Notes on deploying a single site WordPress FPM Edition instance as a docker deployment orchestrated by Docker Compose.
- Use the FPM version of WordPress (6.3.1-fpm)
- Use MySQL as the database (v8)
- Use Nginx as the web server (v1.25)
- Use Adminer as the database management tool (v4)
- Include self-signed SSL certificate (Let's Encrypt localhost format)
DISCLAIMER: The code herein may not be up to date nor compliant with the most recent package and/or security notices. The frequency at which this code is reviewed and updated is based solely on the project lifecycle for which it was written to support, and is not actively maintained outside of that scope. You can use it at your own risk.
WordPress is a free and open-source blogging tool and a content management system (CMS) based on PHP and MySQL, which runs on a web hosting service. Features include a plugin architecture and a template system.
This variant contains PHP-FPM, which is a FastCGI implementation for PHP.
- See the PHP-FPM website for more information about PHP-FPM.
- In order to use this image variant, some kind of reverse proxy (such as NGINX, Apache, or other tools that speak the FastCGI protocol) will be required.
A Docker Desktop is required on the host to run this code
- Install Docker Desktop: https://www.docker.com/products/docker-desktop/
Copy the env.template file as .env and populate it according to your environment
# docker-compose environment file
#
# When you set the same environment variable in multiple files,
# here’s the priority used by Compose to choose which value to use:
#
# 1. Compose file
# 2. Shell environment variables
# 3. Environment file
# 4. Dockerfile
# 5. The variable is not defined
# Wordpress Settings
export WORDPRESS_LOCAL_HOME=./wordpress
export WORDPRESS_UPLOADS_CONFIG=./config/uploads.ini
export WORDPRESS_DB_HOST=database:3306
export WORDPRESS_DB_NAME=wordpress
export WORDPRESS_DB_USER=wordpress
export WORDPRESS_DB_PASSWORD=password123!
export WORDPRESS_HOST=wpdocker.local # put this entry in your host file as 127.0.0.1 wpdocker.local
export WP_HOME=${WORDPRESS_HOST}
export WP_SITEURL=${WORDPRESS_HOST}
export WORDPRESS_DEBUG=true
# MySQL Settings
export MYSQL_LOCAL_HOME=./dbdata
export MYSQL_DATABASE_DUMP=./dbdump
export MYSQL_DATABASE=${WORDPRESS_DB_NAME}
export MYSQL_USER=${WORDPRESS_DB_USER}
export MYSQL_PASSWORD=${WORDPRESS_DB_PASSWORD}
export MYSQL_ROOT_USER=root
export MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=rootpassword123!
# Nginx Settings
export NGINX_TEMPLATE=./templates
export NGINX_SSL_CERTS=./ssl
export NGINX_LOGS=./logs/nginx
# Docker settings
# export DOCKER_DEFAULT_PLATFORM=linux/arm64/v8
# User Settings
# TBDDon't modify templates/default.conf.template for hostname change instead, just set NGINX_HOST in the docker-compose.yml file
# default.conf
# redirect to HTTPS
server {
listen 80;
listen [::]:80;
server_name ${NGINX_HOST};
location / {
# update port as needed for host mapped https
rewrite ^ https://${NGINX_HOST}$request_uri? permanent;
}
}
server {
listen 443 ssl http2;
listen [::]:443 ssl http2;
server_name ${NGINX_HOST};
index index.php index.html index.htm;
root /var/www/html;
server_tokens off;
client_max_body_size 75M;
# update ssl files as required by your deployment
ssl_certificate /etc/ssl/fullchain.pem;
ssl_certificate_key /etc/ssl/privkey.pem;
# logging
access_log /var/log/nginx/wordpress.access.log;
error_log /var/log/nginx/wordpress.error.log;
# some security headers ( optional )
add_header X-Frame-Options "SAMEORIGIN" always;
add_header X-XSS-Protection "1; mode=block" always;
add_header X-Content-Type-Options "nosniff" always;
add_header Referrer-Policy "no-referrer-when-downgrade" always;
add_header Content-Security-Policy "default-src * data: 'unsafe-eval' 'unsafe-inline'" always;
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.php$is_args$args;
}
location ~ \.php$ {
try_files $uri = 404;
fastcgi_split_path_info ^(.+\.php)(/.+)$;
fastcgi_pass wordpress:9000;
fastcgi_index index.php;
include fastcgi_params;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
fastcgi_param PATH_INFO $fastcgi_path_info;
}
location ~ /\.ht {
deny all;
}
location = /favicon.ico {
log_not_found off; access_log off;
}
location = /favicon.svg {
log_not_found off; access_log off;
}
location = /robots.txt {
log_not_found off; access_log off; allow all;
}
location ~* \.(css|gif|ico|jpeg|jpg|js|png)$ {
expires max;
log_not_found off;
}
}
Modify the config/uploads.ini file if the preset values are not to your liking (defaults shown below)
file_uploads = On
memory_limit = 256M
upload_max_filesize = 75M
post_max_size = 75M
max_execution_time = 600Included uploads.ini file allows for Maximum upload file size: 75 MB
Once configured the containers can be brought up using Docker Compose, more-info
docker compose up -d
The WordPress application can be reached at the designated host and port (e.g. https://wpdocker.local/).
