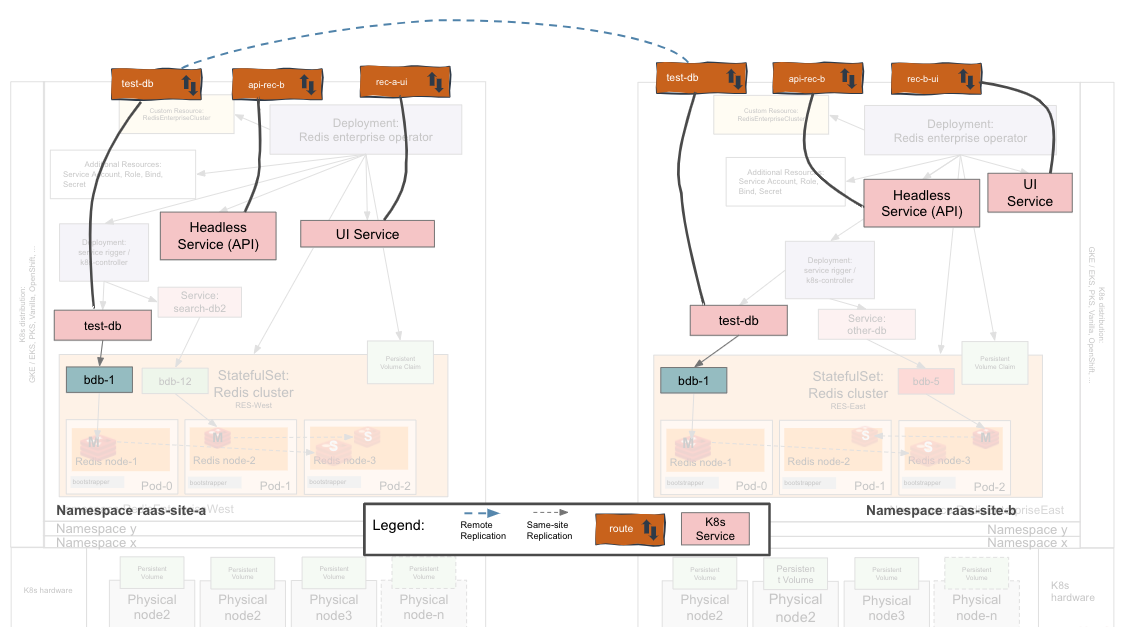
- Two working Redis Enteprise Clusters (REC) in different Openshift environments
- Important Note: the two RECs should have different
names/fqdn. If this is not met, the CRDB creation will result in bad state.
- Important Note: the two RECs should have different
- REC admin role credentials to both RECs
- Appropriate resources available in each REC to create DBs of the requested size.
- Openshift Permissions: a role that allows the creation of Openshift routes
- Command line tools
kubectlorocandjq
The following is the high level workflow which you will follow:
- Document the required parameters.
- Apply the
activeActivespec to both clusters. - Formulate the CRDB creation JSON payload using the parameters from both RECs in a single JSON document.
- POST the JSON payload to one of the REC's API endpoints. (Yes, just one; it will coordinate with the other(s).)
- Run a workload.
The following parameters will be required to form the JSON payload to create the CRDB.
Here is an example when creating a CRDB with database name test-db:
| Parameter Name in REST API | Example value |
|---|---|
name |
rec-a.raas-site-a.svc.cluster.local |
url |
https://api-raas-site-a.apps.bbokdoct.redisdemo.com |
credentials |
username: b@rl.com, password: something |
replication_endpoint |
test-db-raas-site-a.apps.bbokdoct.redisdemo.com:443 |
replication_tls_sni |
test-db-raas-site-a.apps.bbokdoct.redisdemo.com |
Note: My openshift cluster creates routes at the subdomain *.apps.bbokdoct.redisdemo.com by default where my openshift cluster name is bbokdoct.redisdemo.com.
Ensure you've documented the required parameters as in the above section. You'll need these!
Important Note: In the samples below I am creating two Redis Enterprise Clusters (RECs) in the same Openshift cluster but two distinct namespaces. The same steps will apply for RECs in different Openshift clusters.
As in the above section: Required Parameters.
Apply the activeActive spec to both Redis Enterprise clusters appropriately. Details about the REC API are here.
