IAP
-
use Identify Aware Proxy to restrict access to web app.
-
IAP provides user id info to admin.
-
IAP got feautre of Cypto to against Spoofing.
Core Steps:
(1) deploy a simple (python) web page
(2) enable IAP service to restrice access to app
(3) get users id info from IAP
(4) avoid from spoofing using Crypto-Verification
Main Cmd line
gcloud app deploy
gcloud app browse
GAE (most simplest deployment solution)
prework: study how to make app wrapped in GAE using yaml file.
step from 1
Deployment using AGE
-
1.1, in cloud console, open the cloud shell tab, and type follwing cmd line to clone app from github.
git clone https://github.com/QueenieCplusplus/Login_Python_App.git cd Login_Python_App cat [file name] // to do edit or read the code line -
tips & attentions:
the main code is in main.py file, it use framework called flask, which responds requests with contents of template.
- the template file is in templates/index.html, which shows a plain HTML.
- the other template is in templates/privacy.html, which contains privacy policy.
- requirements.txt lists all the libs that app uses.
- app.yaml file tells GCP this app is wrapped in GAE.
-
1.2, deploy GAE
gcloud app deploy -
1.3, select the nearest region for App and type Y.
-
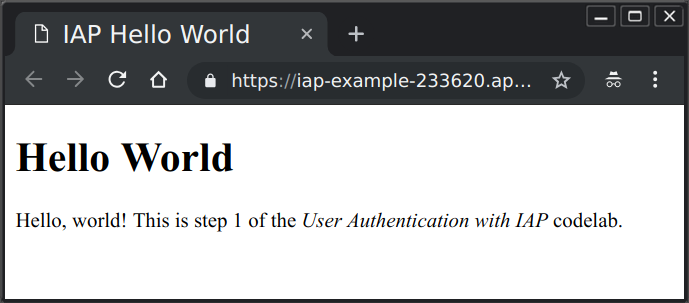
1.4, see result after deployment.
gcloud app browse [result]
IAP
from step 2:
restrict access using IAP
-
2.1, in cloud console, navigate to Secuity > IAP
-
2.2, enable the IAP service, then click on the tab "configure consent screen" for Oauth.
-
2.3, select "internal" for user type, and click on "create".
-
2.4, config the property of the Oauth.
-
2.5, in cloud shell, disable the flexible api.
gcloud services disable appengineflex.googleapis.com (optional) -
tips & attentions:
App Engine has its standard and flexible environments which are optimized for different application architectures. Currently, when enabling IAP for App Engine, if the Flex API is enabled, GCP will look for a Flex Service Account. Your project comes with a multitude of APIs already enabled for the purpose of convenience. However, this creates a unique situation where the Flex API is enabled without a Service Account created.
-
2.6, return to IAP config page in cloud console, and refresh it to see blow GAE row, and select toggle button to enable the IAP service in column.the domain is procted then.
Login Test
- 2.7, before telling IAP which account is allowed through, the login deose not work out.
AC
Access Control
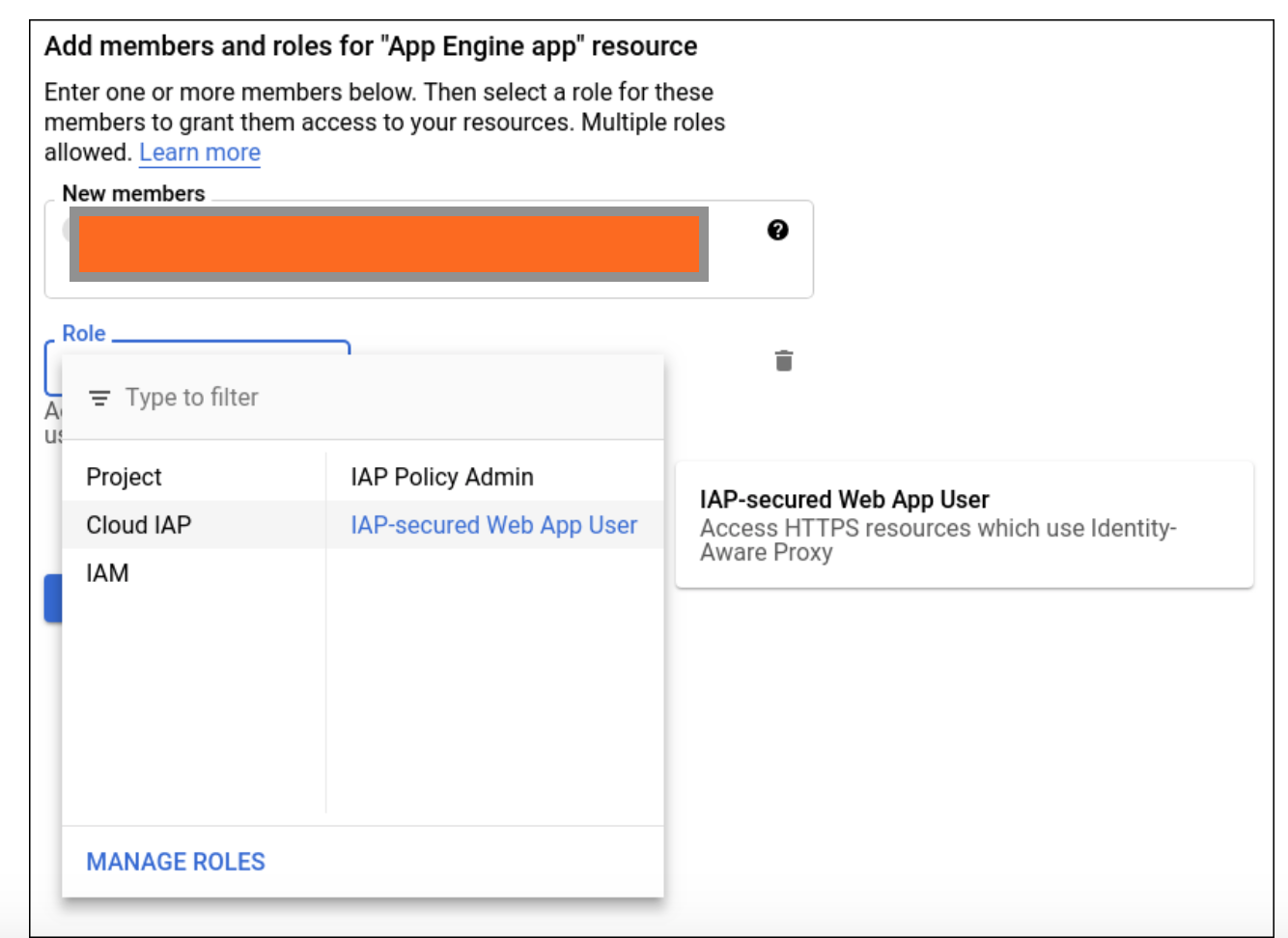
- 2.8, back to IAP config page in cloud console, and set up the AC list.
AC Test
Login Again without Cache
-
2.9, browse to app url, refresh it, ang test login using the following adress.
https://iap-example-999999.appspot.com/_gcp_iap/clear_login_cookie.
-
2.10, do not enter the already-exist account, use "another user account", re-enter username and password to check credentials is allowed.
Spoofing bypass IAP
spoofer might attack website by bypassing the IAP, and turn off the IAP.
from step 3:
User ID will shows in request header it passed thru in web browser. Make an app page to display it.
-
3.1, back to cloud shell, type cm line below.
git clone https://github.com/googlecodelabs/user-authentication-with-iap.git cd user-authentication-with-ia cd 2-HelloUser -
3.2, deploy it with GAE.