- NOTE: you will likely have to acknowledge the security risk if using the included self-signed certificate.
Complete the initial WordPress installation process, and when completed you should see something similar to this as per the WP version.
docker compose downAn Adminer configuration has been included in the docker-compose.yml definition file but commented out. Since it bypasses Nginx it is recommended to only use Adminer as needed and not let it run continuously.
Expose Adminer by uncommenting the adminer section of the docker-compose.yml file
...
# adminer - bring up only as needed - bypasses nginx
adminer:
# default port 8080
image: adminer:4
container_name: wp-adminer
restart: unless-stopped
networks:
- wordpress
depends_on:
- database
ports:
- "9000:8080"
...Pull down all the docker containers and run them again to get the adminer container up and running
docker compose down
docker compose up -dSince Adminer is bypassing our Nginx configuration it will be running over HTTP in plain text on port 9000 (e.g. http://wpdocker.local:9000/), and yes adminer will be accessed only on http protocol and not https
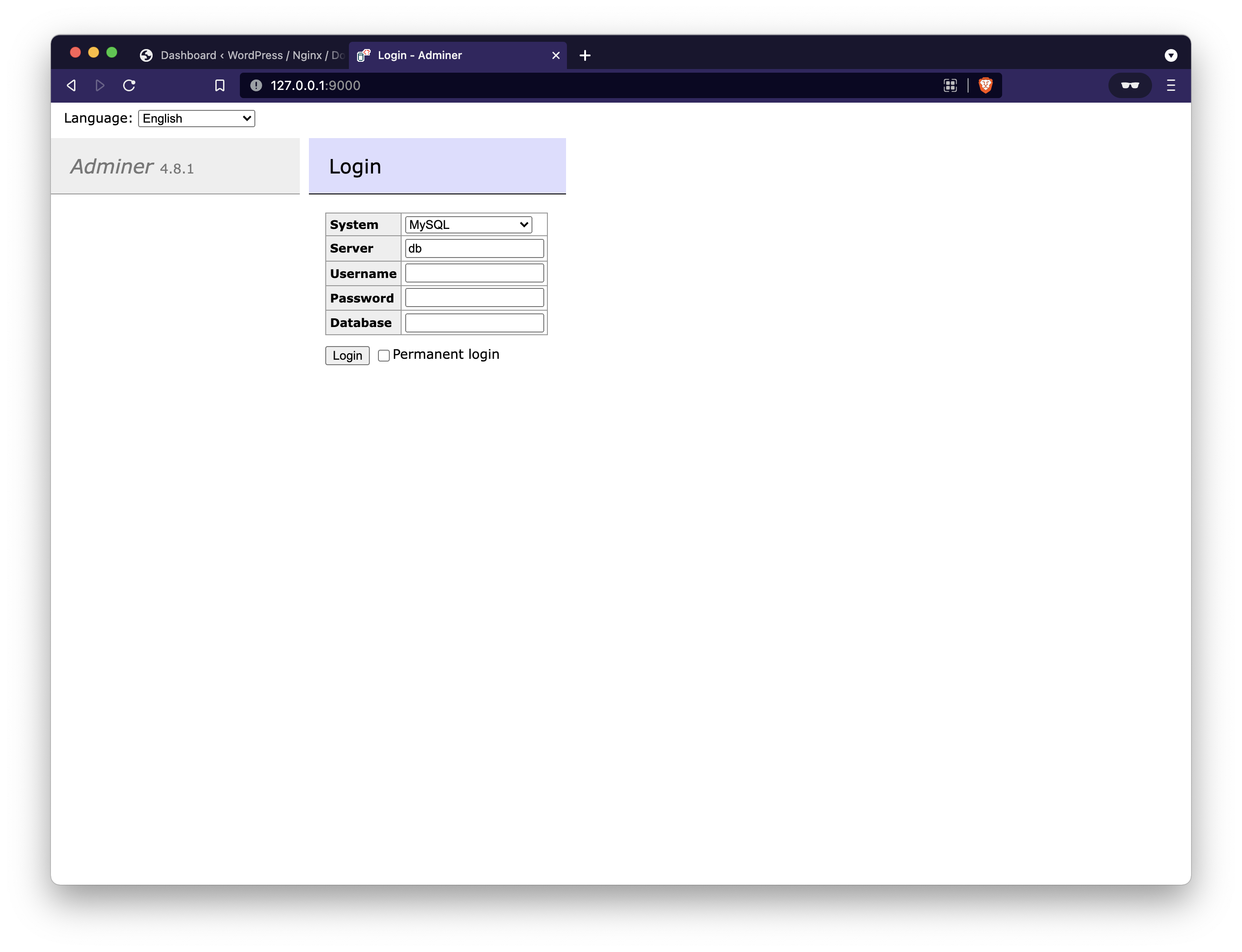
Enter the connection information for your Database and you should see something similar to the image below.
Example connection information:
-
System: MySQL
-
Server: database
-
Username: wordpress
-
Password: password123!
-
Database: wordpress
NOTE: Since
admineris defined in the same docker-compose file as the MySQL Database it will "understand" the Server reference as database, otherwise this would need to be a formal URL reference
