configurable-threejs-app
This project is a configurable 3D web-based application built with Three.js. The webpage is served from an internal Node.js server.
How to start
Install
To use this project you need to download all the required modules from npm, to do that run this commands from the root folder of the project
cd server
npm install
cd WebGLScene
npm install
Or, if you are on Windows, just double click the install.bat file.
Launch the server
To start the server run this command, from the root folder of the project
cd server
cd src
node main portNumber
Or, if you are on Windows, just double click the startServer.bat file, the server will automatically start on port 8999.
The webpage will be available at http://localhost:8080/
The scene
As mentioned before the scene is built with Three.js (WebGL) and runs into your browser.
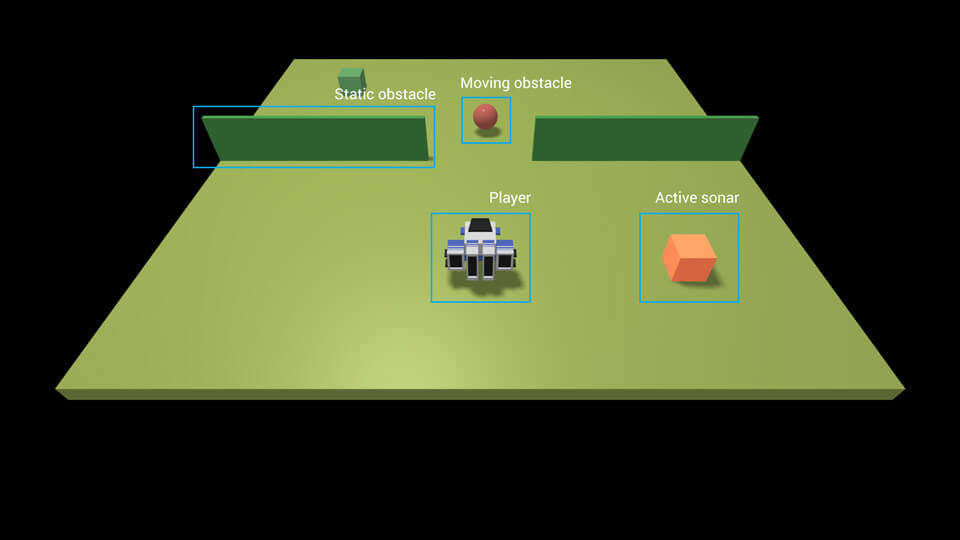
Scene components
-
Player object: an object controlled by the user that can be moved in the scene. It can be controlled via keyboard (w: move forward, s: move backward, r: turn right, f: turn left) or with a remote client (more on that later).
-
Platform (or floor): area on which the player can move and objects can be located.
-
Static obstacle: non-moving obstacle the player can't go through.
-
Moving obstacle: obstacle moving with a periodic movement that the player can't travers.
-
Sonar: sensor that can detect when the player is on its trajectory.
Scene configuration
In order to adapt the scene for different use cases, users don't need any knowledge of Javascript or Three.js, instead they can edit a simple configuration file that is used to set up the scene.
The configuration file can be found here .\WebGLScene\sceneConfig.js. It is a node module, it contains a Javascript object saved into a variable. This Javascript object contains all the information needed to create the scene.
In particulare: it contains one object for every scene componenet.
Floor
The floor object has only one property: a size object.
- The size defines the dimension of the floor on the x and y axes.
floor: {
size: { x: 40, y: 40 }
}
This floor is a square of size 40 in the x axis and 40 in the y axis.
Player
The player object has two properties: position and speed.
- The position can only be expressed with values between 0 and 1 and is relative to the floor. (0,0) is the top left corner of the floor, (1, 1) is the bottom right corner.
- The speed determines how fast the player object moves on the floor, it's not bounded (I suggest keeping it between 0 and 1 though).
player: {
position: { x: 0.5, y: 0.8 },
speed: 0.2
}
Sonar
Sonars is an array, each element in the array is a sonar. Each sonar has three properties: name, position and senseAxis.
- The name is a string.
- The position can only be expressed with values between 0 and 1 and is relative to the floor. (0,0) is the top left corner of the floor, (1, 1) is the bottom right corner.
