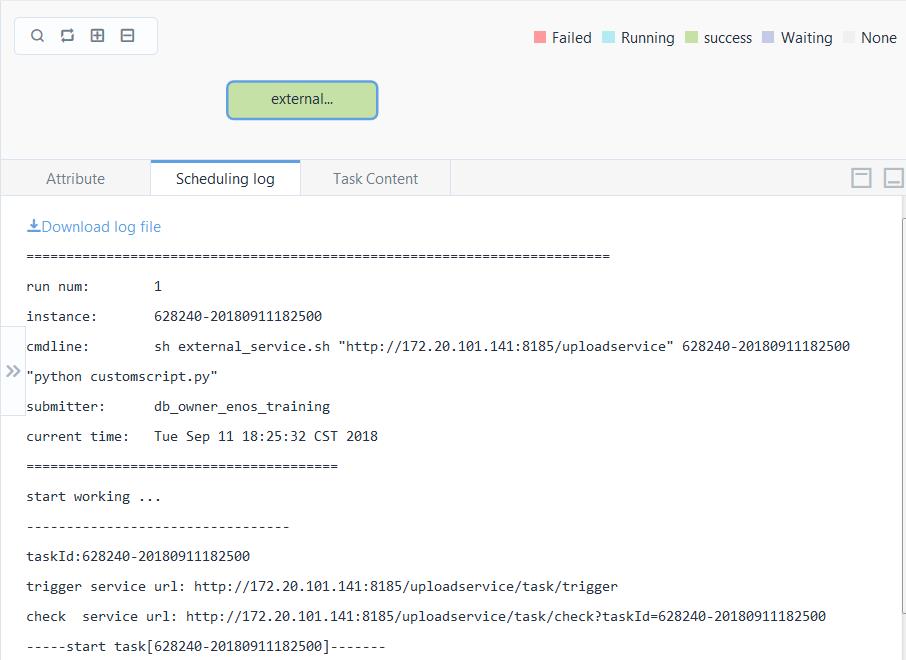
Use the external_service.sh script with EnOS Data IDE to run your owner Python script.
In this example, the external_service.sh script runs the customscript.py python script. You can replace the customscript.py with your own python script.
Step 1. Fork this repo to your local file system.
Step 2. From your file system, open the directory that you forked in Step 1 and replace the customscript.py file with your own Python script.
Step 3. Compress all files in the directory into a .zip file, for example, external_service.zip.
Step 4. Upload the .zip file as a resource of EnOS in the following procedure:
-
In the EnOS Console, click Data IDE > Resource Management from the left navigation panel and click Create Resource.
-
In the Create Resource window, provide the basic settings about the resource.
- Name: Enter the name of resource.
- Description: Provide a descriptive information about the resource.
- Select Directory: Select the directy to save the resource. Click OK.
-
Click New version and upload the
external_service.zipfile with settings as shown in the following figure: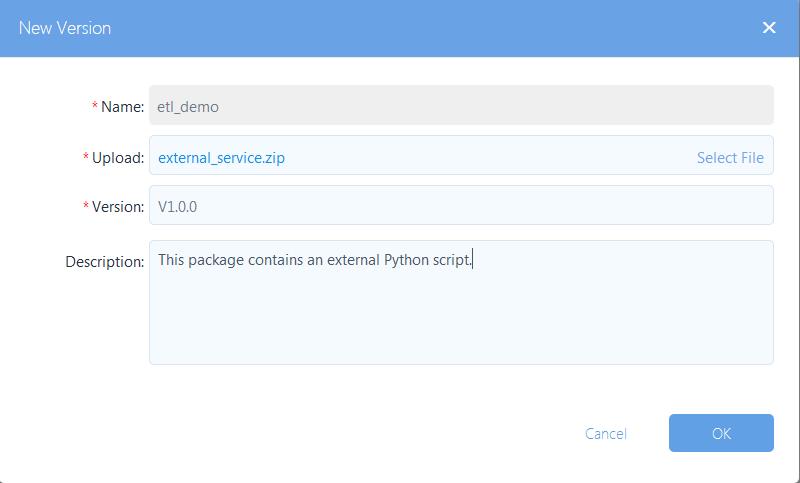
Step 5. Create a workflow with a task that references the resource.
-
In the EnOS Console, click Data IDE > Task Designer from the left navigation panel and click New Workflow.
-
In the New Workflow window, provide the following settings about the workflow:
- Mode: Create.
- Name: external_script_1
- Type: Manual Scheduling
- Select Dir: the directory where you want to store the workflow. Click OK.
-
From the Component panel, drag the SHELL type of task node into the workflow panel.
-
In the New Task Node window, provide name and description of the task. Click Create.
-
Double click the task node that you just created and provide the following settings about the task:
- Command: enter the following command:
sh external_service.sh ${service_url} ${instance_id} ${command}where, - service_url and command are parameters that you'll define in the Parameter Config tab. - instance_id is a system variable that indicates the identifier of the workflow instance.
- Select the resource and resource version that you uploaded in Step 4.
-
Click the Parameter Config tab from the right edge of the task configuration panel and provide the following settings:
service_url="http://172.20.101.141:8185/uploadservice" command="python customscript.py"
Note: If your Python script uses a different file name, you'll need to edit the value of command with the name of your script file.
The following figure shows the task configuration in this example.

- Click Save. Click Back to workflow panel and click Release to publish the workflow.
Step 6. Click Pre-run to run the workflow.
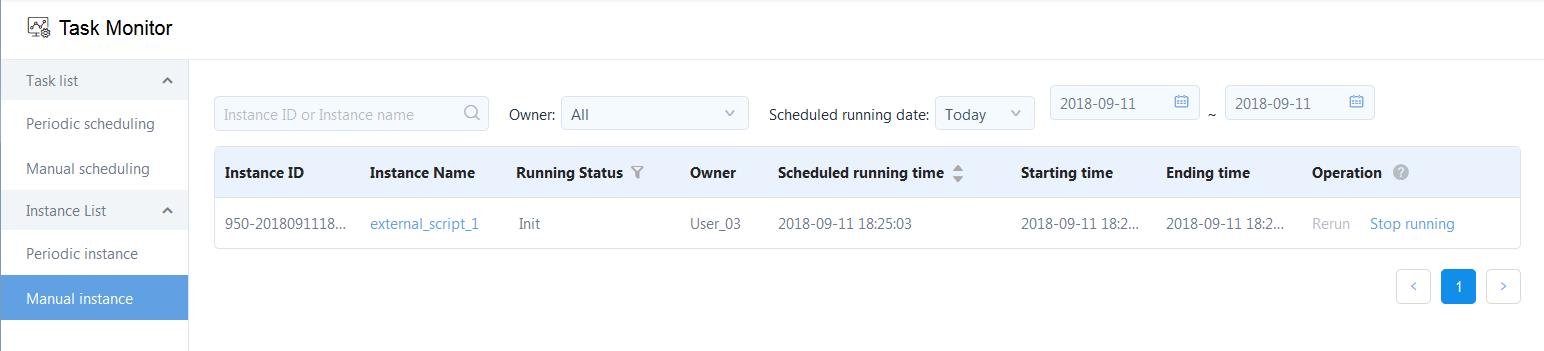
After you pre-run the workflow, a workflow instance is generated. You can then trace the details about the instance through the task monitor:
- In the EnOS Console, click Task Monitor from the left navigation panel.
- Click Manual instance and locate the instance through the name of the workflow. The workflow instance is shown as in the following figure:
- Click the name of instance from the table and double-click the task from the panel. You can then view the log by clicking the Scheduling Log tab.