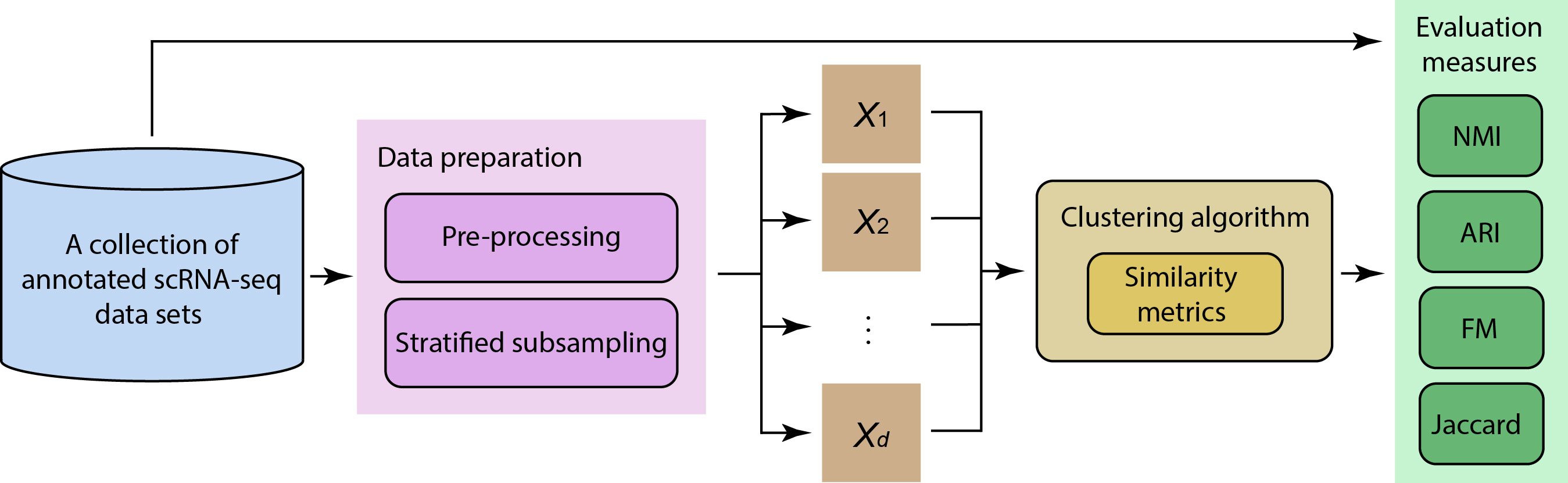
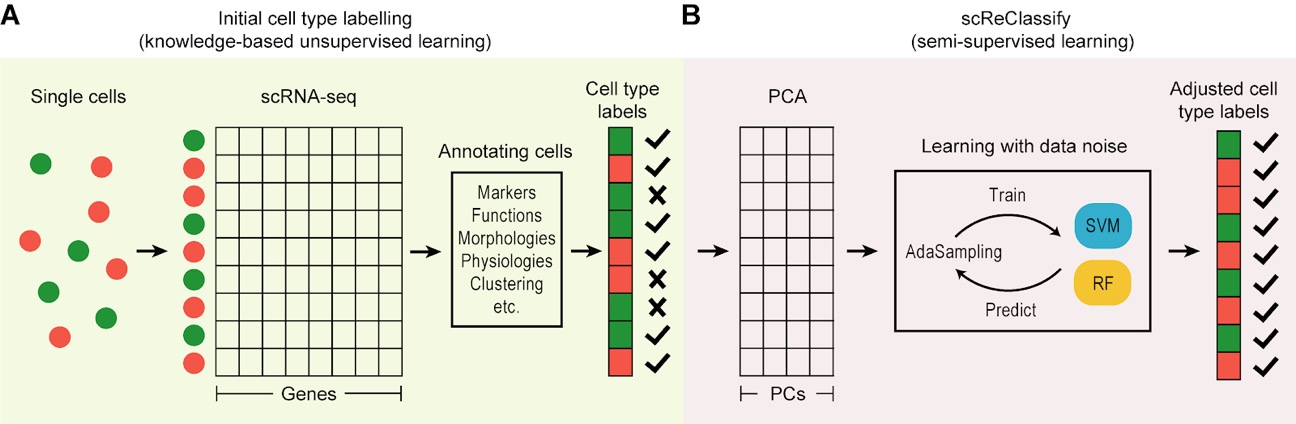
scNet is a R package with collection of single cell RNA-sequencing (scRNA-seq) data analysis functions developed by team of Sydney Precision Bioinformatics Research Group at The University of Sydney.
