Abdelrahman Shaker, Muhammad Maaz, Hanoona Rasheed, Salman Khan, Ming-Hsuan Yang and Fahad Shahbaz Khan
- (Dec 15, 2022): UNETR++ weights are released for Synapse & ACDC datasets.
- (Dec 09, 2022): UNETR++ training and evaluation codes are released.
Abstract: Owing to the success of transformer models, recent works study their applicability in 3D medical segmentation tasks. Within the transformer models, the self-attention mechanism is one of the main building blocks that strives to capture long-range dependencies, compared to the local convolutional-based design. However, the self-attention operation has quadratic complexity which proves to be a computational bottleneck, especially in volumetric medical imaging, where the inputs are 3D with numerous slices. In this paper, we propose a 3D medical image segmentation approach, named UNETR++, that offers both high-quality segmentation masks as well as efficiency in terms of parameters and compute cost. The core of our design is the introduction of a novel efficient paired attention (EPA) block that efficiently learns spatial and channel-wise discriminative features using a pair of inter-dependent branches based on spatial and channel attention. Our spatial attention formulation is efficient having linear complexity with respect to the input sequence length. To enable communication between spatial and channel-focused branches, we share the weights of query and key mapping functions that provide a complimentary benefit (paired attention), while also reducing the overall network parameters. Our extensive evaluations on three benchmarks, Synapse, BTCV and ACDC, reveal the effectiveness of the proposed contributions in terms of both efficiency and accuracy. On Synapse dataset, our UNETR++ sets a new state-of-the-art with a Dice Similarity Score of 87.2%, while being significantly efficient with a reduction of over 71% in terms of both parameters and FLOPs, compared to the best existing method in the literature.
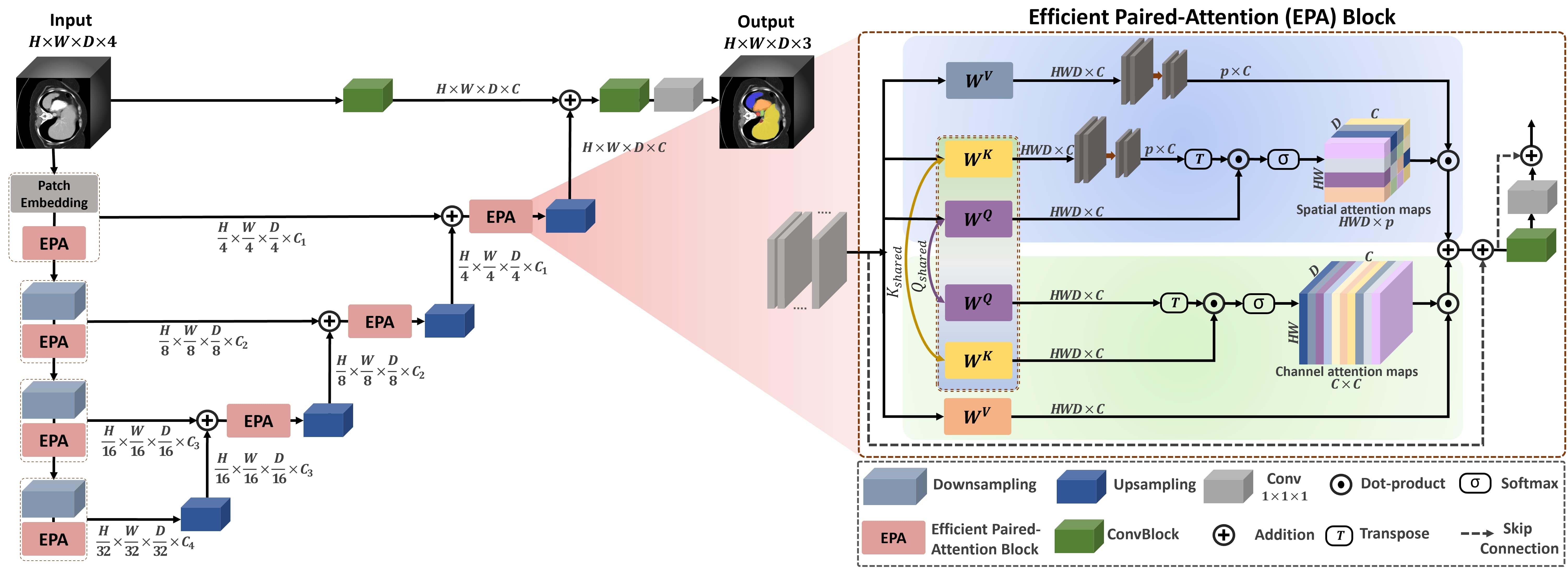
Overview of our UNETR++ approach with hierarchical encoder-decoder structure. The 3D patches are fed to the encoder, whose outputs are then connected to the decoder via skip connections followed by convolutional blocks to produce the final segmentation mask. The focus of our design is the introduction of an efficient paired-attention (EPA) block. Each EPA block performs two tasks using parallel attention modules with shared keys-queries and different value layers to efficiently learn enriched spatial-channel feature representations. As illustrated in the EPA block diagram (on the right), the first (top) attention module aggregates the spatial features by a weighted sum of the projected features in a linear manner to compute the spatial attention maps, while the second (bottom) attention module emphasizes the dependencies in the channels and computes the channel attention maps. Finally, the outputs of the two attention modules are fused and passed to convolutional blocks to enhance the feature representation, leading to better segmentation masks.
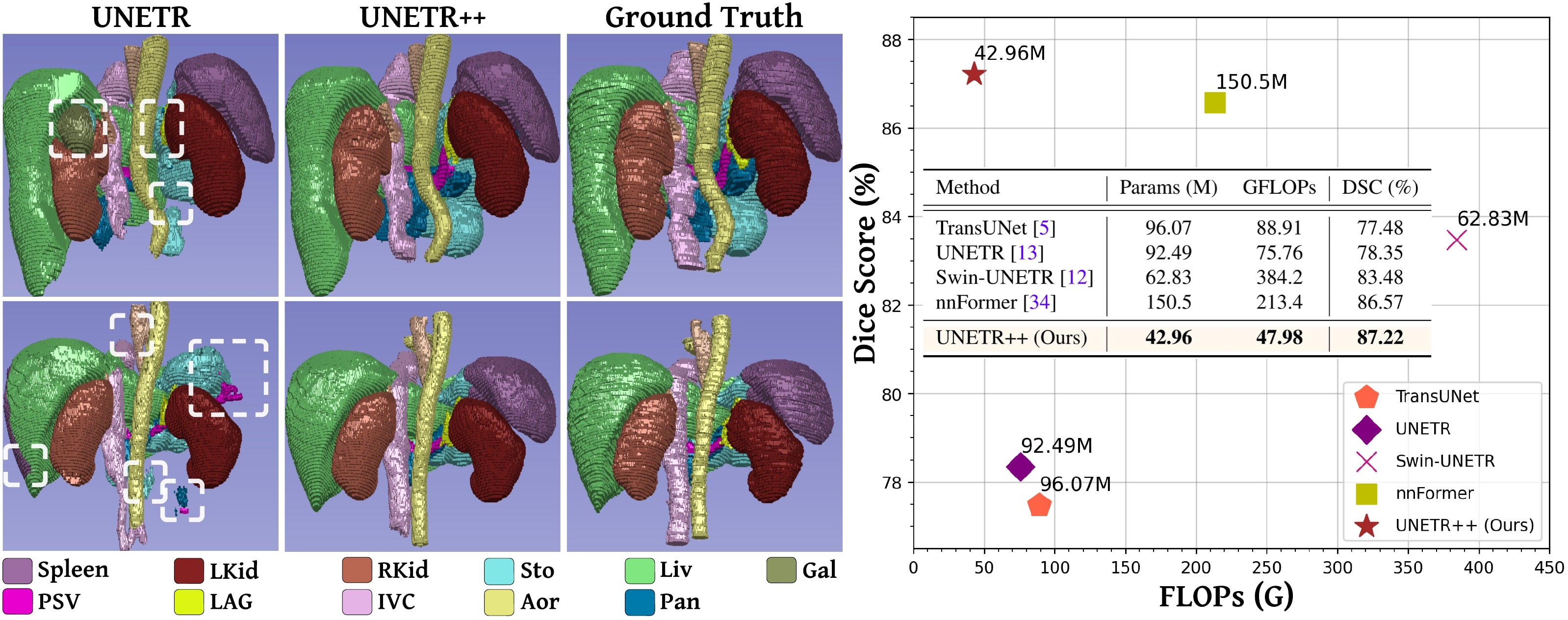
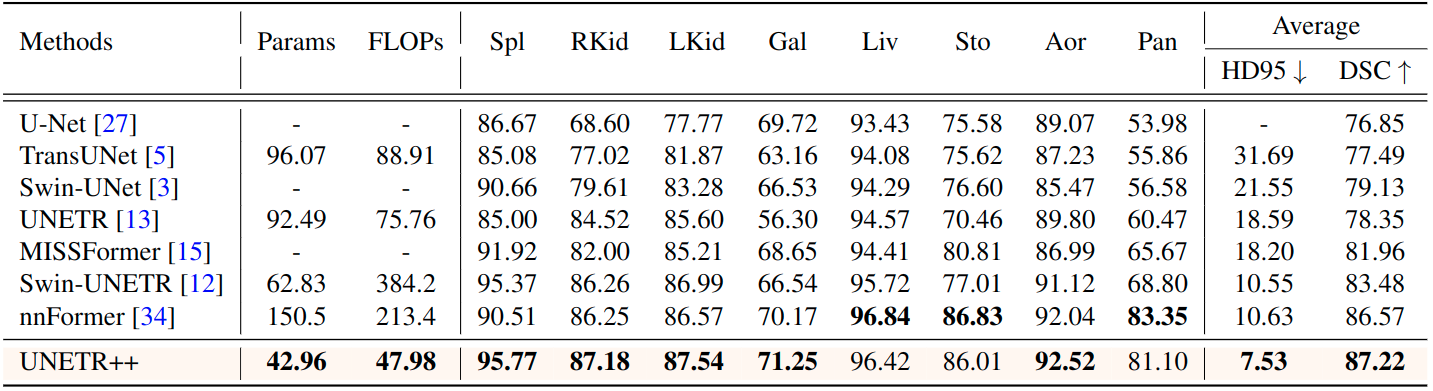
State-of-the-art comparison on the abdominal multi-organ Synapse dataset. We report both the segmentation performance (DSC, HD95) and model complexity (parameters and FLOPs). Our proposed UNETR++ achieves favorable segmentation performance against existing methods, while being considerably reducing the model complexity. Best results are in bold. Abbreviations stand for: Spl: spleen, RKid: right kidney, LKid: left kidney, Gal: gallbladder, Liv: liver, Sto: stomach, Aor: aorta, Pan: pancreas. Best results are in bold.
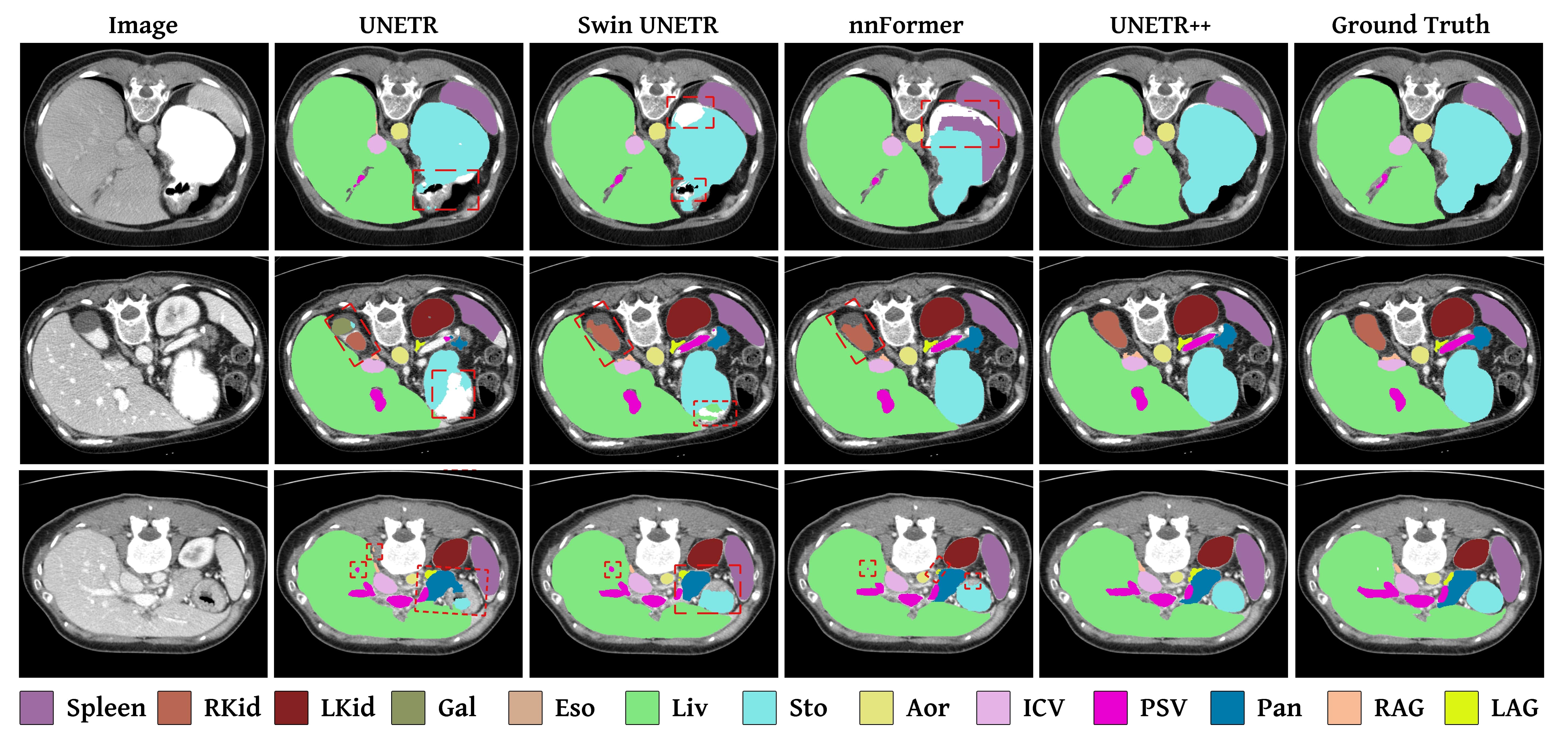
Qualitative comparison on multi-organ segmentation task. Here, we compare our UNETR++ with existing methods: UNETR, Swin UNETR, and nnFormer.
The different abdominal organs are shown in the legend below the examples. Existing methods struggle to correctly segment different organs (marked in red dashed box).
Our UNETR++ achieves promising segmentation performance by accurately segmenting the organs.
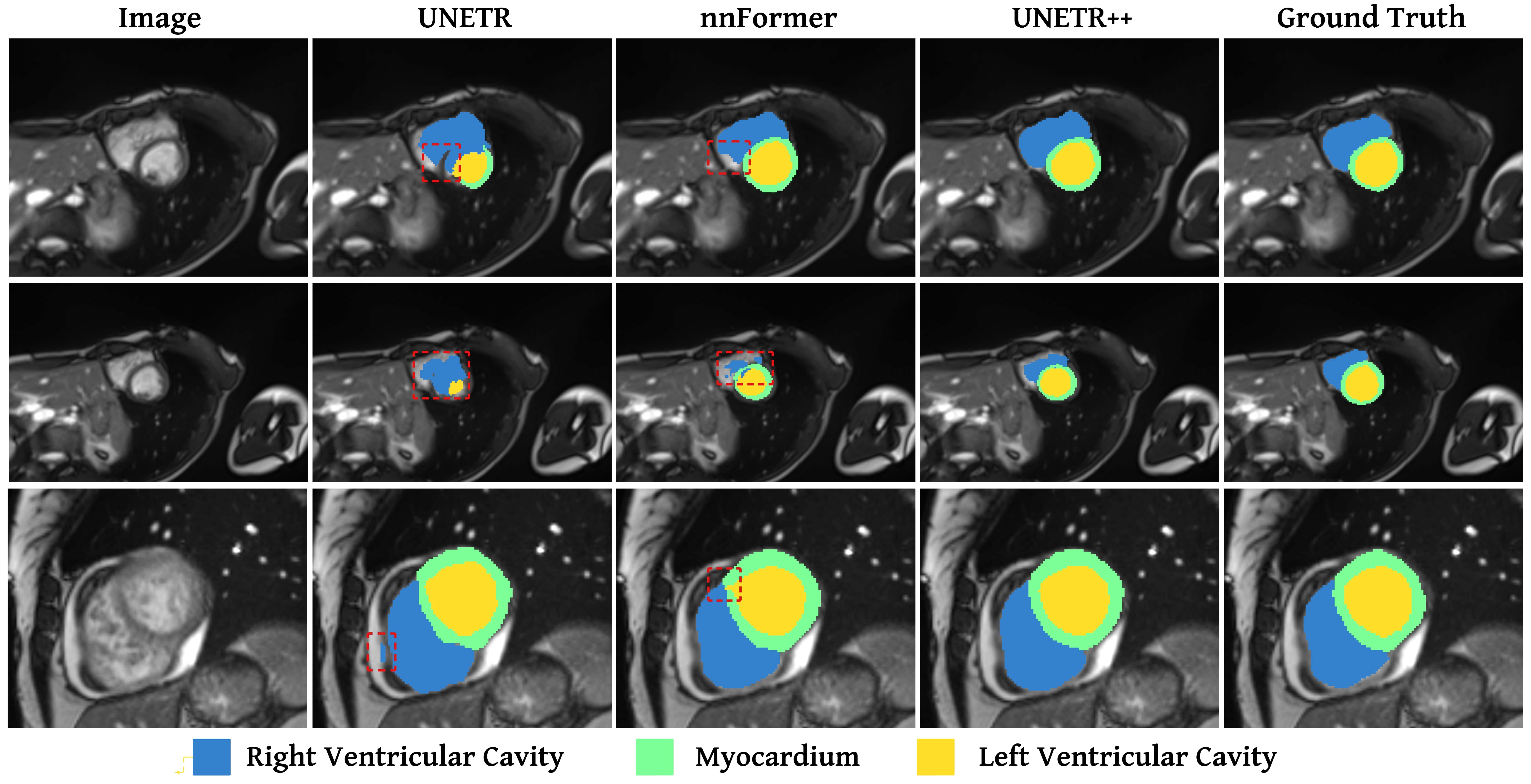
Qualitative comparison on the ACDC dataset. We compare our UNETR++ with existing methods: UNETR and nnFormer. It is noticeable that the existing methods struggle to correctly segment different organs (marked in red dashed box). Our UNETR++ achieves favorable segmentation performance by accurately segmenting the organs. Our UNETR++ achieves promising segmentation performance by accurately segmenting the organs.
The code is tested with PyTorch 1.11.0 and CUDA 11.3. After cloning the repository, follow the below steps for installation,
- Create and activate conda environment
conda create --name unetr_pp python=3.8
conda activate unetr_pp- Install PyTorch and torchvision
pip install torch==1.11.0+cu113 torchvision==0.12.0+cu113 --extra-index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu113- Install other dependencies
