LDRD Jupyter Repo Summer 2017
Matthew Henderson,
Oliver Evans,
Shreyas Cholia,
Fernando Perez
@ Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
(Readme in progress)
- Execute scientific workflows from Jupyter. The workflow may encompass command line tasks, batch jobs, and notebooks (interactive and non-interactive)
- Monitor and interact with running jobs from Jupyter.
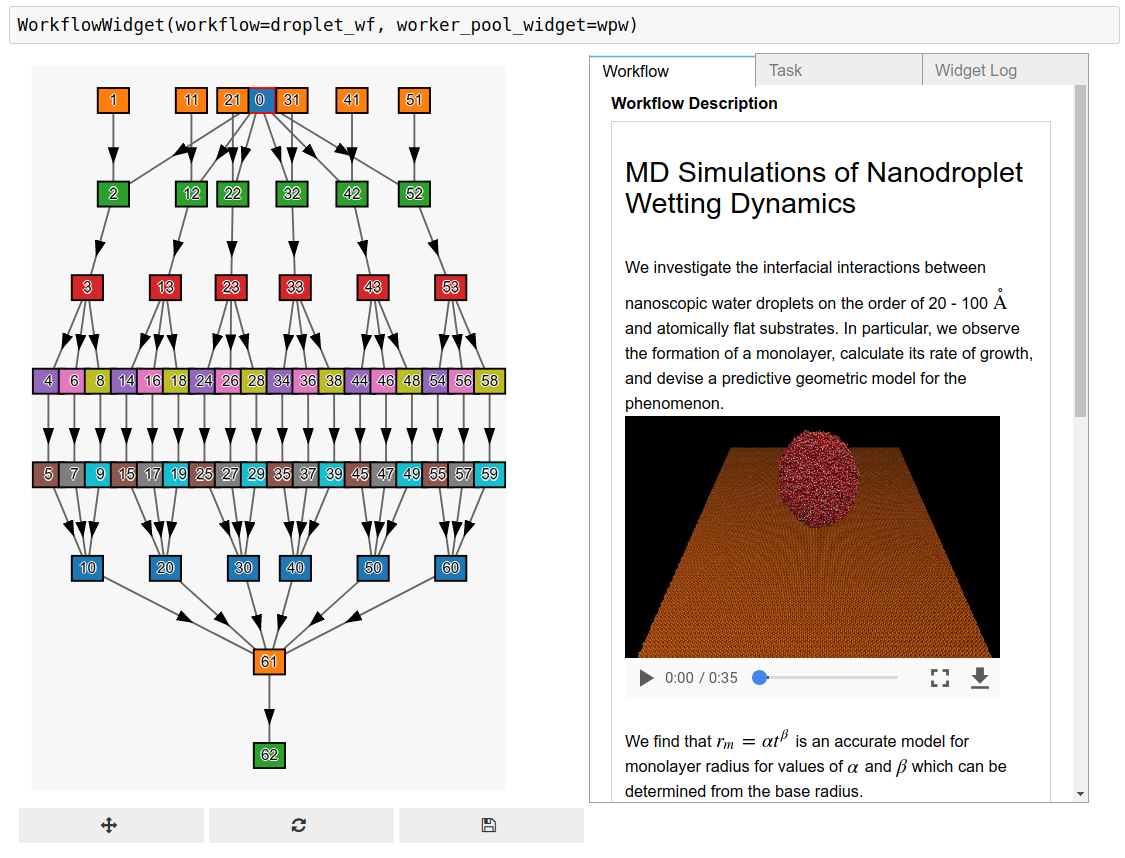
Example workflow
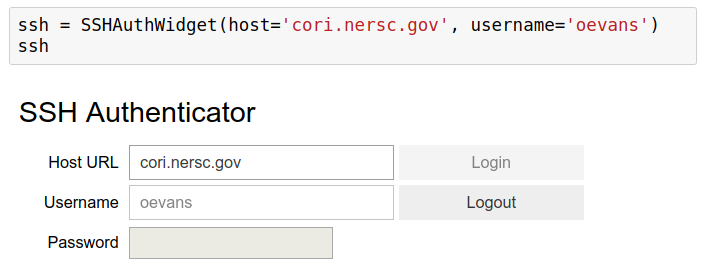
Connect to cluster via SSH
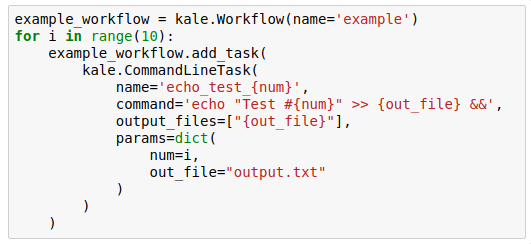
Example workflow definition
Jupyter brings several key features to the world of computational science:
- Exploration
- Narrative
- Interactivity
While these are powerful qualities, Jupyter presently operates at the level of an individual notebook in one language. We seek to harness the power of Jupyter to bring these qualities to full scientific workflows, which often involve many steps across a variety of languages.
Scientists love to explore. But being constrained by computational resources, scientific computing tends to focus on maximizing computational efficiency, while sacrificing human involvement. By combining the raw power of high performance computing resources with the flexibility of Jupyter, we can go from idea to implementation in minutes, even on the biggest problems.
Having Markdown and LaTeX right next to your code allows you to tell the full story of what's going on in a notebook in a clear and cohesive manner. With formulas, images, tables, and even movies embedded right in the document, communicating complex concepts is so much more feasible than through code comments alone. While sharing code is essential for open science and reproducibility, it usually doesn't go very far without context.
By bringing the power of narrative from the individual notebook to full workflows, we hope to make HPC workflows as easy to share effectively as small individual notebooks.
Being able to touch your data and models provides a deeper ability to understand them. The Jupyter widget ecosystem provides a wide range of interactive elements that allow for the visualization and exploration of high dimensional spaces. In HPC systems, interactivity has generally been at the bottom of the food chain. We hope to bridge that gap by providing an easy means by which to examine simulations and analysis codes as they run, and to be able to have interactive pieces of a scientific workflow, where you know that you're going to need human interaction in between computational tasks.
- Freedom to write anything
- Reusable code cells
- Build something, modify it easily, try again, repeat.
- Easy to develop something, then easy to paste it into a python script or continue running it directly from the notebook.
- Markdown, LaTeX, code all together
- Tell the full story all in one place
- Cohesive way to communicate complex ideas
- Widgets - sliders, text input, controllers, etc.
- Allow you to interact directly with data & models
- Visualization & experimentation
- Easily create workflows from the ground up. Start with one notebook and expand to two. Add some C++. etc.
- Rich descriptions for workflows and notebooks
- Communicate full HPC workflows
- Provenance, reproducibility
- Monitor HPC jobs as they're running
- Interactive notebooks as workflow steps
- Modular, widget interface