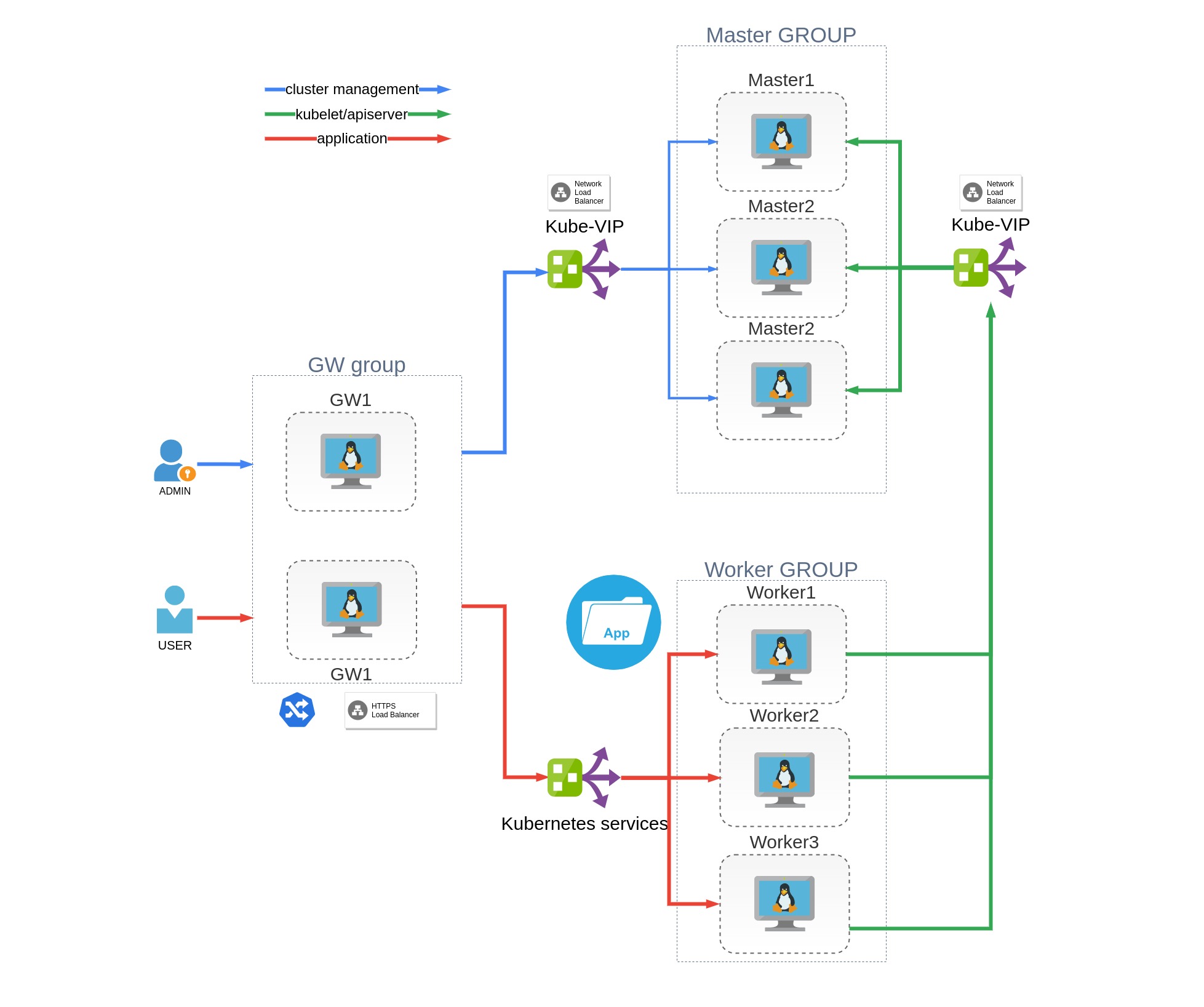
Deploy HA kubernetes cluster with 3 contol-plane nodes, 3 worker nodes and 2 GW nodes for external access to cluster using Vagrant
- 4 Processor core
- 16 GB of RAM
- Linux OS 64-bit (prefferd Ubuntu 18.04 and newer)
- Ansible verison 2.9 or newer
- Ansible Collection Community.Kubernetes
Install:
ansible-galaxy collection install community.kubernetes - Ansible Collection Community.Crypto
Install:
ansible-galaxy collection install community.crypto
- Vagrant version 2.2.14 or newer
This cluster used only for education purpose. :warning: DO NOT USE IN PRODUCTION
Cluster consist of 8 Virtual Machines
- 3 Control Plane nodes
- 3 Worker nodes
- 2 Gateway nodes
Control plane nodes doesn't allow any pods run on them except kubernetes contol plane pods. Gateway nodes use for NGINX ingress-controller pods deployment and also doesn't allow any other pods. Application pods and cluster service pods - such as Vault, Cert-Manager, Local-path-provisioner, EFK and Prometheus/Grafana, bare-metal load balancer provisioner runs only on worker nodes.
