reason about and scale their applications.
-
Type Safety: Pinia leverages TypeScript to provide type safety for application state. By defining types for store state and actions, developers can catch type-related errors at compile time, reducing the likelihood of runtime errors and improving code robustness.
-
Devtools Integration: Pinia integrates seamlessly with Vue Devtools, a browser extension that provides advanced debugging and inspection tools for Vue.js applications. With Devtools, developers can visualize and debug Pinia stores, making it easier to understand and troubleshoot application state.
-
Simplicity: Pinia's API is designed to be simple and intuitive, making it easy for developers to get started with state management in Vue.js applications. With its clear and concise syntax, developers can focus on building features rather than wrestling with complex state management logic.
-
Performance: Pinia's reactivity system is optimized for performance, ensuring that updates to the state are efficient and responsive. By leveraging Vue 3's reactivity features, Pinia minimizes unnecessary re-renders and delivers smooth user experiences even in large-scale applications.
-
Flexibility: Pinia offers flexibility in how developers structure and manage application state. Whether you're building a small prototype or a complex enterprise application, Pinia adapts to your needs, allowing you to customize stores and actions to fit your specific requirements.
-
Compatibility: Pinia is fully compatible with Vue 3 and the Composition API, ensuring seamless integration with modern Vue.js applications. Whether you're starting a new project or migrating an existing one to Vue 3, Pinia provides a reliable and future-proof solution for state management.
To get started with Pinia, you'll need to install it in your Vue.js project using npm or yarn:
npm install pinia
# or
yarn add piniaOnce installed, you can create Pinia stores using the defineStore function and access them in your components using the useStore hook. Here's a simple example of a Pinia store:
import { defineStore } from 'pinia';
export const useCounterStore = defineStore('counter', {
state: () => ({
count: 0,
}),
actions: {
increment() {
this.count++;
},
decrement() {
this.count--;
},
},
});In your Vue component, you can use the useStore hook to access the store and its state and actions:
<script setup>
import { useCounterStore } from './stores/counter';
const counterStore = useCounterStore();
</script>
<template>
<div>
<h1>Count: {{ counterStore.count }}</h1>
<button @click="counterStore.increment">Increment</button>
<button @click="counterStore.decrement">Decrement</button>
</div>
</template>Pinia is a powerful state management solution for Vue.js applications, offering simplicity, performance, and flexibility. By centralizing state management in reactive stores, Pinia enables developers to build scalable and maintainable applications with ease. Whether you're working on a small project or a large-scale application, Pinia provides the tools and features you need to manage application state effectively.
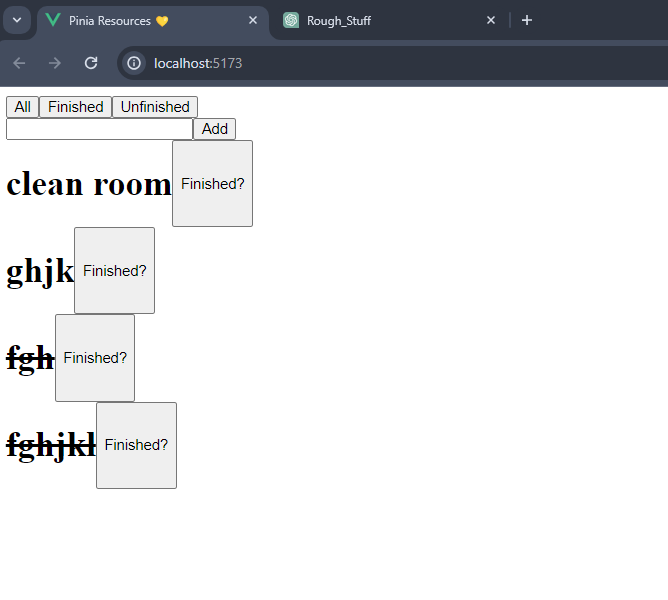
In your template, you are trying to use the todos array directly without accessing it from the storeToRefs result. Also, you need to use the addTodo function correctly by passing the newTodo value as an argument. Here's the corrected code:
<script setup>
import { useTodosStore } from './store/todos';
import { ref } from 'vue';
import { storeToRefs } from 'pinia';
const newTodo = ref('');
const todosStore = useTodosStore();
const { todos } = storeToRefs(todosStore);
const { addTodo } = todosStore;
</script>
<template>
<main>
<input v-model="newTodo" />
<button @click="() => addTodo(newTodo)">Add</button>
<div v-for="todo in todos.value" :key="todo.id" style="display: flex">
<h1>{{ todo.txt }}</h1>
<button>Finished?</button>
</div>
</main>
</template>In the template: