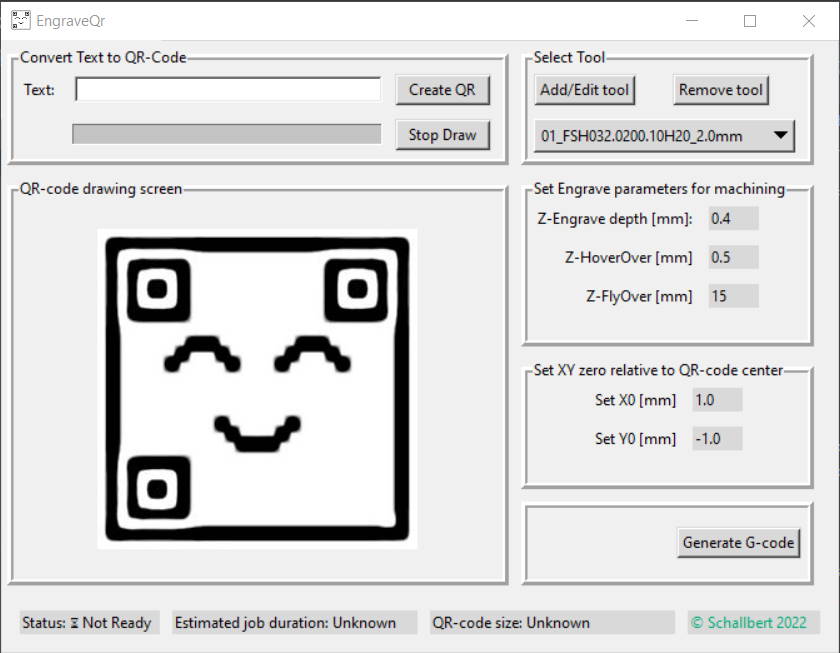
This is a small python application that takes a string, converts it into a QR-code (with help of @nayuki's excellent QR-code generator) and then allows to create CNC toolpaths that enables efficient and quick engraving.
The project is written in Python. The program is not very fast or creates super elegant tool paths, but special care has to be taken to get the machining time low while maintaining a high readability of the QR-code.
The full documentation is available on my website.
Releases of this software are provided to users as-is. Although I created this application with all due care, created unit tests, and tested its output code on my own machine, I cannot take any responsibility for how and for what this software is used.
WARNING
This application outputs G-code instructions for real machinery that does actually do things
in the physical world. There might be code errors or bugs that could potentially lead to machine crashes or even worse.
I do not take liability for work accidents, system failures, equipment breakdown, loss of production, flow disturbances,
or other negative effects that may be caused by the code this application generates.
NOTE
It is the machine operator's responsibility to carefully review the output G-code of this application,
and to make sure that it works as intended without causing any harm.
Download the latest release (button on the panel on the right). It provides a .zip file containing the application
and all related files. Start the application by double-clicking QR-codengrave.exe.
Alternatively, clone the repository and run from within your favourite python interpreter. Of course you're free to fork this repository and modify the code under your own responsibility.
Once running, just enter the text for the QR-code you want to have engraved. Press Create Qr. For drawing I used the (slow)
turtle provided with tkinter, so you can optionally skip this by pressing Stop Draw.
Then add or select the tool you want to use for engraving. The QR-code's workpiece size directly depends on tool tip diameter. The tool list is persisted so no data is lost on application restart.
Click the parameter values to change. You can adjust
- flyover height (moving to workpiece XY-0)
- hover height (in-job moves between bit pixels)
- engrave depth which will be reflected in the G-code.
Click the parameter values to change. You can select between an edge/center of the QR-code as XY-0 or enter a custom value, e.g. relevant if the qr-code is to be placed somewhere on a larger workpiece
This will run a StringIO generator that creates a file object containing the instructions for a milling machine
to engrave your QR-code. Currently, it is optimized for my machine type and uses no postprocessor (I'm not familiar
with other machines and their control software, so you might have to adjust the generator for your machine.)