When finished, stop and remove the adminer container.
$ docker-compose stop adminer
[+] Running 1/1
⠿ Container wp-adminer Stopped 0.1s
$ docker-compose rm -fv adminer
Going to remove wp-adminer
[+] Running 1/0
⠿ Container wp-adminer Removed 0.0sFor a complete teardown all containers must be stopped and removed along with the volumes and network that were created for the application containers
Commands
docker-compose stop
docker-compose rm -fv
docker-network rm wp-wordpress
# removal calls may require sudo rights depending on file permissions
rm -rf ./wordpress
rm -rf ./dbdata
rm -rf ./logsExpected output
$ docker-compose stop
[+] Running 3/3
⠿ Container wp-nginx Stopped 0.3s
⠿ Container wp-wordpress Stopped 0.2s
⠿ Container wp-database Stopped 0.8s
$ docker-compose rm -fv
Going to remove wp-nginx, wp-wordpress, wp-database
[+] Running 3/0
⠿ Container wp-nginx Removed 0.0s
⠿ Container wp-database Removed 0.0s
⠿ Container wp-wordpress Removed 0.0s
$ docker network rm wp-wordpress
wp-wordpress
$ rm -rf ./wordpress
$ rm -rf ./dbdata
$ rm -rf ./logs- WordPress Docker images: https://hub.docker.com/_/wordpress/
- MySQL Docker images: https://hub.docker.com/_/mysql
- Nginx Docker images: https://hub.docker.com/_/nginx/
- Adminer Docker images: https://hub.docker.com/_/adminer
General information regarding standard Docker deployment of WordPress for reference purposes
Use: https://github.com/RENCI-NRIG/ez-letsencrypt - A shell script to obtain and renew Let's Encrypt certificates using Certbot's --webroot method of certificate issuance.