REC at site A:
activeActive: # edit values according to your cluster
apiIngressUrl: api-raas-site-a.apps.bbokdoct.redisdemo.com
dbIngressSuffix: -raas-site-a.apps.bbokdoct.redisdemo.com
method: openShiftRoute
REC at site B:
activeActive: # edit values according to your cluster
apiIngressUrl: api-raas-site-b.apps.bbokdoct.redisdemo.com
dbIngressSuffix: -raas-site-b.apps.bbokdoct.redisdemo.com
method: openShiftRoute
You can validate that these were applied by describing the rec as follows:
$ oc get rec -n raas-site-a -o json | jq '.items[].spec.activeActive'
{
"apiIngressUrl": "api-raas-site-a.apps.bbokdoct.redisdemo.com",
"dbIngressSuffix": "-db-raas-site-a.apps.bbokdoct.redisdemo.com",
"method": "openShiftRoute"
}
$ oc get rec -n raas-site-b -o json | jq '.items[].spec.activeActive'
{
"apiIngressUrl": "api-raas-site-b.apps.bbokdoct.redisdemo.com",
"dbIngressSuffix": "-db-raas-site-b.apps.bbokdoct.redisdemo.com",
"method": "openShiftRoute"
}
This will result in the API route api-<clustername> being added in both sites as below:
Redis Enterprise Cluster in Site A
$ oc get all
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/rec-a-0 2/2 Running 0 13m
pod/rec-a-services-rigger-7864cf7987-bsl4m 1/1 Running 0 13m
pod/redis-enterprise-operator-5d4dcf5dfc-7gklr 1/1 Running 0 152m
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/rec-a ClusterIP None <none> 9443/TCP,8001/TCP,8070/TCP 13m
service/rec-a-ui ClusterIP 172.30.225.190 <none> 8443/TCP 13m
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/rec-a-services-rigger 1/1 1 1 13m
deployment.apps/redis-enterprise-operator 1/1 1 1 152m
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
replicaset.apps/rec-a-services-rigger-7864cf7987 1 1 1 13m
replicaset.apps/redis-enterprise-operator-5d4dcf5dfc 1 1 1 152m
NAME READY AGE
statefulset.apps/rec-a 1/1 13m
NAME HOST/PORT PATH SERVICES PORT TERMINATION WILDCARD
route.route.openshift.io/api-rec-a api-raas-site-a.apps.bbokdoct.redisdemo.com rec-a api passthrough None
route.route.openshift.io/rec-ui-a rec-ui-a-raas-site-a.apps.bbokdoct.redisdemo.com rec-a-ui ui passthrough None
Redis Enterprise Cluster in Site B:
$ oc get all
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/rec-b-0 2/2 Running 0 150m
pod/rec-b-services-rigger-5d5d8ffb44-vp5xr 1/1 Running 0 150m
pod/redis-enterprise-operator-5d4dcf5dfc-w2v4g 1/1 Running 0 150m
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/rec-b ClusterIP None <none> 9443/TCP,8001/TCP,8070/TCP 150m
service/rec-b-ui ClusterIP 172.30.223.236 <none> 8443/TCP 150m
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/rec-b-services-rigger 1/1 1 1 150m
deployment.apps/redis-enterprise-operator 1/1 1 1 150m
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY AGE
replicaset.apps/rec-b-services-rigger-5d5d8ffb44 1 1 1 150m
replicaset.apps/redis-enterprise-operator-5d4dcf5dfc 1 1 1 150m
NAME READY AGE
statefulset.apps/rec-b 1/1 150m
NAME HOST/PORT PATH SERVICES PORT TERMINATION WILDCARD
route.route.openshift.io/api-rec-b api-raas-site-b.apps.bbokdoct.redisdemo.com rec-b api passthrough None
route.route.openshift.io/rec-b-ui rec-b-ui-raas-site-b.apps.bbokdoct.redisdemo.com rec-b-ui ui passthrough None
Create the JSON payload for CRDB creation request as in this example using the required parameters. Save the file as crdb.json in your current working directory.