gcloud app deploy -
tips & attentions:
vesrion 2 program has been changed to retrieve the user information that IAP provides in request headers, and the template now displays that data. X-Goog-Authenticated-User- headers are provided by IAP.
// in main.py in 2-HelloUser
user_email = request.headers.get('X-Goog-Authenticated-User-Email')
user_id = request.headers.get('X-Goog-Authenticated-User-ID')
// render template
page = render_template('index.html', email=user_email, id=user_id)
// index.html in 2-HellowUser
Hello, {{ email }}! Your persistent ID is {{ id }}.
// template
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<title>IAP Hello User</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello World</h1>
<p>
Hello, totally fake email! Your persistent ID is None.
</p>
<p>
This is step 2 of the <em>User Authentication with IAP</em>
codelab.
</p>
</body>
</html>
-
3.3, run gae browse
gcloud app browse [result in browse] -
3.4, Hacker start to spoof.
curl -X GET <apps url> -H "X-Goog-Authenticated-User-Email: totally fake email"
Oauth
"make sure the IAP sevice is opened by admin" & "make sure developer is code with jwt lib for login"
If there is a risk of IAP being turned off or bypassed, your app can check to make sure the id info it receives is valid.
This uses a web request header added by IAP, called X-Goog-IAP-JWT-Assertion. The value of the header is a crypto-signed object that also contains the user id data. Your app can verify the digital signature and use the data provided in this object to be certain that it was provided by IAP without alteration.
Digital signature verification requires several extra steps, such as retrieving the latest set of Google public keys. You can decide whether your app needs these extra steps based on the risk that someone might be able to turn off or bypass IAP, and the sensitivity of the application.
If IAP is turned off or bypassed, the verified data would either be missing, or invalid, since it cannot have a valid signature unless it was created by the holder of Google's private keys.
Crypto
from step 4:
a protection to avoid http header spoofing
-
4.1, in cloud shell, deploy version 3 app
git clone https://github.com/QueenieCplusplus/Login_Python_App.git cd Login_Python_App gcloud app deploy gcloud app browse -
tips & attentions:
The assertion is the cryptographically signed data provided in the specified request header.
The code uses jwt lib to validate and decode that data.
Validation uses the "public keys" that Google provides for checking data it signs, and knowing the audience that the data was prepared for (essentially, the Google Cloud project that is being protected). Helper functions keys() and audience() gather and return those values.
The signed object has two pieces of data we need: the verified email address, and the unique ID value (provided in the sub, for subscriber, standard field).
code is like this:
def user():
assertion = request.headers.get('X-Goog-IAP-JWT-Assertion')
if assertion is None:
return None, None
info = jwt.decode(
assertion,
keys(), // provided by google
algorithms=['ES256'],
audience=audience() // provided by google
)
return info['email'], info['sub']
Ref Doc
https://cloud.google.com/armor/docs/security-policy-overview
https://cloud.google.com/armor/docs/configure-security-policies
Ref code
5562