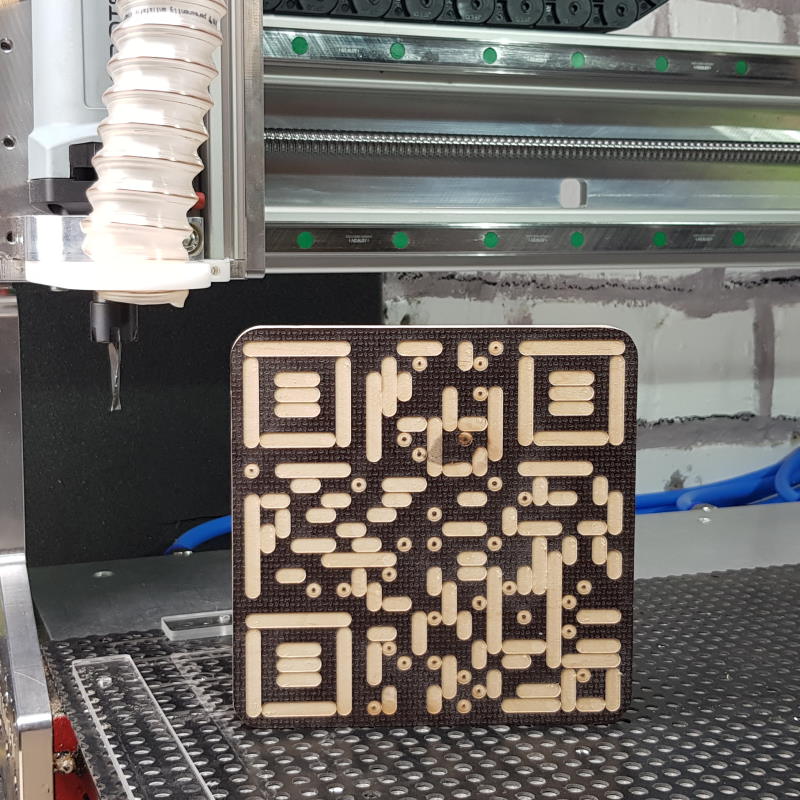
For testing purposes I created a QR-code to my website schallbert.de and had it engraved to
a piece of coated pylwood. I used an 6mm endmill which resulted in a qr-code size of 144x144 mm.

- 1.0 Initial release. Basic inward-pointing spiral as path algorithm.
- 1.1 Algo upgrade release. Uses a faster, single-pixel avoiding algo. Includes several minor bugfixes.
- 1.2 Implement tapered tool angle and engrave depth to QR-code size calculation. Major bugfix (missing tool change macro call)
- Navigate into
src/assetsof your QR-codengrave folder. - copy
Persistence.datto a temporary folder or e.g. your Desktop. - Remove the current installation.
- Download the latest release, move it where your previous release was deployed.
- Move the
Persistence.datintosrc/assetsof your new installation and start the application.
All tools you entered in your old version, your engrave settings, and zero offsets should be available to you.
The application consists of three modules:
- vectorize_qr
- gui
- cam
Contains all classes and helper functions to create a QR-code and convert it into vectors of "black" and "white" fields. It also defines the machining strategy by selecting the toolpath. Current implementation only supports inwards-spiral paths.
The interface of the application to the user. Offers fields to enter the string to convert to QR-code, manages tools for the CAM module, and displays toolpaths and QR parameters (size, dimensions, etc). Also enables the user to select engrave depth parameters and to set the workpiece's XY zero offset.
Class that is able to generate G-code instructions for a Computerized Numerical Control milling machine from QR-code bitfield vectors
from line_path with help of parameters entered through the gui module.
The application features unit tests for the developed algorithms. It spares out the gui though which has been tested
manually only.
- to my wife who always has my back.
- @likosdev who gifted the lovely QRUWU logo.