{
"default_db_config": {
"name": "<db_name>",
"replication": false,
"memory_size": 10240000,
"aof_policy": "appendfsync-every-sec",
"shards_count": 1
},
"instances": [
{
"cluster": {
"url": "<site_a_api_endpoint>",
"credentials": {
"username": "<site_a_username>",
"password": "<site_a_password>"
},
"name": "<site_a_rec_name/fqdn>",
"replication_endpoint": "<site_a_replication_endpoint>443",
"replication_tls_sni": "<site_a_replication_endpoint>"
}
},
{
"cluster": {
"url": "<site_b_api_endpoint>",
"credentials": {
"username": "<site_b_username>",
"password": "<site_b_password>"
},
"name": "<site_b_rec_name/fqdn>",
"replication_endpoint": "<site_b_replication_endpoint>:443",
"replication_tls_sni": "<site_b_replication_endpoint>"
}
}
],
"name": "<db_name>",
"encryption": true,
"compression": 0
}
In this step you will make the Active-Active DB request to just one cluster member. Why just one? This request is coordinated among members: You request one member to initiate the coordination by including the list of, and credentials for, each Active-Active DB member.
Apply the following to the API endpoint at just one cluster API endpoint:
curl -k -u b@rl.com:<snip> https://api-raas-site-a.apps.bbokdoct.redisdemo.com/v1/crdbs -X POST -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d @crdb.json
Note: curl some users are having difficulty specifying the payload with the -d argument. Please consult your curl manual or try postman.
You should see a reply from the API as in the following which indicates the payload was well formed and the request is being actioned:
{
"id": "aac6ff9a-ff54-49c2-8398-f62b1896c69a",
"status": "queued"
}
Note Did you get something other than queued as a response? Then proceed to the troubleshooting section of the document.
You can get the status of the above task by issuing a GET on /v1/crdbs_tasks/<id>. Here is an example of a failed task:
$ curl -k -u b@rl.com:<snip> https://api-raas-site-a.apps.bbokdoct.redisdemo.com/v1/crdb_tasks/aac6ff9a-ff54-49c2-8398-f62b1896c69a
{
"crdb_guid": "5f04ae65-6d4c-4c22-8081-08906864560a",
"id": "aac6ff9a-ff54-49c2-8398-f62b1896c69a",
"status": "finished"
}
If successful, you will see the DB created in the Redis Enterprise UI for a healthy and syncing CRDB:
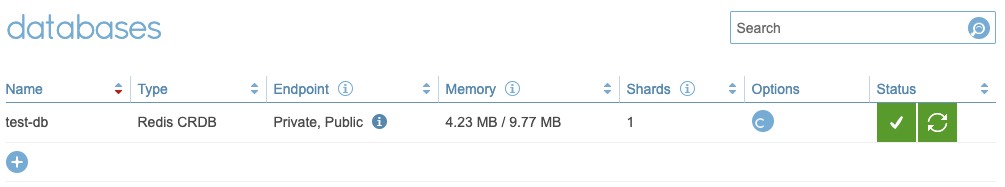
You will also see two new services per cluster: test-db and test-db-headless, as well as a new route which is used for the replication: test-db-raas-site-a.apps.bbokdoct.redisdemo.com
$ oc get svc,routes -n raas-site-a
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/rec-a ClusterIP None <none> 9443/TCP,8001/TCP,8070/TCP 38m
service/rec-a-ui ClusterIP 172.30.14.235 <none> 8443/TCP 38m
service/test-db ClusterIP 172.30.177.110 <none> 17946/TCP 31m
service/test-db-headless ClusterIP None <none> 17946/TCP 31m
NAME HOST/PORT PATH SERVICES PORT TERMINATION WILDCARD
route.route.openshift.io/api-rec-a api-raas-site-a.apps.bbokdoct.redisdemo.com rec-a api passthrough None
route.route.openshift.io/rec-ui-a rec-ui-a-raas-site-a.apps.bbokdoct.redisdemo.com rec-a-ui ui passthrough None
route.route.openshift.io/test-db test-db-raas-site-a.apps.bbokdoct.redisdemo.com test-db 17946 passthrough None
$ oc get svc,routes -n raas-site-b
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
service/rec-b ClusterIP None <none> 9443/TCP,8001/TCP,8070/TCP 3h48m
service/rec-b-ui ClusterIP 172.30.223.236 <none> 8443/TCP 3h48m
service/test-db ClusterIP 172.30.204.212 <none> 17946/TCP 31m
service/test-db-headless ClusterIP None <none> 17946/TCP 31m
NAME HOST/PORT PATH SERVICES PORT TERMINATION WILDCARD
route.route.openshift.io/api-rec-b api-raas-site-b.apps.bbokdoct.redisdemo.com rec-b api passthrough None
route.route.openshift.io/rec-b-ui rec-b-ui-raas-site-b.apps.bbokdoct.redisdemo.com rec-b-ui ui passthrough None
route.route.openshift.io/test-db test-db-raas-site-b.apps.bbokdoct.redisdemo.com test-db 17946 passthrough None
It's time to test your deployment. You can use the redis benchmarking tool memtier_benchmark [link]. Here are a couple of examples deployment manifests:
- Benchmark without TLS.
