Master - Production code. Jenkins jobs will point to this branch
Develop - this branch contains pre-production code. When the features are finished then they are merged into develop
Feature - this branches are used to develop new features for the upcoming releases. Branch off from develop and must merge into develop
After code has been merge from feature to develop, pull requst for code review will be done from develop to master
- In Pipeline configuration, from Definition field, choose the Pipeline script from SCM option
- From the CSM field, choose Bitbucket as the source control system
- Complete the fields specific to your repository’s source control system
- In the Script Path field, specify the location (and name) of your Jenkinsfile. This location is the one that Jenkins checks out/clones the repository containing your Jenkinsfile, which should match that of the repository’s file structure. The default value of this field assumes that your Jenkinsfile is named "Jenkinsfile" and is located at the root of the repository.
Allocates an executor on a node (typically a build agent) and runs further code in the context of a workspace on that Agent
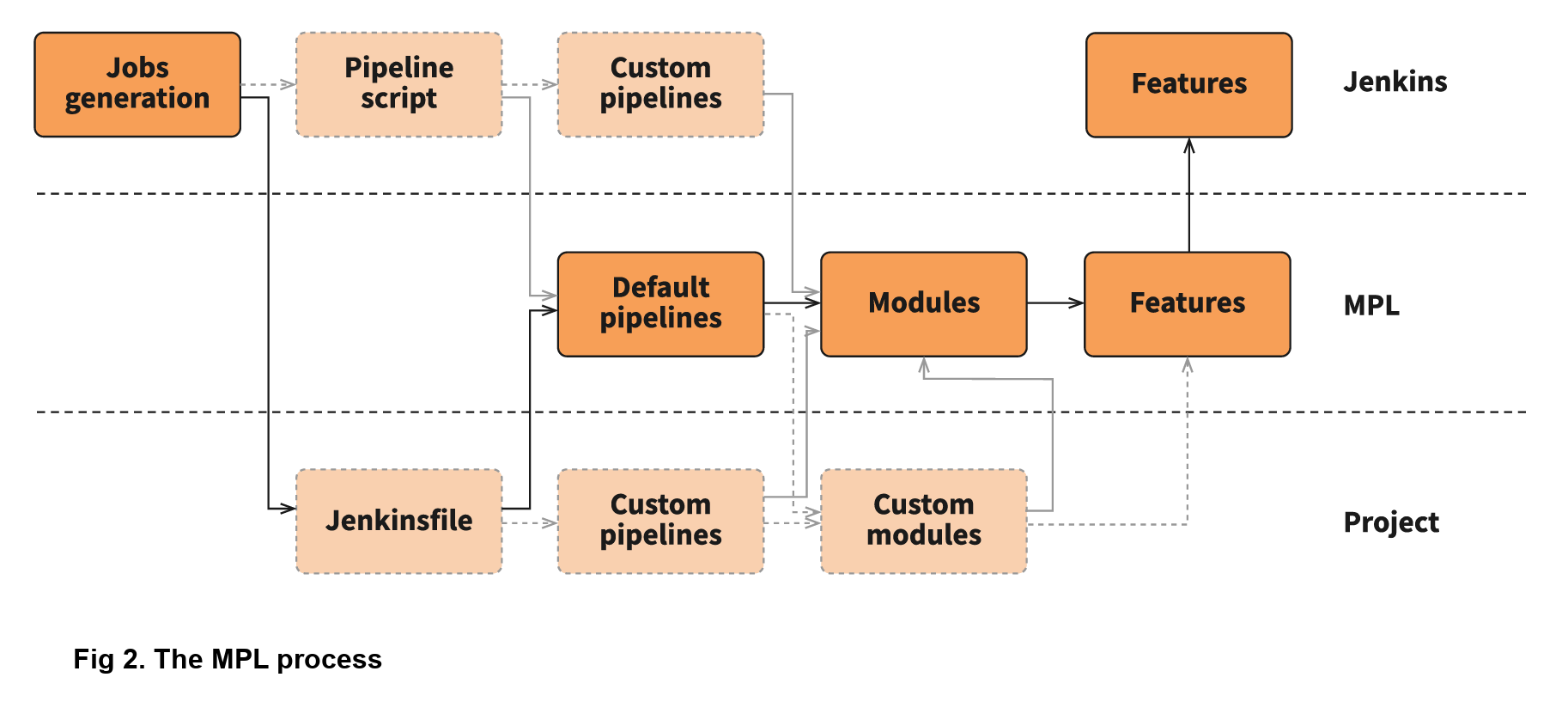
Provides an extensible set of tools for modeling simple-to-complex delivery pipelines "as code". The definition of a Jenkins Pipeline is typically written into a text file called Jenkinsfile which can be checked into a project's source control repository. Contains the entire Jenkins Pipeline definition
Jenkins build pipeline plugin ensures the same feature present in the pipeline that are created in the Declarative method. Normally, the agent will be declared at the top-level as a global agent declaration. Defines the agent used for the entire Pipeline or a stage.
