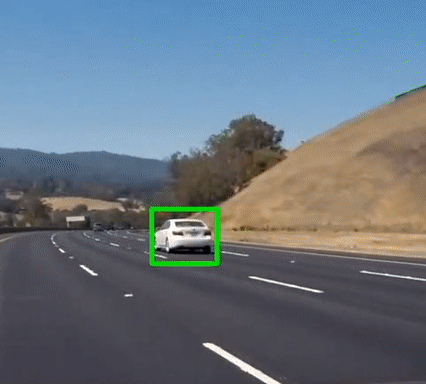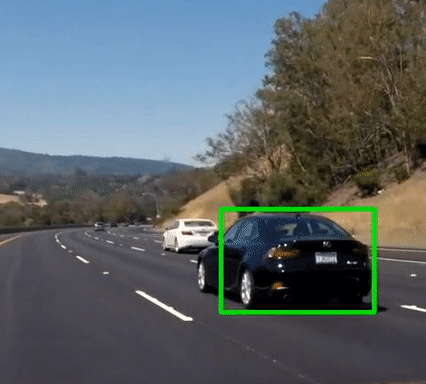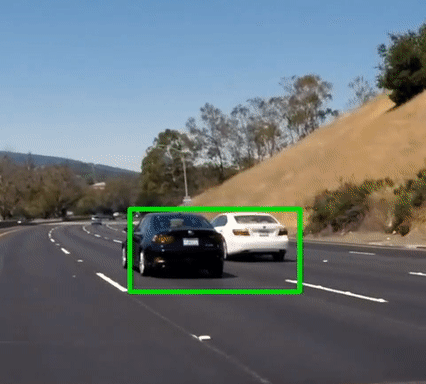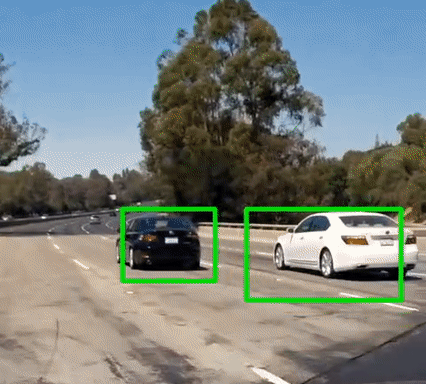
Vehicle Detection
Final output
Histogram of Oriented Gradients (HOG)
Example of vehicle and non vehicle"
I created a function called get_hog_features. After a bit of research, I found that I could use cv2.HOGDescriptor, and provide a feature space to it. For getting the feature space of an image, here's a code snippet
def get_feature_space(img, cspace):
if cspace != 'RGB':
if cspace == 'HLS':
features = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_RGB2HLS)
elif cspace == 'YCrCb':
features = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_RGB2YCrCb)
elif cspace == 'HSV':
features = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_RGB2HSV)
elif cspace == 'LUV':
features = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_RGB2LUV)
elif cspace == 'YUV':
features = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_RGB2YUV)
elif cspace == 'Lab':
features = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_RGB2Lab)
return features
def get_hog_features(img, cspace):
return np.ravel(
cv2.HOGDescriptor((64,64), (16,16), (8,8), (8,8), 9) \
.compute(get_feature_space(img, cspace))
)2. Final choice of HOG parameters.
First, I defined a function extract_features get_hog_features. This function loops through all images, and creates an array of hogs features of each image. This array is then used as the feature array for training. Here's a code snippet:
def extract_features(imgs, cspace='RGB', size = (64,64)):
features = []
for filename in imgs:
image = imread(filename)
if size != (64,64):
image = cv2.resize(image, size)
features.append(
np.ravel(
cv2.HOGDescriptor((64,64), (16,16), (8,8), (8,8), 9) \
.compute(get_feature_space(image, cspace))
)
)
return featuresOf all color spaces, YUV was the best at detecting vehicles. I normalized and split by data into train and test sets.
3. Training a classifier using selected HOG features.
I trained using both an SVM and an MLP. MLP had a higher test accuracy. Here are the results.
| Classifier | Training Accuracy | Test Accuracy |
|---|---|---|
| svm | 1.00 | .950 |
| mlp | 1.00 | .9926 |
###Sliding Window Search
1. Sliding window search, scales, and overlaps.
I did a bit of research to look for and modify an efficient and accurate sliding window algorithm.
- get HOGS features for each window
- only search for vehicle in the bottom half of image
- multiple window scaled, to ensure we detect both closeby and distant images.
- 80% xy overlap, through trial and error
def slide_window(img, x_start_stop=[None, None], y_start_stop=[None, None],
xy_window=(64, 64), xy_overlap=(0.75, 0.75)):
if x_start_stop[0] == None:
x_start_stop[0] = 0
if x_start_stop[1] == None:
x_start_stop[1] = img.shape[1]
if y_start_stop[0] == None:
y_start_stop[0] = 0
if y_start_stop[1] == None:
y_start_stop[1] = img.shape[0]
xspan = x_start_stop[1] - x_start_stop[0]
yspan = y_start_stop[1] - y_start_stop[0]
nx_pix_per_step = np.int(xy_window[0]*(1 - xy_overlap[0]))
ny_pix_per_step = np.int(xy_window[1]*(1 - xy_overlap[1]))
nx_windows = np.int(xspan/nx_pix_per_step)
ny_windows = np.int(yspan/ny_pix_per_step)
window_list = []
for ys in range(ny_windows):
for xs in range(nx_windows):
startx = xs*nx_pix_per_step + x_start_stop[0]
endx = (xs+1)*nx_pix_per_step + x_start_stop[0]
starty = ys*ny_pix_per_step + y_start_stop[0]
endy = (ys+1)*ny_pix_per_step + y_start_stop[0]
window_list.append(((startx, starty), (endx, endy)))
return window_listVideo Implementation
Here's a link to my video result
The MLP has a method called predict_proba which returns the confidence/probability of each class. Only classifications with a score >0.99 where chosen.
Aftermath
This pipleline may fail when trying to deteced motorcycles or bicycles. To fix this, we would have to append our trainining and test sets with images of classified images of bikes, etc and adjust our feature extraction algorithm.