- senseAxis determines in which direction this sonar will sense the player. It can be only x, y, or both.
sonars: [
{
name: "sonar-1",
position: { x: 0.8, y: 0.8 },
senseAxis: { x: true, y: false }
}
]
Moving obstacle
MovingObstacles is an array, each element in the array is a moving obstacle. Each moving obstacle has five properties: name, position, directionAxis, speed and range.
- The name is a string.
- The position can only be expressed with values between 0 and 1 and is relative to the floor. (0,0) is the top left corner of the floor, (1, 1) is the bottom right corner.
- directionAxis determines the direction of the periodic movement of the obstacle. It can be only x, y, or both.
- speed determines how fast the obstacle moves.
- range determines the range of the periodic movement.
movingObstacles: [
{
name: "moving-obstacle-1",
position: { x: .5, y: .4 },
directionAxis: { x: true, y: false },
speed: 1,
range: 4
}
]
Static obstacle
StaticObstacles is an array, each element in the array is a static obstacle. Each static obstacle has three properties: name, centerPosition and size.
- The name is a string.
- The centerPosition can only be expressed with values between 0 and 1 and is relative to the floor. (0,0) is the top left corner of the floor, (1, 1) is the bottom right corner.
- The size can only be expressed with values between 0 and 1 and is relative to the floor. If x = 1 the static obstacle will have the same x dimension of the floor.
staticObstacles: [
{
name: "static-obstacle-1",
centerPosition: { x: 0.2, y: 0.5},
size: { x: 0.4, y: 0.01}
}
]
Complete configuration object
const config = {
floor: {
size: { x: 40, y: 40 }
},
player: {
position: { x: 0.5, y: 0.8 },
speed: 0.2
},
sonars: [
{
name: "sonar-1",
position: { x: 0.8, y: 0.8 },
senseAxis: { x: true, y: false }
}
],
movingObstacles: [
{
name: "moving-obstacle-1",
position: { x: .5, y: .4 },
directionAxis: { x: true, y: false },
speed: 1,
range: 4
}
],
staticObstacles: [
{
name: "static-obstacle-1",
centerPosition: { x: 0.2, y: 0.5},
size: { x: 0.4, y: 0.01}
}
]
}
Realtime scene configuration
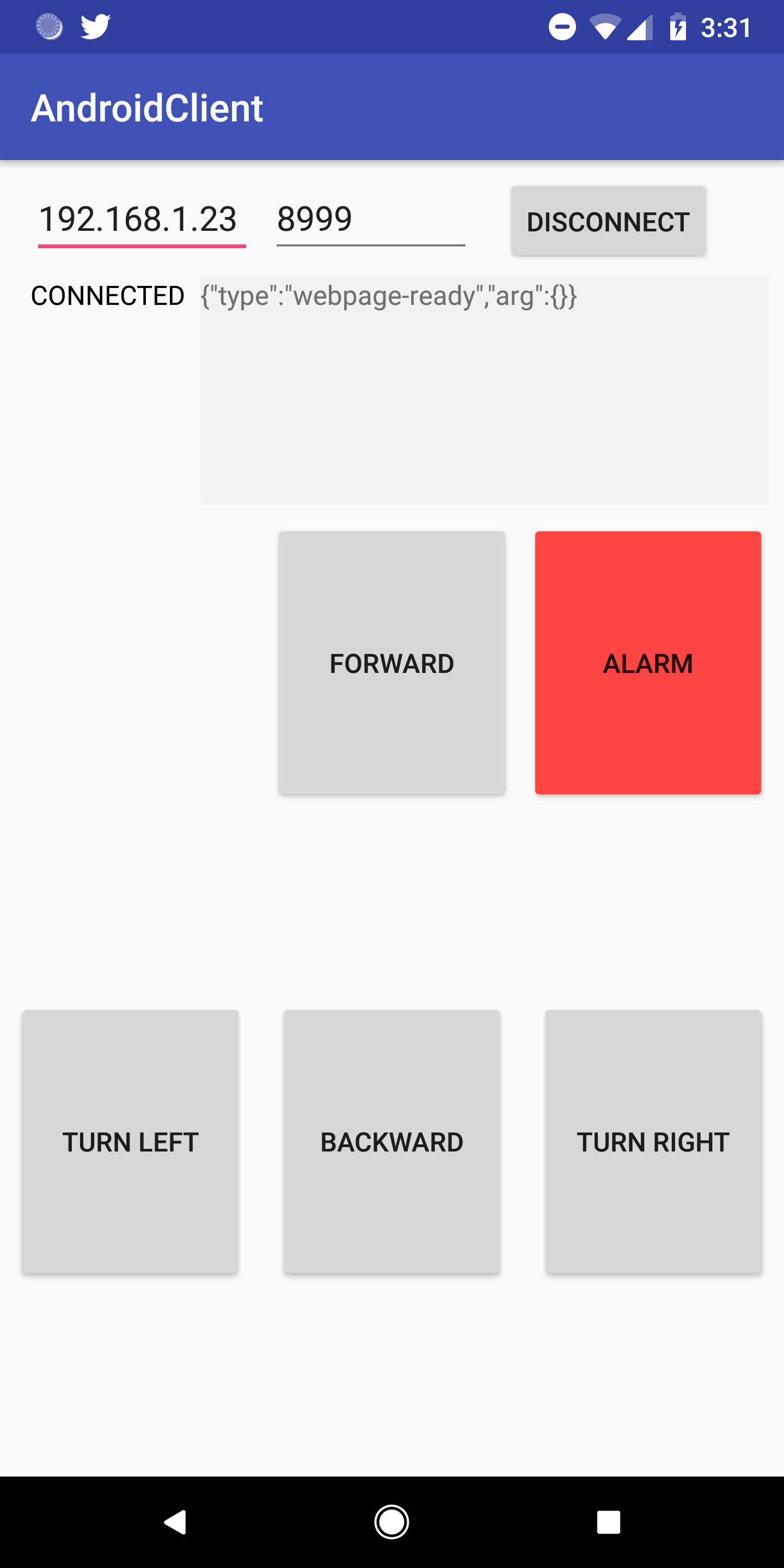
The webapp contains a control window that can be used to update in realtime all the configurations in the config file.
Changes made here won't be permanent. You alwyas need to manually update the values in the config file.
Control the player remotely
It's possible to send and receive messages from the server with a TCP connection.
In order to connect to the server you need to establish a simple TCP connection with it using the server ip an port (the ip is the ip of the machine on which it is running, the port is the one you have decided when starting the server).
IO interface