Gateway nodes needs an external load balancer ether for cluster administration and application access.
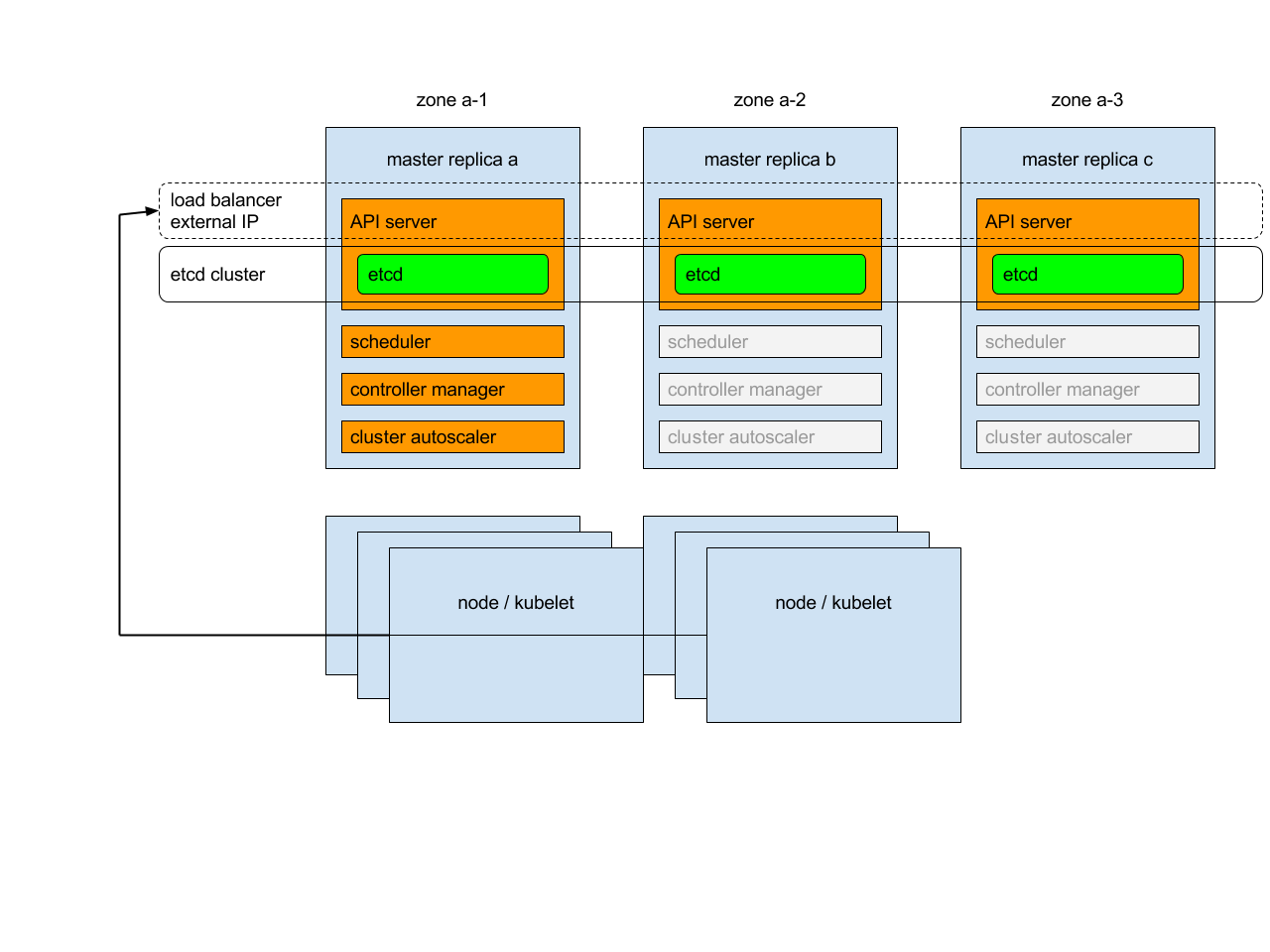
Each control plane node runs an instance of the kube-apiserver, kube-scheduler, and kube-controller-manager. The kube-apiserver is exposed to worker nodes using a load balancer.