pip install -r requirements.txtWe follow the same dataset preprocessing as in nnFormer. The raw dataset folders should be organized as follows:
./DATASET/
├── unetr_pp_raw/
├── unetr_pp_raw_data/
├── Task01_ACDC/
├── imagesTr/
├── imagesTs/
├── labelsTr/
├── labelsTs/
├── dataset.json
├── Task02_Synapse/
├── imagesTr/
├── imagesTs/
├── labelsTr/
├── labelsTs/
├── dataset.json
├── unetr_pp_cropped_data/
Please refer to Setting up the datasets on nnFormer repository for more details. Alternatively, you can download the preprocessed dataset for both Synapse and ACDC from this link and extract it under the project directory.
The following scripts can be used for training our UNETR++ model on Synapse and ACDC datasets,
bash run_training_synapse.sh
bash run_training_acdc.shTo reproduce the results of UNETR++:
1- Download Synapse weights and paste it in the following path
unetr_pp/evaluation/unetr_pp_synapse_checkpoint/unetr_pp/3d_fullres/Task002_Synapse/unetr_pp_trainer_synapse__unetr_pp_Plansv2.1/fold_0/2- Download ACDC weights and paste it in the following path
unetr_pp/evaluation/unetr_pp_acdc_checkpoint/unetr_pp/3d_fullres/Task001_ACDC/unetr_pp_trainer_acdc__unetr_pp_Plansv2.1/fold_0/3- The following scripts can be used for evaluating our UNETR++ model on Synapse and ACDC datasets,
bash run_evaluation_synapse.sh
bash run_evaluation_acdc.shIf you use our work, please consider citing:
@article{Shaker2022UNETR++,
title={UNETR++: Delving into Efficient and Accurate 3D Medical Image Segmentation},
author={Shaker, Abdelrahman and Maaz, Muhammad and Rasheed, Hanoona and Khan, Salman and Yang, Ming-Hsuan and Khan, Fahad Shahbaz},
journal={arXiv:2212.04497},
year={2022},
}Should you have any question, please create an issue on this repository or contact at abdelrahman.youssief@mbzuai.ac.ae.