- any – This means pipeline will run in any available node. (agent any)
- none – Ideally None mean, the pipeline will run in not run in any agent at top-level, but each stage should be defined with its own agent ( agent none ).
- label – This means the pipeline will be mentioned as label name and pipeline will look for the available node with the label name mentioned ( agent {label ‘my label name for node’} )
- node – mentioning node in the agent is same as mentioning label but this will give us more option like custom Workspace ( agent {node{label ‘my label name’}}).
- docker – By mentioning docker, the pipeline will run in a docker environment. ( agent{ docker {image ‘ruby3:develop’ label ‘my label name’ arg ‘—port 3000:80’} } ) )
The “tools” directive can be added either at a pipeline level or at the stage one. It allows you to specify which maven, jdk or gradle version to use on your script. Any of these tools, the three supported at the time of writing, must be configured on the “Global tool configuration” Jenkins menu.
Triggers allows Jenkins to automatically trigger pipelines by using any of the available ones:
- cron: By using cron syntax, it allows to define when the pipeline will be re-triggered.
- pollSCM: By using cron syntax, it allows you to define when Jenkins will check for new source repository updates. The Pipeline will be re-triggered if changes are detected. (Available starting with Jenkins 2.22).
- upstream: Takes as input a list of Jenkins jobs and a threshold. The pipeline will be triggered when any of the jobs on the list finish with the threshold condition.
The environment is the directive that contains the Key-value pairs of the environment variable that should be available for the steps that are going to be executed in the stages.
Ideally, Environment directive supports a special helper method called credentials type which is very helpful for dynamically passing the credentials into the steps. So, Following are the types of credentials that can be passed into the environments
Can be defined at stage or pipeline level
Shared Libraries marked Load implicitly allows Pipelines to immediately use classes or global. variables defined by any such libraries. To access other shared libraries, the Jenkinsfile needs to use the @Library annotation, specifying the library’s name.
Options derivatives will provide options for configuring the pipeline with in the pipeline. So, Let us discuss the options one by one.
Can be defined at stage or pipeline level
- buildDiscarder
- Persist artifacts and console output for the specific number of recent Pipeline runs.
Options
- daysToKeepStr: history is only kept up to this days.
- numToKeepStr: only this number of build logs are kept.
- artifactDaysToKeepStr: artifacts are only kept up to this days.
- artifactNumToKeepStr: only this number of builds have their artifacts kept.
- Persist artifacts and console output for the specific number of recent Pipeline runs.
Options
- checkoutToSubdirectory('foldername')
- Perform the automatic source control checkout in a subdirectory of the workspace.
- disableConcurrentBuilds
- Disallow concurrent executions of the Pipeline. Can be useful for preventing simultaneous accesses to shared resources, etc.
- disabledResume
- Do not allow the piplien to resume if teh controller restarts
- overrideIndexTriggers
- Allows overriding default treatment of branch indexing triggers. If branch indexing triggers are disabled at the multibranch or organization label
- parallelsAwaysFailFast
- Set failfast true for all subsequent parallel stages in the pipeline.
- preserveStashes
- Preserve stashes from completed builds, for use with stage restarting.
- quietPeriod Set the quiet period, in seconds, for the Pipeline, overrideing the global default
- retry
- On failure, retry the entire Pipeline the specified number of times.
- skipDefaultCheckout
- Skip checking out code from source control by default in the agent directive.