From kubernets documentation:
Each of master replicas will run the following components in the following mode:
- etcd instance: all instances will be clustered together using consensus;
- API server: each server will talk to local etcd - all API servers in the cluster will be available;
- controllers, scheduler, and cluster auto-scaler: will use lease mechanism - only one instance of each of them will be active in the cluster;
- add-on manager: each manager will work independently trying to keep add-ons in sync.
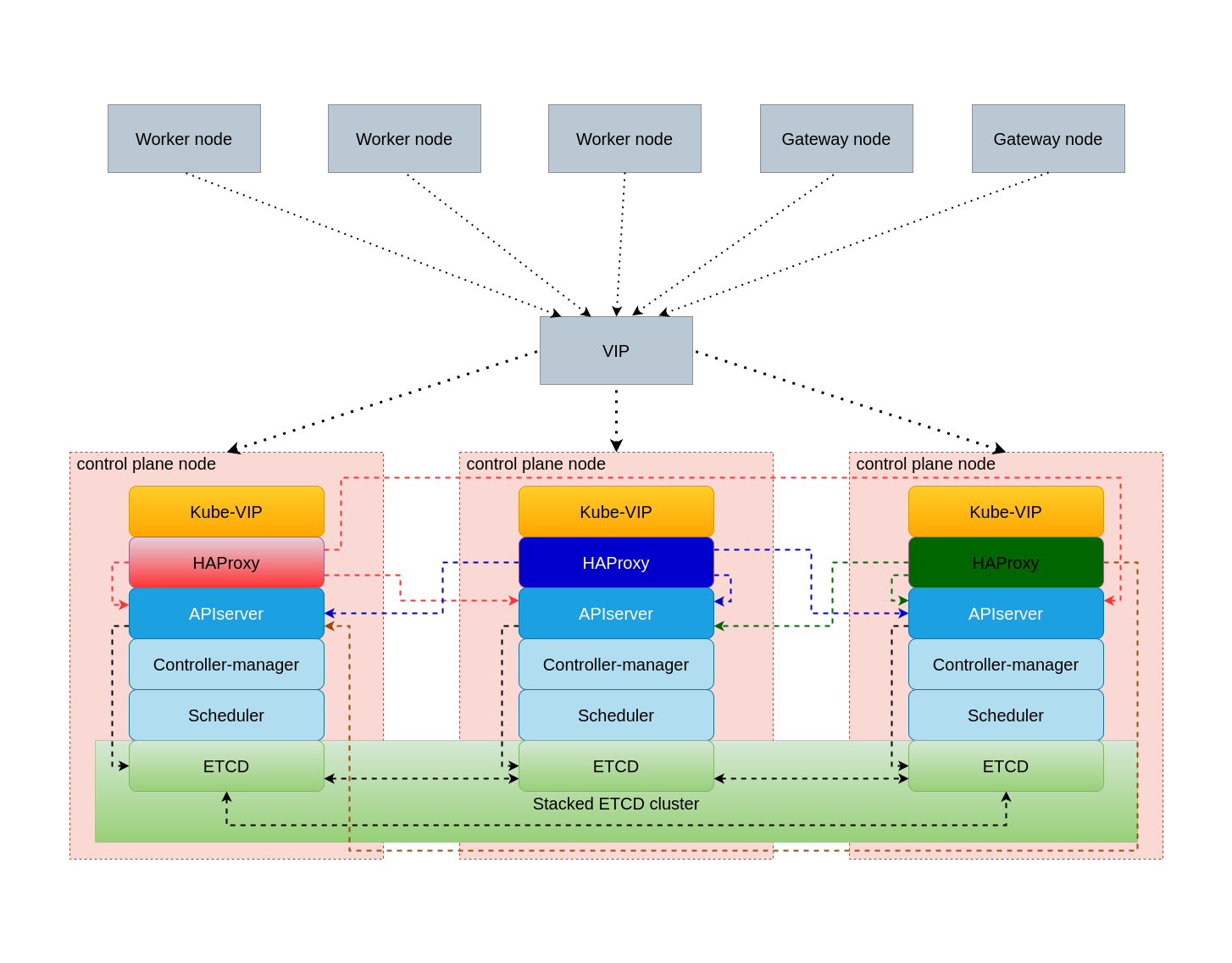
For load balancing workers access to control-plane we using Kube-VIP. The leader within the cluster will assume the VIP and will have it bound to the selected interface that is declared within the configuration. When the leader changes it will evacuate the VIP first or in failure scenarios the VIP will be directly assumed by the next elected leader. Kube-VIP deployed by static pods This configuration provide failure toleration but not load balancing. For load balancing we deploy HAProxy server on all control-plane nodes. HaProxy listen 0.0.0.0:8443 on contol-plane nodes and proxy request to kubernetes apiserver using round-robin algoritm.