- Benchmark with TLS, required when working through Openshift Routes.
Below is an example invocation of memtier_benchmark as from the commandline which is as-is reflected in the manifest file linked above: Benchmark with TLS. This invocation should yield somewhere between 3k and 10k requests per second. If you want to generate more workload, adjust the Limits and requests values in this manifest: memtier_benchmark will consume as much resources as are given to it.
memtier_benchmark -a YkBybC5jb20= -s db-raas-site-a.apps.bbokdoct.redisdemo.com -p 443 --tls --tls-skip-verify --sni db-raas-site-a.apps.bbokdoct.redisdemo.com --ratio=1:3 --data-size-pattern=R --data-size-range=128-2800 --requests=20000000 --pipeline=1 --clients=4 --threads=5 --run-count=3
What do the arguments above mean?
-a <password>,-s <server>,-p <port>: use Redis basicAuth(without a specified user) to connect to a Redisserveron a specifiedport.--tls --tls-skip-verify: Use TLS but to not verify server identity. If you've installed your own server certs or installed our CA then--tls-skip-verifyis likely unnecessary.- Other options are fairly straight forward:
- Use a
1:3W:R ratio - Randomize the data size between
128and2800Bytes - Execute
20Mcommands with only one command per requests (--pipeline=1) - Create
4clients with5working threads each - Do all the above 3 times.
- Use a
To apply the benchmark workload:
- Edit the arguments in the file.
- You can specify values directly with
env: {name, value}pairs:env: - name: REDIS_PORT value: "443" - You can also get the values from K8s Secrets as in the following:
- name: REDIS_PASSWORD valueFrom: secretKeyRef: key: password name: redb-redis-db1
- You can specify values directly with
- Apply the manifest:
oc apply -f benchmark-tls.yaml. If the arguments are properly specified then you will see a deployment and pod created for this workload.
$ oc get all
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
pod/redis-benchmark-tls-fd5df8549-wm4xs 1/1 Running 0 8m9s
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
deployment.apps/redis-benchmark-tls 1/1 1 1 88m
Alas, this is not a memtier_benchmark tutorial. Feel free to try out some of the other command line options.
-
Symptom: API endpoint not reachable The API endpoint is not reachable from one cluster to the other.
-
Open a shell side a one of the Redis Enterprise cluster pods:
oc exec -it rec-a-0 -- /bin/bash $ curl -ivk https://api-raas-site-b.apps.bbokdoct.redisdemo.com ... HTTP/1.1 401 UNAUTHORIZED ... WWW-Authenticate: ... realm="rec-b.raas-site-b.svc.cluster.local"It is expected that you will get a "401" response but check that the returned "realm" reflects the remote cluster's FQDN as in Required Parameters:
name. -
Perform the same step as above from the other site, to the former.
-
If one or both of these steps above do not result in "401" with the appropriate "realm" then the contact your Openshift administrator for help troubleshooting an Openshift Route to the REC API endpoint.
-
-
API response 400, bad request:
{ "detail": "None is not of type 'object'", "status": 400, "title": "Bad Request", "type": "about:blank" }- Your payload is not being passed to the API or the payload is not valid JSON. Please Lint your JSON or try Postman with built-in JSON validate.
-
The Active-Active DB request was accepted and completed, but replication is not taking place. This is likely the case if either or both DB ingress routes are not working properly. Please contact your K8s/OpenShift administrator to validate these routes.
- Generate some workload against the Active-active DB as in this manifest using
memtier_benchmark.