The server sends and expects specific messages. The messages are simple JSON strings, each string has to start and finish with a ; symbol.
Message format: ;{ json };.
Server output
Messages from the server to the client have this format: ;{ "type": "event-type", "arg": { ... } };.
-
webpage-ready -
{ "type": "webpage-ready, "arg": {} }: This message is sent by the server to its clients when the webapp is ready. If a client connects after the page is ready, it will receive the message anyway. Therefore a client connecting to the server can always expect a webpage-ready message. -
sonar-activated -
{ "type:" "sonar-activated", "arg": { "sonarName": "sonarName", "distance": 1, "axis": "x" } }: This message is sent by the server to its clients when a sonar is sensing the player.sonarNameis the name of the sonar that is sensing the player.distanceis the distance of the player from the sonar.axisis the axis on which the sonar is sensing the player. -
collision -
{ "type": "collision", "arg": { "objectName": "obstacle-1" } }: This message is sent by the server to its clients when the player collides with an obstacle in the scene.objectNameis the name of the object the player is colliding with.
Server input
Messages from the client to the server.
-
moveForward -
{ "type": "moveForward", "arg": 300 }: This message is used to move the player in its current forward direction.argis the duration in seconds of the movement. The duration can be negative, in that case the player will move until in encouters an obstacle. -
moveBackward -
{ "type": "moveBackward", "arg": 300 }: This message is used to move the player in its current backward direction.argis the duration in seconds of the movement. The duration can be negative, in that case the player will move until in encouters an obstacle. -
turnRight -
{ "type": "turnRight", "arg": 300 }: This message is used to rotate the player. The player will always make a 90° rotation.argis the amount of time the 90° rotation will require. -
turnLeft -
{ "type": "turnLeft", "arg": 300 }: This message is used to rotate the player. The player will always make a 90° rotation.argis the amount of time the 90° rotation will require. -
alarm -
{ "type": "alarm" }: This message will stop the player's movement. Rotations aren't stoppable.
Client examples
Two examples of client are provided in this repo, in the ClientExamples folder.
- Android client, it can be used as a reference to write Java/Kotlin/.. clients. The app is written in Kotlin, translating the IO module to other object oriented langues should be trivial. The apk of the app can be downloaded here.
- Node.js client, it can be used as a reference to write other Node.js clients. This client requires two arguments: ip and port of the server.