- skipStagesAfterUnstable
- Skip stages once the build status has gone to UNSTABLE.
- checkoutToSubdirectory
- Allows you to override the location that the automatic SCM checkout will use. Using
- newContainerPerStage
- This is used in top-level agent declaration and this will allow the process to run in the different Container each time.
- timeout
- Set a timeout period for the Pipeline run, after which Jenkins should abort the Pipeline
- timestamps
- Prepend all console output generated by the Pipeline run with the time at which the line was emitted.
This directive allows you to define a list of parameters to be used in the script. Parameters should be provided once the pipeline is triggered. It should be defined at a “pipeline” level and only one directive is allowed for the whole pipeline.
The triggers directive defines the automated ways in which the Pipeline should be re-triggered
Defining tools to auto-install and put on the PATH. This is ignored if agent none is specified.
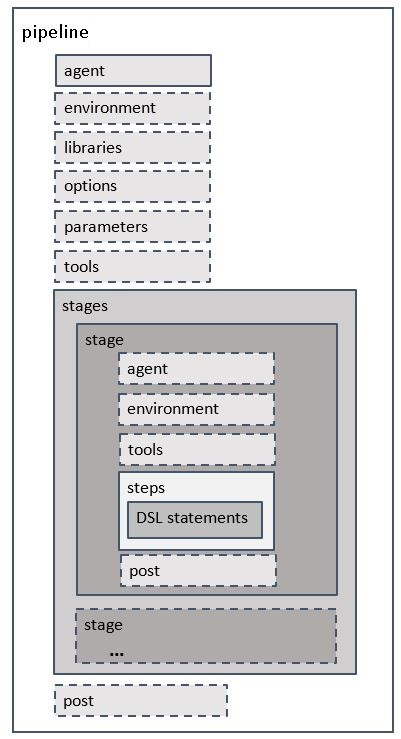
Stages is the section which contain one or more stage tag. So, In this section we can write the part of continuous delivery process. Contains Pipeline stages and steps
This is the section that contains steps section or agent section which is isolated for the particular stage and other directives. So, A Stage section will have a command that runs processes like Build, Deploy, Test, or any other Continuous Delivery process.
Defined at stage
A stage can have multiple commands to run for completing the continuous delivery process. basically, Step is the set of commands that performs an action and It will be executed one by one.. The last required section is “steps”, which is defined into a “stage”. At least one step must be defined in the “steps” section.
Jenkins pipeline Stages can have other stages nested inside that will be executed in parallel. This is done by adding the “parallel” directive to your script.
Pipeline steps could be executed depending on the conditions defined in a “when” directive. If conditions match, the steps defined in the corresponding stage will be run. It should be defined at a stage level.
- Branch – This will execute the stage only when the branch in SCM is matching. (when { branch 'master' })
- buildingTag – This executes only when the Build is building the tag (when { buildingTag() })
- changelog – Stage will run only when the changelog is having a specified pattern in it. (when { changelog '.*^\[SERVICE2\] .+$' })
- changeset – This will run only when the SCM changeset is having the specified pattern in file (when { changeset "**/*.js" })
- changeRequest – ChangeRequest is like the pull request in GitHub and the stage will run only after the change request is raised (when { changeRequest target: 'master' })
- environment – Stage will execute only when the specified environment variable is matching (when { environment name: 'DEPLOY_TO', value: 'production' })
- equals – Executes only when the expected value and the actual value is matching in the condition (when { equals expected: 2, actual: currentBuild.number })
- expression – Condition is created with groovy expression and expects the Boolean true to pass. (when { expression { return params.DEBUG_BUILD } })
- tag – Stage will be executed only after the specified tag name pattern matches the stage tag (when { tag "release-*" })
- not – This is like “NOT” in the “IF” condition. (when { not { branch 'master' } })
- allOf – This is for nested condition and this will expect all should be true. This is like “AND” in “IF” Condition (when { allOf { branch 'master'; environment name: 'DEPLOY_TO', value: 'production' } })
- anyOf – anyOf is like “OR” in the “IF” condition. (when { anyOf { branch 'master'; branch 'staging' } })
- triggeredBy – the stage will execute only when it is triggered by the specified build. (when { triggeredBy 'SCMTrigger' })
This step is used to add Scripted Pipeline sentences into a Declarative one, thus providing even more functionality. This step must be included at "stage" level.
