evm-source-verification
Ethereum smart contract source code verification.
Verifies contract source code and saves the output metadata to contracts/<chainId>/<contractAddress>.
With evm-source-verification you can:
- Submit your own smart contracts for verification. See Submitting a contract
- Verify contracts locally. See Commands
- View other verified contracts in
contracts/<chainId>/<contractAddress>
Special thanks to Sourcify and Etherscan.
Table of Contents
- Contract files
- Verified Contracts
- Submitting a contract
- Opening a verified contract in Remix IDE
- Getting Started
- Commands
Contract Files
Contracts require an input.json and configs.json file for verification. input.json specifies the contract's source files and configs.json specifies it's identity.
Contract that are successfully verified will have a metadata.json file containing the verification output.
All contracts in contracts/<chainId>/<contractAddress> are verified.
You can verify your own contracts using the verify command.
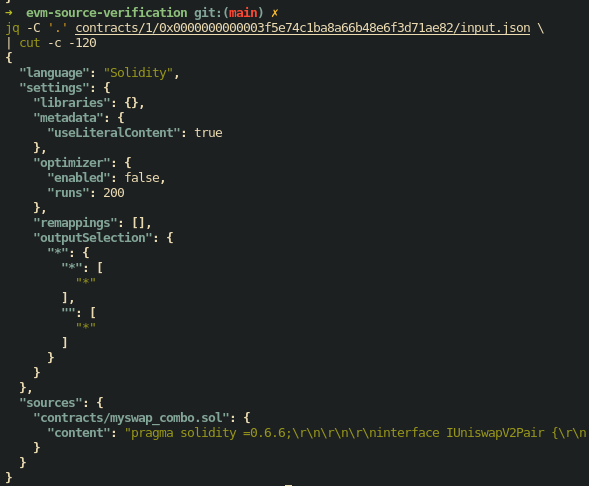
input.json
input.json specifies the source files for compiler input for the contract. It includes the source files and compilation options.
For Solidity, input.json is the Solidity --standard-json input format.
For example:
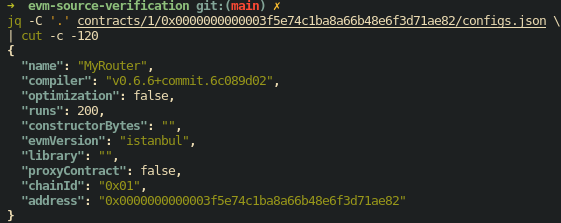
configs.json
configs.json provides the additional information about specifying the contract's identity.
For example:
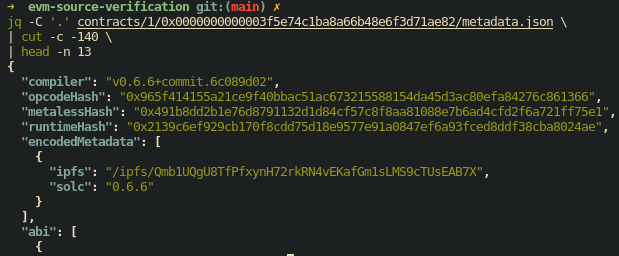
metadata.json
metadata.json provides information on the verified output of the contract. Only contracts that have been verified can have a metadata.json.
metadata.json contains the contract's ABI, opcode hash, metaless hash, runtime hash, encoded metadata, and more.
For example:
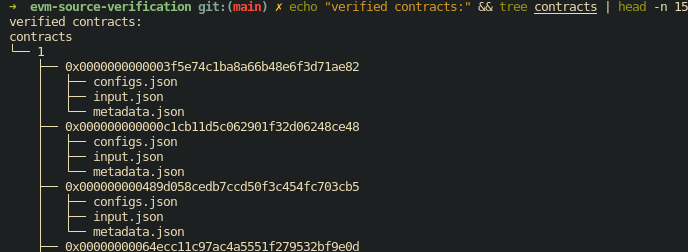
Verified Contracts
Verified contracts are stored under contracts/<chainId>/<contractAddress> with their input.json, configs.json and metadata.json.
The chainId for mainnet is 1.
Submitting a contract
By Pull Request
You can submit your own contract for verification.
- Fork the EthVM/evm-source-verification repository.
- Create a folder
contracts/<chainId>/<contractAddress>/with:configs.json: a JSON file specifying your contractinput.json: the contract's Solidity --standard-json compiler inpun.
- Submit your fork with a pull request to the EthVM/evm-source-verification main brach.
- A Github Action will execute to verify your contract. If successful, your pull request will be closed and a new one will be opened with your contract's verified metadata to be pulled into the main branch.
- Your contract and will then be merged into the main branch!
Using EthVM
TODO
Opening a verified contract in Remix IDE
TODO
Getting Started
The following steps will enable you to develop evm-source-verification or verify your contracts locally.
