- Sorting Algorithm: In computer science, a sorting algorithm is an algorithm that puts elements of a list into an order. The most frequently used orders are numerical order and lexicographical order, and either ascending or descending.
- Big O Notation: Big O Notation in Data Structure is used to express algorithmic complexity using algebraic terms. It describes the upper bound of an algorithm's runtime and calculates the time and amount of memory needed to execute the algorithm for aninput value.
At the end of this project, you are expected to be able to explain to anyone, without the help of Google:
- At least four different sorting algorithms
- What is the Big O notation, and how to evaluate the time complexity of an algorithm
- How to select the best sorting algorithm for a given input
- What is a stable sorting algorithm
- Allowed editors:
vi,vim,emacs - All your files will be compiled on
Ubuntu 20.04LTS usinggcc, using the options-Wall-Werror-Wextra-pedantic-std=gnu89 - All your files should end with a new line
- A
README.mdfile, at the root of the folder of the project, is mandatory - Your code should use the Betty style. It will be checked using
betty-style.plandbetty-doc.pl - You are not allowed to use global variables
- No more than 5 functions per file
- Unless specified otherwise, you are not allowed to use the standard library. Any use of functions like
printf,puts, … is totally forbidden. - The prototypes of all your functions should be included in your header file called
sort.hDon’t forget to push your header file - All your header files should be include guarded
- A list/array does not need to be sorted if its size is less than 2.
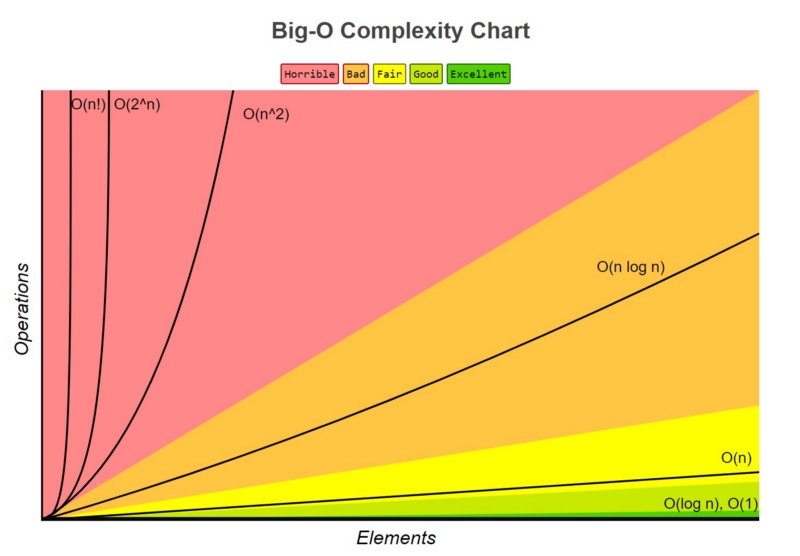
- The following format is expected for big O notation:
O(1)O(n)O(n!)- n squared ->
O(n^2) - log(n) ->
O(log(n)) - n * log(n) ->
O(nlog(n)) - n + k ->
O(n+k)
Please use the "short" notation (don't use constants). Example: O(nk) or O(wn) should be written O(n). If an answer is required within a file, all your answers files must have a newline at the end.
-
0. Bubble sort
- 0-bubble_sort.c: C function that sorts an array of integers in ascending order using the Bubble Sort algorithm.
- Prints the array after each swap.
- 0-O: Text file containing the best, average, and worst case time complexities of the Bubble Sort algorithm, one per line.
-
1. Insertion sort
- 1-insertion_sort_list.c: C function that sorts a
listint_tdoubly-linked list of integers in ascending order using the Insertion Sort algorithm. - Prints the list after each swap.
- 1-O: Text file containing the best, average, and worst case time complexities of the Insertion Sort algorithm, one per line.
- 1-insertion_sort_list.c: C function that sorts a
-
2. Selection sort
- 2-selection_sort.c: C function that sorts an array of integers in ascending order using the Selection Sort algorithm.
- Prints the array after each swap.
- 2-O: Text file containing the best, average, and worst case time complexities of the Selection Sort algorithm, one per line.
-
3. Quick sort
- 3-quick_sort.c: C function that sorts an array of integers in ascending order using the Quick Sort algorithm.
- Implements the Lomuto partition scheme.
- Always uses the last element of the partition being sorted as the pivot.
- Prints the array after each swap.
- 3-O: Text file containing the best, average, and worst case time complexities of the Quick Sort Lomuto Partition scheme algorithm, one per line.
-
4. Shell sort - Knuth Sequence
- 100-shell_sort.c: C function that sorts an array of integers in ascending order using the Shell sort algorithm.
- Implements the Knuth interval sequence.
- Prints the array each time the interval is decreased.
-
5. Cocktail shaker sort
- 101-cocktail_sort_list.c: C function that sorts
a
listint_tdoubly-linked list of integers in ascending order using the Cocktail Shaker Sort algorithm. - Prints the list after each swap.
- 101-O: Text file containing the best, average, and worst case time complexities of the Cocktail Shaker Sort algorithm, one per line.
- 101-cocktail_sort_list.c: C function that sorts
a
-
6. Counting sort
- 102-counting_sort.c: C function that sorts an array of integers in ascending order using the Counting Sort algorithm.
- Assumes that the array will only contain numbers
>= 0. - Prints the counting array after it has been initialized.
- 102-O: Text file containing the best, average, and worst case time complexities of the Counting Sort algorithm, one per line.
-
7. Merge sort
- 103-merge_sort.c: C function that sorts an array of integers in ascending order using the Merge Sort algorithm.
- Implements the
top-downMerge Sort algorithm.- When an array is divided, the size of the left subarray is always less than or equal to the size of the right subarray.
- Always sorts the left subarray before the right one.
- Prints subarrays each time they are merged.
- 103-O: Text file containing the best, average, and worst case time complexities of the Merge Sort algorithm, one per line.
-
8. Heap sort
- 104-heap_sort.c: C function that sorts an array of integers in ascending order using the Heap Sort algorithm.
- Implements the
sift-downHeap Sort algorithm. - Prints the array after each swap.
- 104-O: Text file containing the best, average, and worst case time complexiites of the Heap Sort algorithm, one per line.
-
9. Radix sort
- 105-radix_sort.c: C function that sorts an array of integers in ascending order using the Radix Sort algorithm.
- Implements the Least-Significant-Digit (LSD) Radix Sort algorithm.
- Assumes that the array will only contain numbers
>= 0. - Prints the array for each significant digit increase.
- 105-O: Text file containing the best, average, and worst case time complexities of the Radix Sort algorithm, one per line.
-
10. Bitonic sort
- 106-bitonic_sort.c: C function that sorts an array of integers in ascending order using the Bitonic Sort algorithm.
- Assumes that
sizeis a power of 2 (ie.sizecan be expressed as2^kwherek >= 0). - Prints subarrays each time they are merged.
- 106-O: Text file containing the best, average, and worst case time complexities of the Bitonic Sort algorithm, one per line.
-
11. Quick Sort - Hoare Partition scheme
- 107-quick_sort_hoare.c: C function that sorts an array of integers in ascending order using the Quick Sort algorithm.
- Implements the Hoare partition scheme.
- Always uses the last elemement of the partition being sorted as the pivot.
- Prints the array after each swap.
- 107-O: Text file containing the best, average, and worst case time complexities of the Quick Sort Hoare Partition cheme algorithm, one per line.
-
12. Dealer
- 1000-sort_deck.c: C function that sorts a
deck_node_tdoubly-linked list deck of cards. - Assumes that there are exactly
52elements in the doubly-linked list. - Orders the deck from spades to diamonds and from aces to kings.
- 1000-sort_deck.c: C function that sorts a