Kubernetes does not offer an implementation of network load-balancers (Services of type LoadBalancer) for bare metal clusters. The implementations of Network LB that Kubernetes does ship with are all glue code that calls out to various IaaS platforms (GCP, AWS, Azure…). If you’re not running on a supported IaaS platform (GCP, AWS, Azure…), LoadBalancers will remain in the “pending” state indefinitely when created.
Bare metal cluster operators are left with two lesser tools to bring user traffic into their clusters, “NodePort” and “externalIPs” services. Both of these options have significant downsides for production use, which makes bare metal clusters second class citizens in the Kubernetes ecosystem.
MetalLB aims to redress this imbalance by offering a Network LB implementation that integrates with standard network equipment, so that external services on bare metal clusters also “just work” as much as possible.
In this realisation Metallb work in Layer2 mode.
MetalLB is a load-balancer implementation for bare metal Kubernetes clusters
Local Path Provisioner provides a way for the Kubernetes users to utilize the local storage in each node. Based on the user configuration, the Local Path Provisioner will create hostPath based persistent volume on the node automatically. It utilizes the features introduced by Kubernetes Local Persistent Volume feature, but make it a simpler solution than the built-in local volume feature in Kubernetes. Currently the Kubernetes Local Volume provisioner cannot do dynamic provisioning for the local volumes.
With Local Path Provisioner we can create dynamic provisioning the volume using hostPath. We dont have to create static persistent volume. Local Path Provisioner do all provisioning work for us.
Kube-prometheus-stack a collection of Kubernetes manifests, Grafana dashboards, and Prometheus rules combined with documentation and scripts to provide easy to operate end-to-end Kubernetes cluster monitoring with Prometheus using the Prometheus Operator.
Logging consists of two parts:
-
Elastic Cloud on Kubernetes extends the basic Kubernetes orchestration capabilities to support the setup and management of Elasticsearch, Kibana, APM Server, Enterprise Search, and Beats on Kubernetes. This operator response for Elasticsearch and Kibana instance managment
-
Fluentbit is a Fast and Lightweight Log Processor, Stream Processor and Forwarder for Linux, OSX, Windows and BSD family operating systems. It has been made with a strong focus on performance to allow the collection of events from different sources without complexity.
