This repository contains the codes for the paper "MetaLR: Meta-tuning of Learning Rates for Transfer Learning in Medical Imaging" [PDF] early accepted at MICCAI 2023.
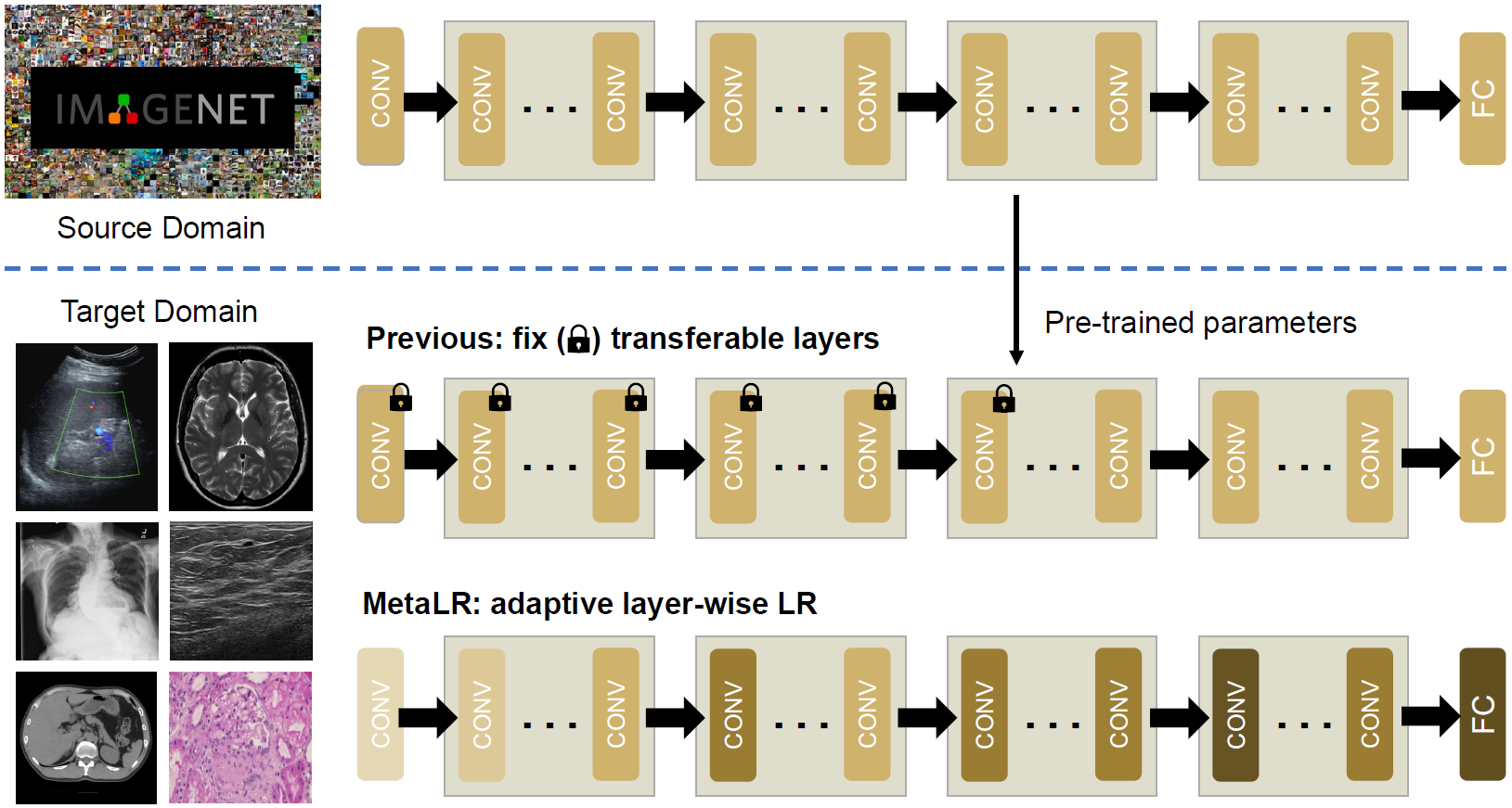
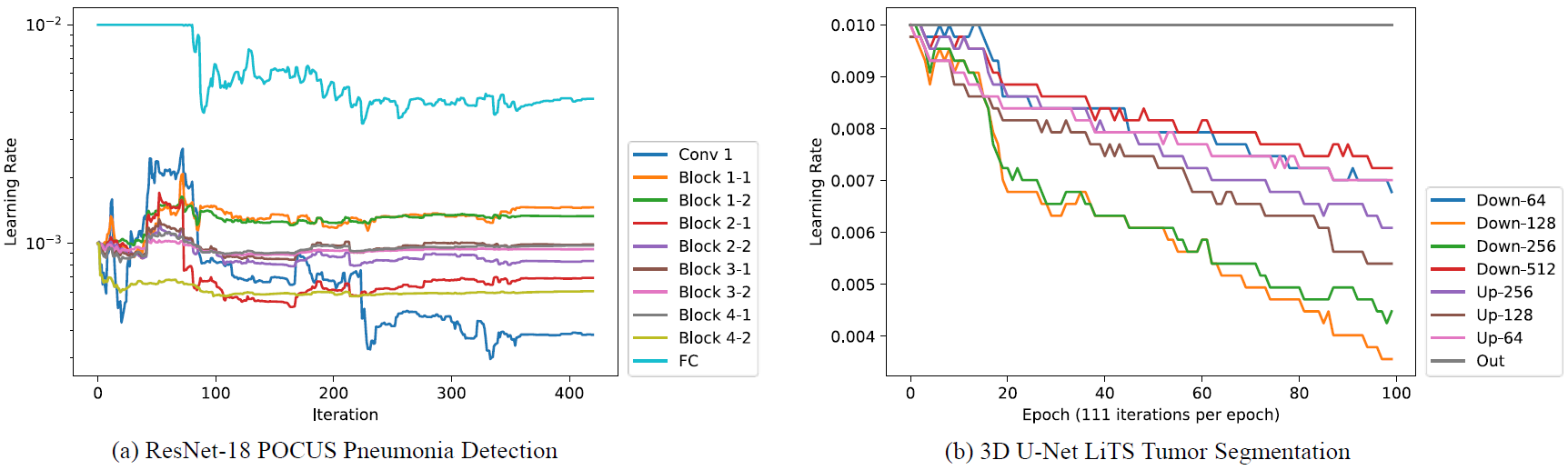
In medical image analysis, we find that model fine-tuning plays a crucial role in adapting medical knowledge to target tasks. We propose a meta-learning-based LR tuner, MetaLR, to make different layers efficiently co-adapt to downstream tasks according to their transferabilities across different domains.
Previous works fix transferable layers in pre-trained models to prevent them from catastrophic forgetting, which is inflexible and labor-expensive to find the optimal scheme. MetaLR learns appropriate LRs for different layers from feedback on model generalization, preventing highly transferable layers from forgetting their medical representation abilities and driving less transferable layers to adapt actively to new domains.
We use online meta-learning to tune layer-wise LRs. We denote the LR and model parameters for the layer
(1) At the iteration
(2) This step of updating aims to get feedback for LR of each layer. After taking derivative of the validation loss w.r.t.
where
(3) Finally, the updated LRs can be employed to optimize the model parameters through gradient descent truly.
To reproduce MetaLR, you need to
-
Unzip POCUS dataset in MetaLR_POCUS/data folder and unzip the USCL pre-trained model in MetaLR_POCUS/pretrained folder.
-
Run
cd MetaLR_POCUS
python -u train.py --seed 0 --workers 4\
--max-epoch 30 --batch-size 128\
--lr 0.01 --hyper-lr 0.1
The code is developed with an Intel(R) Xeon(R) W-2235 CPU @ 3.80GHz and a single NVIDIA RTX A6000 GPU.
The install script requirements.txt has been tested on an Ubuntu 20.04.4 LTS system.
☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️☁️
Licensed under an MIT license.