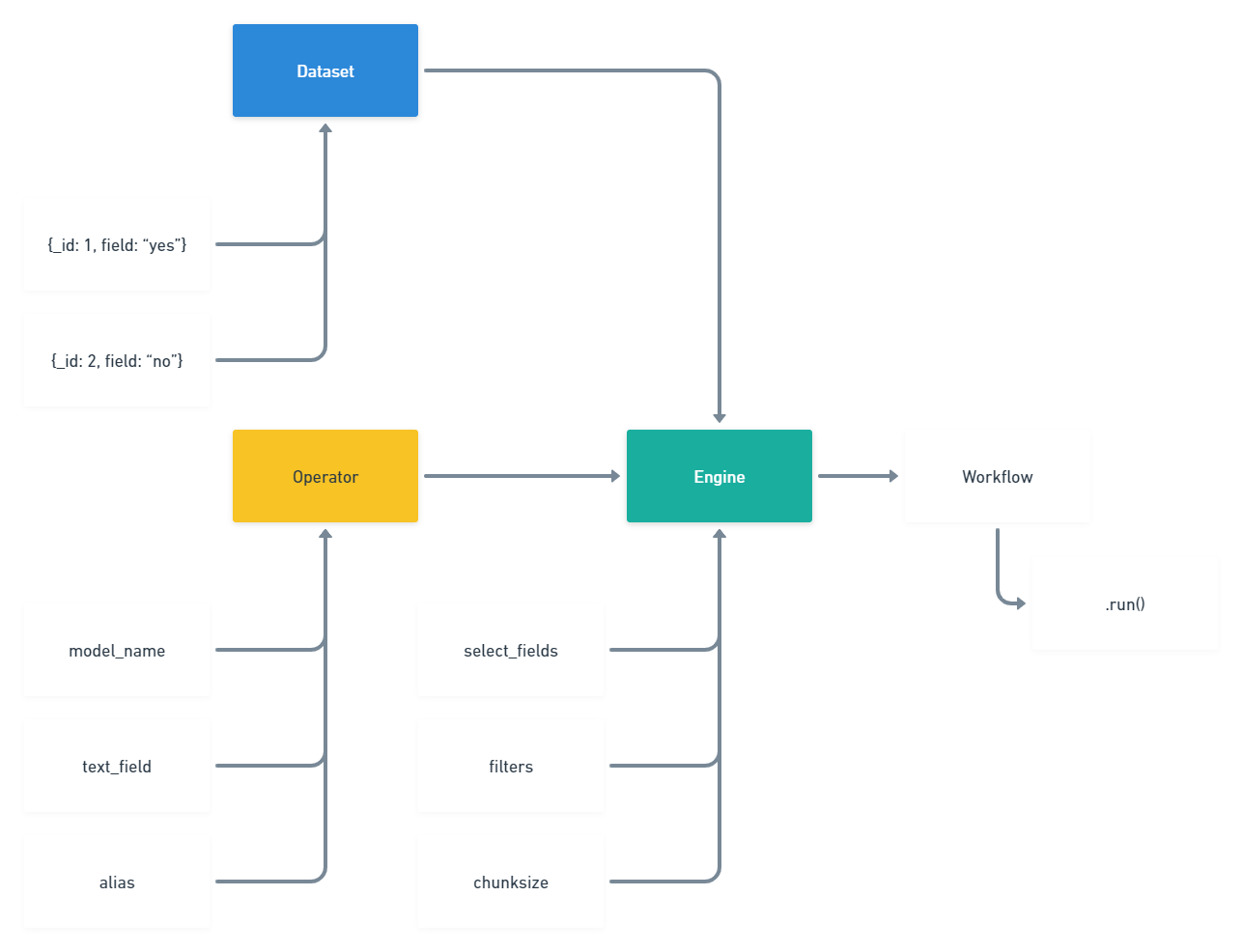
Below is a hierarchy diagram for all the moving parts of a workflow.
Fresh install
pip install ai-transform
to upgrade to the latest version
pip install --upgrade ai-transform
To get started, please refer to the example scripts in scripts/
import random
from ai_transform.api.client import Client
from ai_transform.engine.stable_engine import StableEngine
from ai_transform.workflow.helpers import decode_workflow_token
from ai_transform.workflow import Workflow
from ai_transform.operator.abstract_operator import AbstractOperator
from ai_transform.utils.random import Document
class RandomOperator(AbstractOperator):
def __init__(self, upper_bound: int=10):
self.upper_bound = upper_bound
def transform(self, documents):
for d in documents:
d['random_number'] = random.randint(0, self.upper_bound)
client = Client()
ds = client.Dataset("sample_dataset")
operator = RandomOperator()
engine = StableEngine(
dataset=ds,
operator=operator,
chunksize=10,
filters=[],
)
workflow = Workflow(engine)
workflow.run()Workflows have Workflow IDs such as sentiment - for example: sentiment.py is called sentiment and this is how the frontend triggers it. Workflow Name is what we call the workflow like Extract Sentiment . Each instance of a workflow is a job and these have job_id so we can track their status.
This the safest and most basic way to write a workflow. This engine will pull chunksize
number of documents, transform them according to the transform method in the respective operator
and then insert them. If chunksize=None, the engine will attempt to pull the entire dataset
transform the entire dataset in one go, and then reinsert all the documents at once. Batching is limited
by the value provided to chunksize.
This Engine is intended to be used when operations are done on the whole dataset at once.
The advantage this has over StableEngine with chunksize=None is that the pulling and
pushing documents is done in batch, but the operation is done in bulk. With StableEngine,
this would have involved extremely large API calls with larger datasets.
Sometimes you will want to wait until the Relevance AI
schema updates before proceeding to the next step. For more information - look at workflow/helpers.py file.
poll_until_health_updates_with_input_field(
dataset=dataset,
input_field=...,
output_field=...,
minimum_coverage=0.95,
sleep_timer=10
)
To cut a release, go to "Releases" and create a new version from main branch.
There are a few reasons for the pydantic choice:
- good strong validation
- outputs nicely to OpenAPI which allows us to generate workflow docs automatically in future for Workflow APIs
- used in FastAPI stack so workflows can also be FastAPI compatible in the future.
When developing with Workflows Core, we have the following philosophies:
- Support for only 1 entrypoint where possible
- Readable comments for anything that others might not understand