This package contains useful functions for analysis of scRNA-seq data including clustering, cell type identification, etc.
devtools::install_github("taiyunkim/scNet", build_opts = c("--no-resave-data", "--no-manual"))
library(scNet)For devtools (< 2.0.0),
devtools::install_github("taiyunkim/scNet", build_vignettes = TRUE)
library(scNet)Building the vignette may take some time. If you wish not to create the vignette during installation, try:
devtools::install_github("taiyunkim/scNet")
library(scNet)NOTE: For mac users, the official cran mirror of R tools for OS X and R tools for OS X on r.research.att.com that lists the gfortran binary are out of date. You will need to update gfortran and add the following line FLIBS=-L/usr/local/Cellar/gcc/X.Y.Z/lib/gcc/X (where X.Y.Z is your gcc version) to ~/.R/Makevars prior to this package installation.
Current version of this package is implemented to run SIMLR (Wang et al, 2017) or k-means clustering methods with various similarity metrics.
Available metrics include:
SIMLR - "pearson" correlation, "spearman" corelation and "euclidean" distance.
K-means - "pearson" correlation, "spearman" correlation, "euclidean" distance, "manhattan" distance and "maximum" distance.
data(GSE82187.sample)
mat <- GSE82187
mat <- log2(mat+1)
# set number of clusters (classes defined in colnames)
nCs <- length(table(colnames(mat))To run scClust,
# SIMLR
simlr.result <- scClust(mat, nCs, similarity = "pearson", method = "simlr", seed = 1, cores.ratio = 0)
# K-means
kmeans.result <- scClust(mat, nCs, similarity = "pearson", method = "kmeans", seed = 1, nstart = 10, iter.max = 10)This function allows you to perform clustering with a user specified similarity metrics. The return values of scClust are identical to clustering methods for Kmeans and SIMLR functions.
This section is to compare a set of similarity metrics on clustering methods to benchmark their perfomance accuracy.
To run scClustBench,
# SIMLR
simlr.result <- scClustBench(mat, nCs, method = "simlr", rep = 2, seed = 1, cores = 1, cores.ratio = 0)
# K-means
kmeans.result <- scClustBench(mat, nCs, method = "kmeans", rep = 2, seed = 1, cores = 1, nstart = 10, iter.max = 10)You can evaluate this result with the function evalScClustBench and plot with plotSimlrEval or plotKmeansEval.
For further demonstrations, see:
browseVignettes("scNet")Current version of this package is implemented to run with svm and radomForest classifiers.
data(GSE87795_liver.development.data)
dat <- GSE87795_liver.development.data$data
cellTypes <- GSE87795_liver.development.data$cellTypes
# number of clusters
nCs <- length(table(cellTypes))
# This demo dataset is already pre-processed
dat.processed = datdat.selected = matPCs(dat.processed, 0.7)Here in this example, we will synthetically generate varying degree of noise in sample labels.
lab <- cellTypes
set.seed(1)
noisyCls <- function(dat, rho, cls.truth){
cls.noisy <- cls.truth
names(cls.noisy) <- colnames(dat)
for(i in 1:length(table(cls.noisy))) {
# class label starts from 0
if (i != length(table(cls.noisy))) {
cls.noisy[sample(which(cls.truth == names(table(cls.noisy))[i]), floor(sum(cls.truth == names(table(cls.noisy))[i]) * rho))] <- names(table(cls.noisy))[i+1]
} else {
cls.noisy[sample(which(cls.truth == names(table(cls.noisy))[i]), floor(sum(cls.truth == names(table(cls.noisy))[i]) * rho))] <- names(table(cls.noisy))[1]
}
}
print(sum(cls.truth != cls.noisy))
return(cls.noisy)
}
cls.noisy01 <- noisyCls(dat.selected, rho=0.1, lab)
cls.noisy02 <- noisyCls(dat.selected, rho=0.2, lab)
cls.noisy03 <- noisyCls(dat.selected, rho=0.3, lab)
cls.noisy04 <- noisyCls(dat.selected, rho=0.4, lab)
cls.noisy05 <- noisyCls(dat.selected, rho=0.5, lab)Here, we will only Support Vector machine (svm) as base classifier.