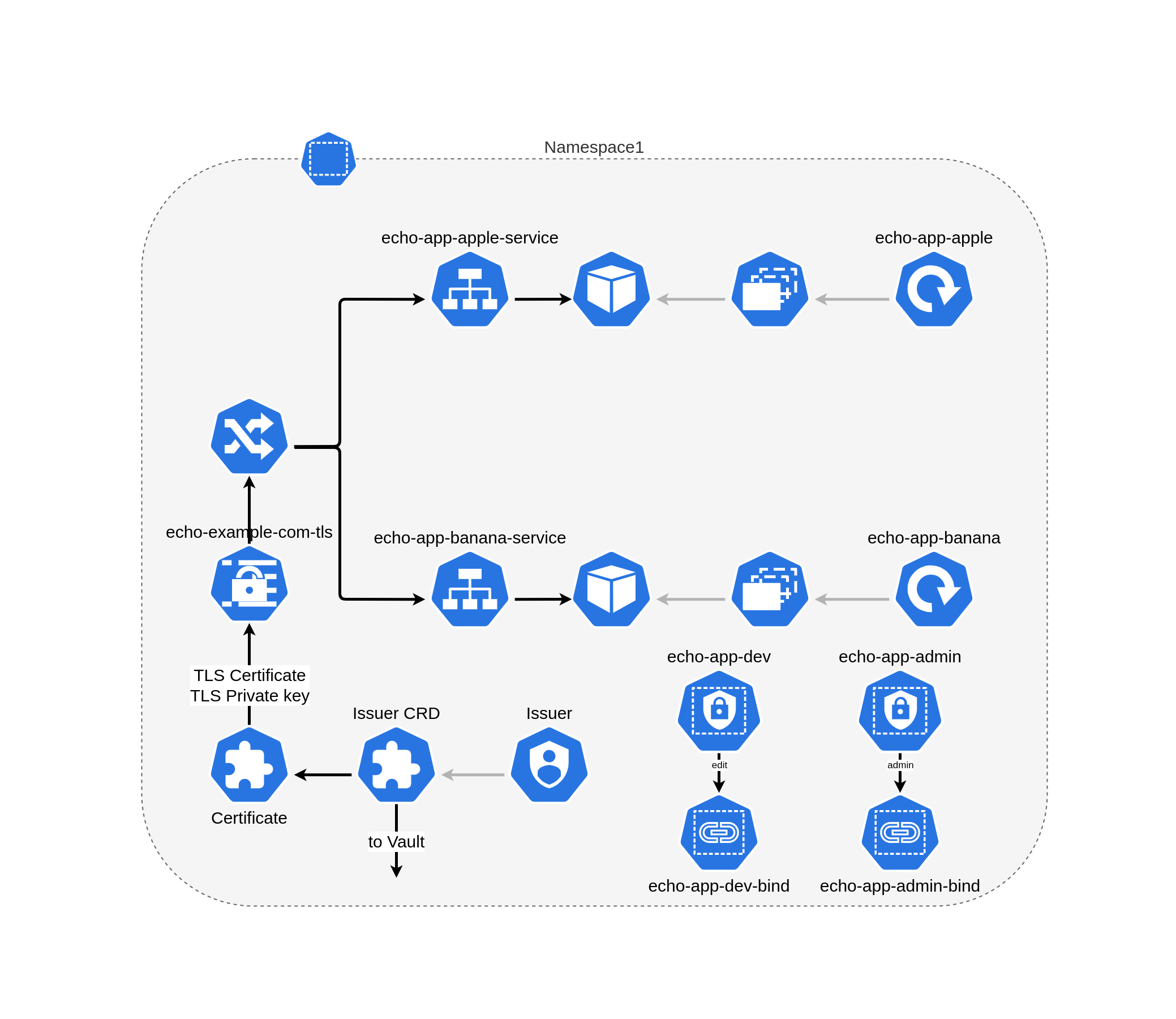
Example application is just two servers that return word apple and banana on GET request. In Kubernetes term application consist of 2 deployments(one for apple and one for banana), 1 replica per deployment. External access to application provided by NGINX ingress controller and ingress.
Access to apple app - https://echo.example.com/apple
Access to banana app - https://echo.example.com/banana
(A record in /etc/hosts file which matches IP address of LoadBalance service, provided by Metallb and hostname echo.example.com)
Certificate for encrypted HTTPS connection provided by Cert-manager, which use Hashicorp Vault as root Certificate Authority(CA). Certificate for ingress issued for 15 min(can be changed by max_cert_ttl variable) and automatically renewed by Vault. Cert-manager store certificate in kuberntes secret.
For application administration we create two users:
echo-app-admin- bind to kubernetesadminrole in application namespace scopeecho-app-dev- bind to kuberneteseditrole in application namespace scope
Access method to kubernetes apiserver is key/certificate.
All Private key, certificate for that users and kubectl config file stored in ~/.kube folder on ansible executor host.