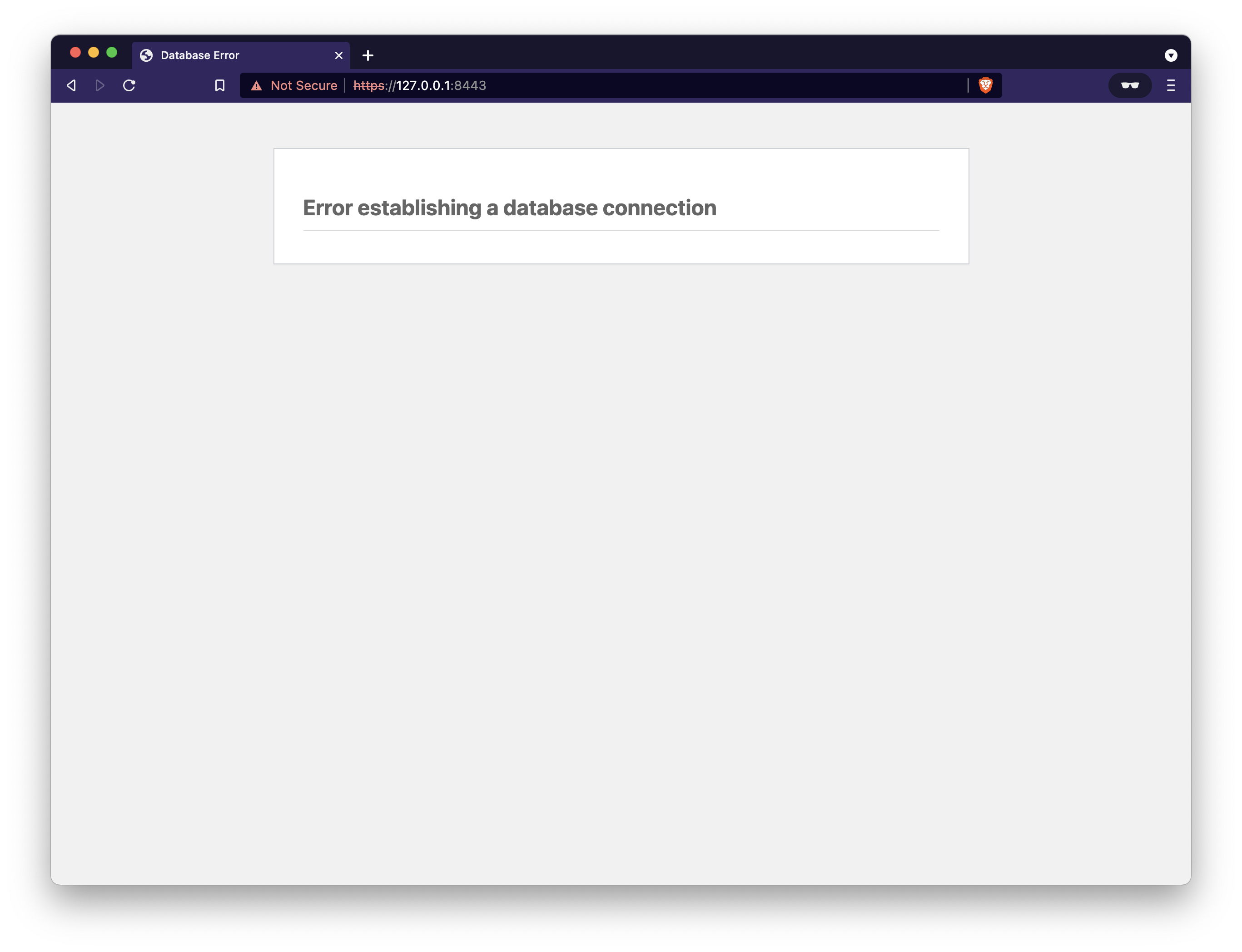
This can happen when the wordpress container attempts to reach the database container prior to it being ready for a connection.
This will sometimes resolve itself once the database fully spins up, but generally it's advised to start the database first and ensure it's created all of its user and wordpress tables and then start the WordPress service.
Neither the wordpress container nor the database container have publicly exposed ports. They are running on the host using a docker defined network which provides the containers with access to each others ports, but not from the host.
If you wish to expose the ports to the host, you'd need to alter the stanzas for each in the docker-compose.yml file.
For the database stanza, add
ports:
- "3306:3306"
For the wordpress stanza, add
ports:
- "9000:9000"
Add below to your host file to access the WP setup on wpdocker.local
127.0.0.1 wpdocker.local