###################################
# SVM
###################################
acc01 <- acc02 <- acc03 <- acc04 <- acc05 <- c()
ari01 <- ari02 <- ari03 <- ari04 <- ari05 <- c()
base <- "svm"
for(j in 1:10) {
final <- multiAdaSampling(dat.selected, cls.noisy01, seed=j, classifier=base, percent=1, L=10)$final
ari01 <- c(ari01, mclust::adjustedRandIndex(lab, final))
acc01 <- c(acc01, bAccuracy(lab, final))
final <- multiAdaSampling(dat.selected, cls.noisy02, seed=j, classifier=base, percent=1, L=10)$final
ari02 <- c(ari02, mclust::adjustedRandIndex(lab, final))
acc02 <- c(acc02, bAccuracy(lab, final))
final <- multiAdaSampling(dat.selected, cls.noisy03, seed=j, classifier=base, percent=1, L=10)$final
ari03 <- c(ari03, mclust::adjustedRandIndex(lab, final))
acc03 <- c(acc03, bAccuracy(lab, final))
final <- multiAdaSampling(dat.selected, cls.noisy04, seed=j, classifier=base, percent=1, L=10)$final
ari04 <- c(ari04, mclust::adjustedRandIndex(lab, final))
acc04 <- c(acc04, bAccuracy(lab, final))
final <- multiAdaSampling(dat.selected, cls.noisy05, seed=j, classifier=base, percent=1, L=10)$final
ari05 <- c(ari05, mclust::adjustedRandIndex(lab, final))
acc05 <- c(acc05, bAccuracy(lab, final))
}
result = list(
acc01 = acc01,
acc02 = acc02,
acc03 = acc03,
acc04 = acc04,
acc05 = acc05,
ari01 = ari01,
ari02 = ari02,
ari03 = ari03,
ari04 = ari04,
ari05 = ari05
)
plot.new()
par(mfrow = c(1,2))
boxplot(acc01, acc02, acc03, acc04, acc05, col="lightblue", main="SVM Acc", ylim=c(0.45, 1))
points(x=1:5, y=c(bAccuracy(lab, cls.noisy01), bAccuracy(lab, cls.noisy02),
bAccuracy(lab, cls.noisy03), bAccuracy(lab, cls.noisy04),
bAccuracy(lab, cls.noisy05)), col="red3", pch=c(2,3,4,5,6), cex=1)
boxplot(ari01, ari02, ari03, ari04, ari05, col="lightblue", main="SVM ARI", ylim=c(0.25, 1))
points(x=1:5, y=c(mclust::adjustedRandIndex(lab, cls.noisy01), mclust::adjustedRandIndex(lab, cls.noisy02),
mclust::adjustedRandIndex(lab, cls.noisy03), mclust::adjustedRandIndex(lab, cls.noisy04),
mclust::adjustedRandIndex(lab, cls.noisy05)), col="red3", pch=c(2,3,4,5,6), cex=1)# PCA procedure
dat.pc <- matPCs(dat.processed, 0.7)
dim(dat.pc)
# run scReClassify
cellTypes.reclassify <- multiAdaSampling(dat.pc, cellTypes, seed = 1, classifier = "svm", percent = 1, L = 10)
# Verification by marker genes
End <- c("KDR", "LYVE1")
# check examples
idx <- which(cellTypes.reclassify != cellTypes)
library(dplyr)
cbind(original=cellTypes[idx], reclassify=cellTypes.reclassify[idx]) %>%
DT::datatable()
c1 <- dat.processed[, which(cellTypes=="Endothelial Cell")]
c2 <- dat.processed[, which(cellTypes=="Erythrocyte")]
c3 <- dat.processed[, which(cellTypes=="Hepatoblast")]
c4 <- dat.processed[, which(cellTypes=="Macrophage")]
c5 <- dat.processed[, which(cellTypes=="Megakaryocyte")]
c6 <- dat.processed[, which(cellTypes=="Mesenchymal Cell")]
cs <- rainbow(length(table(cellTypes)))
# (example 1 E13.5_C20)
#####
par(mfrow=c(1,2))
marker <- End[1]
boxplot(c1[marker,], c2[marker,], c3[marker,], c4[marker,], c5[marker,], c6[marker,], col=cs, main=marker)
points(1, dat.processed[marker, which(colnames(dat.processed) %in% "E13.5_C20")], pch=16, col="red", cex=2)
marker <- End[2]
boxplot(c1[marker,], c2[marker,], c3[marker,], c4[marker,], c5[marker,], c6[marker,], col=cs, main=marker)
points(1, dat.processed[marker, which(colnames(dat.processed) %in% "E13.5_C20")], pch=16, col="red", cex=2)
#####
†: Corresponding author
- scClust: Kim, T., Chen, I., Lin, Y., Wang, A., Yang, J., & Yang, P.† (2018) Impact of similarity metrics on single-cell RNA-seq data clustering. Briefings in Bioinformatics [https://doi.org/10.1093/bib/bby076]
Taiyun Kim, University of Sydney
Dr Pengyi Yang, University of Sydney