- To design and implement image caption generation deep neural network architecture.
- Python SciPy environment, ideally with Python 3.
- Keras (2.2 or higher) is installed with the TensorFlow
- Libraries such as scikit-learn, Pandas, NumPy, and Matplotlib
- GPU (accessible through Google Collaboratories). Following libraries are imported to map GPU requirements
import psutil import humanize import os import GPUtil as GPU
Detailed Documentation is available in Image and Video Captioning .pdf
Flickr8k dataset
It consists of 8,000 images that are each paired with five different captions which provide clear descriptions of the salient entities and events. The reason to select is because it is realistic and relatively small to download it and build models using a Gogle Colab GPU.
- Flickr8k_Dataset.zip (1 Gigabyte) An archive of all photographs.
- Flickr8k_text.zip (2.2 Megabytes) An archive of all text descriptions for photographs.
A deep learning model based on the “merge-model” described by Marc Tanti, et al. in their 2017 papers: Where to put the Image in an Image Caption Generator, 2017. and What is the Role of Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) in an Image Caption Generator?, 2017.
-
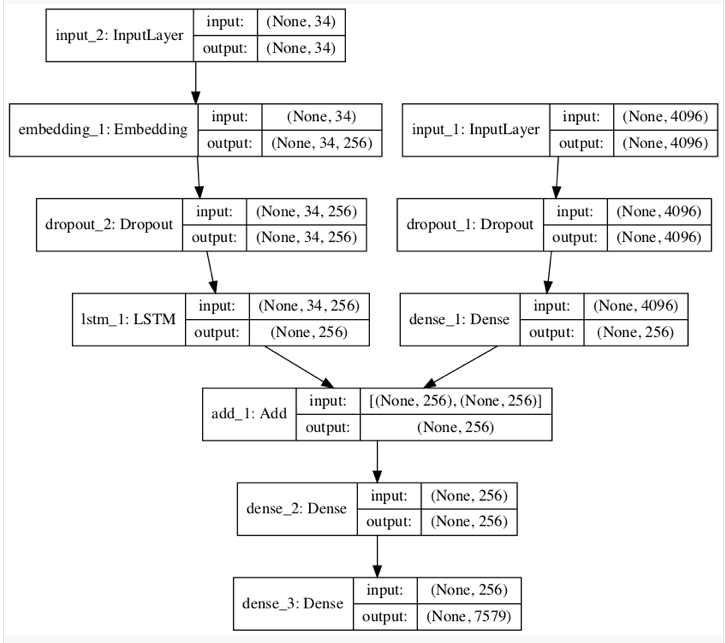
Photo Feature Extractor. This is a 16-layer VGG model pre-trained on the ImageNet dataset. Already pre-processed the photos with the VGG model (without the output layer) and use the extracted features predicted by this model as input. It expects input photo features to be a vector of 4,096 elements. These are processed by a Dense layer to produce a 256 element representation of the photo.
-
Sequence Processor. This is a word embedding layer for handling the text input, followed by a Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) recurrent neural network layer. It expects input sequences with a pre-defined length (34 words) which are fed into an Embedding layer that uses a mask to ignore padded values. This is followed by an LSTM layer with 256 memory units.
Both the input models produce a 256 element vector. Further, both input models use regularization in the form of 50% dropout. This is to reduce overfitting the training dataset, as this model configuration learns very fast.
- Decoder : Both the feature extractor and sequence processor output a fixed-length vector. These are merged together and processed by a Dense layer to make a final prediction. The Decoder model merges the vectors from both input models using an addition operation. This is then fed to a Dense 256 neuron layer and then to a final output Dense layer that makes a softmax prediction over the entire output vocabulary for the next word in the sequence.
Model Summary
This was my first hands on project in Neural Networks and was done as part of my Laboratory Project for course CS F366 at BITS Pilani.