Script Security - https://plugins.jenkins.io/script-security/
Some of your scripts may require Script Approval. Scripts should Use Groovy Sandbox .
approve the scripts. In-process Script Approval - https://www.jenkins.io/doc/book/managing/script-approval/
Input Directive is declared inside stage and it will help us getting input by prompting users. Basically, The stage section will wait until any Input is submitted. So, the following are the configuration options.
- message
- This is a required option where the message to be displayed to the user is specified.
- id
- Optional identifier for the input. By default the "stage" name is used.
- ok
- Optional text for the Ok button.
- submitter
- Optional list of users or external group names who are allowed to submit the input. By default any user is allowed.
- submitterParameter
- Optional name of an environment variable to set with the submitter name, if present.
- parameters
- Optional list of parameters to be provided by the submitter.
Post sections can be added at a pipeline level or on each stage block and sentences included in it are executed once the stage or pipeline completes. Several post-conditions can be used to control whether the post executes or not:
- always
- Run the steps in the post section regardless of the completion status of the Pipeline’s or stage’s run.
- changed
- Only run the steps in post if the current Pipeline’s or stage’s run has a different completion status from its previous run.
- fixed
- Only run the steps in post if the current Pipeline’s or stage’s run is successful and the previous run failed or was unstable.
- regression
- Only run the steps in post if the current Pipeline’s or stage’s run’s status is failure, unstable, or aborted and the previous run was successful.
- aborted
- Only run the steps in post if the current Pipeline’s or stage’s run has an "aborted" status, usually due to the Pipeline being manually aborted. This is typically denoted by gray in the web UI.
- failure
- Only run the steps in post if the current Pipeline’s or stage’s run has a "failed" status, typically denoted by red in the web UI.
- success
- Only run the steps in post if the current Pipeline’s or stage’s run has a "success" status, typically denoted by blue or green in the web UI
- unstable
- Only run the steps in post if the current Pipeline’s or stage’s run has an "unstable" status, usually caused by test failures, code violations, etc. This is typically denoted by yellow in the web UI.
- unsuccessful
- Only run the steps in post if the current Pipeline’s or stage’s run has not a "success" status. This is typically denoted in the web UI depending on the status
- cleanup
- Run the steps in this post condition after every other post condition has been evaluated, regardless of the Pipeline or stage’s status
Repo configuration
<repo root>
/resources
/scr
/vars
-
resources
- Any supporting resources for your library will go here. As an example, we build documentation for all of our shared libraries. This documentation is then uploaded to S3.
-
scr
- This is a regular Java-style source code directory. All source code and classes in here can be imported into your pipeline using an import statement.
-
vars
- this is where you put all of your global functions, the ones you will call from your project’s Jenkinsfile. For us, this is where the vast majority of our code lives
@Library('CommonService@') _
or
@Library('CommonService@master') _
@Library('CommonService@main') _
or branch
@Library('CommonService@feature/...') _ import org.*;
// Class Reference
def commonLibrary = library 'CommonService'
def console = commonLibrary.org.ConsoleLog.new();
println console.Info("Processing CSM");
println console.Error(" ${e.toString()} ");
println console.Warning("Agent is currently in uses ");import org.*;
def constant = commonLibrary.org.Constants.new();
userRemoteConfigs: [[
...
url: constant.GIT_REPO_URL
...
]]
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
abortPreviousBuilds |
function | Stops previous Jobs |
identifyOSPlatform |
function | Returns string on what OS Jenkins is running off |
publishCucumberReports |
variable | Wrapper to execute Cucumber Reports. Required plugin - https://github.com/jenkinsci/cucumber-reports-plugin |
publishHTMLReports |
function | Wrapper to publish HTML Reports. Required plugin https://github.com/jenkinsci/htmlpublisher-plugin |
sendEmails |
function | Send Email, optional attachment |
Pipeline - stageCSM |
Pipeline | Source control configuration stage |
timestamp |
function | Convert Console Output time to local time |
validatingParameter |
function | Iterate parameters to validate inforamtion was provided |
zip |
function | Zip file using PowerShell command |