Configure Vagrantfile with your variable
| Name | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
k8s_master_num |
3 | number of control plane nodes |
k8s_worker_num |
3 | number of worker nodes |
k8s_gw_num |
2 | number of gateway nodes |
bridge |
- | Ethernet interface with internet access nodes connected to |
vm_cidr |
192.168.1 | First 3 octets of nodes ip address |
vm_ip_addr_start |
130 | Nodes start ip address last octet. Increase incremently |
Create and start VM
vagrant up
Provision VM with ansible
ansible-playbook -i inventories/k8s-ha-cluster/hosts.yml --ask-become-pass k8s-cluster-deploy.yml
With --ask-become-pass key Ansible ask the sudo pass on ansible-playbook executor host. This password used for add entry for gateway1 host to /etc/hosts file. Using this entry provide access outside of cluster to Kubernetes apiserver for cluster administration and to Example application as regular user.
Change ansible_host variable in all files in inventories/k8s-ha-cluster/host_vars to ip address you choose in section Cluster installation. Private key and user generated by Vagrant and dont needed to be changed.
| Name | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
kubernetes_kubeproxy_mode |
ipvs | Which proxy mode to use: 'iptables' or 'ipvs' |
kubernetes_apiserver_advertise_address |
- | The IP address the API Server will advertise it's listening on. If not set the default network interface will be used. |
kubernetes_cluster_domain_name |
cluster.local | Cluster domain name |
kubernetes_cgroupDriver |
systemd | cgroup driver : 'systemd' or 'cgroup' |
kubernetes_cri_socket |
/run/containerd/containerd.sock | CRI socket. In this realistion only container.d |
kubernetes_cluster_name |
kubernetes | Cluster name |
| Name | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
root_ca_name |
"Demo Root Certificate Authority" | Name of CA |
root_ca_cert_filename |
demo-root-ca | CA parameters filename |
| Name | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
prometheus_stack_release_name |
monitoring | Helm release name for Kube-Prometheus-Stack |
prometheus_stack_namespace |
monitoring | Namespace for Kube-Prometheus-Stack |
grafana_ingress_host |
monitoring | Grafana address |
prometheus_stack_taint |
node-role.kubernetes.io/worker | Toleration for Kube-Prometheus-Stack |
| Name | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
elastic_operator_version |
"1.6.0" | Elastic operator version |
elastic_namespace |
logging | Namespace for Elastic operator |
elastic_operator_taint |
node-role.kubernetes.io/worker | Toleration for Elastic operator |
elastic_version |
7.10.0 | Elasticsearch and Kibana version |
elastic_name |
elasticsearch | Elasticsearch Custom Resource name |
kibana_name |
kibana | Kibana Custom Resource name |
elastic_count |
1 | Elasticsearch Custom Resource replica count |
kibana_count |
1 | Kibana Custom Resource replica count |
logging_namespace |
logging | Kibana, Elastic, Fluentbit pods namespace |
fluentbit_toleration |
- | Toleration for Flient bit |
fluentbit_service |
- | Fluentbirt service config |
fluentbit_inputs |
- | Fluentbirt input config |
fluentbit_filter |
- | Fluentbirt filter config |
fluentbit_output |
- | Fluentbirt output config |
fluentbit_customParsers |
- | Fluentbirt custom parsers |
| Name | Default Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
chart_name_app |
echo-app | Helm release name for echo-app |
issuer_name |
echo.example.com-issuer | Kubernetes cert-manager issuer CRD name |
cert_name |
echo.example.com-cert | Kubernetes cert-manager certificate CRD name |
secret_name |
echo-example-com-tls | Kubernetes secret name used by ingress |
server_name |
echo.example.com | A common name to be used in TLS Certificate |
dns_server_name |
echo.example.com | A list of DNS subjectAltNames to be set in the TLS Certificate |
pki_policy_name |
example-dot-com | Vault pki policy name |
k8s_namespace |
namespace1 | Application kubernetes namespace name |
domain_name |
example.com | Domain name used for certificate generation |
allow_subdomains |
true | Allow certificate generation for subdomains |
max_cert_ttl |
15m | Maximum certificate ttl |
chart_name_users |
echo-app-users | Helm release name for echo-app-users chart |
k8s_users_namespace |
same as k8s_namespace |
Namespace for user access. Must be same as k8s_namespace |
users |
- username: echo-app-admin default_role: admin - username: echo-app-dev default_role: edit |
List of users. If bind to kubernetes default role set up default role field. If bind to custom role - provide rolename field instead |
TODO:
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/cloud-on-k8s/current/k8s-kibana-http-configuration.html