Clone the Repository
# via ssh
git@github.com:EthVM/evm-source-verification.git
# or via https
https://github.com/EthVM/evm-source-verification.gitSet NodeJS and npm versions
Ensure the correct versions of NodeJS and NPM are installed.
We recommend using Node Version Manager (nvm) to manage your NodeJS versions. You can find the NodeJS version in ./.nvmrc and npm version in ./package.json#engines#npm.
- Install the project's dependencies
# from within the project's root directory
npm installBuild the project
This will build the project into the dist folder
# from within the project's root directory
npm run build:prodYou can now run develop on the project, execute Commands, and run tests.
Commands
evm-source-verification exposes cli commands to assist in contract verification.
To execute commands, first download and build the project. For steps, see Getting Started
Verify
The verify command takes takes directories with input.json and configs.json files and compiles and verifies them against the blockchain.
For additional information on the verify command, use node dist/bin.js verify --help.
bin.js verify
compile source file and verify the code on evm based chain
Positionals:
--chainId Verify contracts of this chainId. [string]
--address Verify the contract with this address and the given chainId.
Requires --chainId. [string]
--dirs Verify contracts within the provided directories. Expects a
new-line separated string of directories. Reads from stdin if
--dirs=- [string]
--skip Skip contracts that have already been verified i.e. contracts
that have metadata [boolean] [default: false]
--save Save metadata of successfully verified contracts
[boolean] [default: false]
--failFast Exit on first error [boolean] [default: false]
--jump Jump past this many contracts before starting to verify[number]
--concurrency Number of contracts to verify in parallel. Defaults to the
number of CPUs. [number] [default: 16]Below are some examples using the verify command:
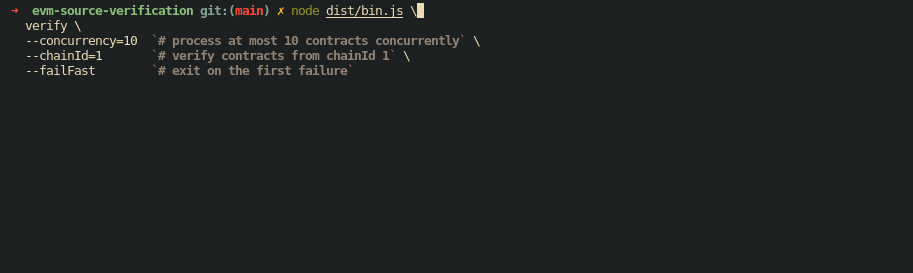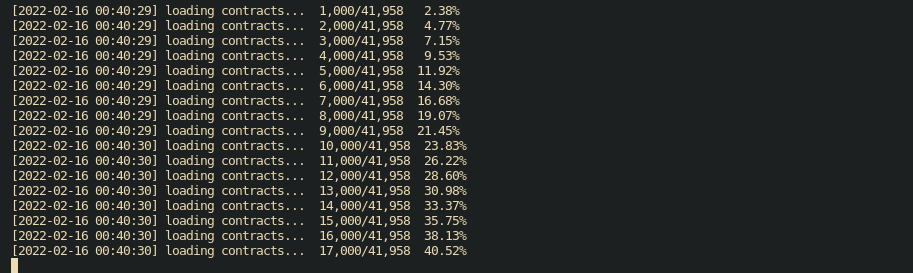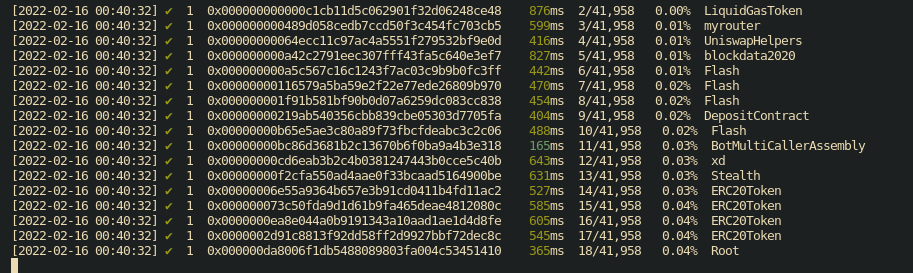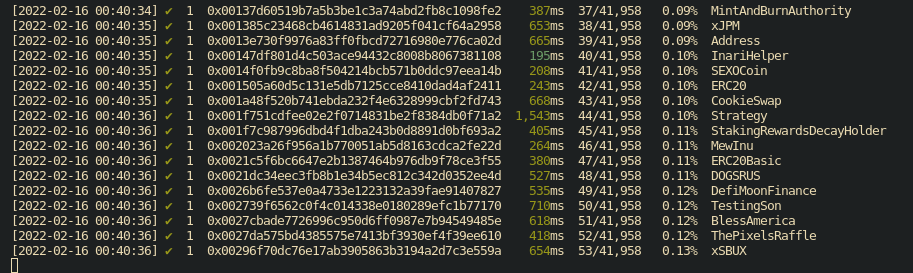
Verify mainnet contracts
node dist/bin.js \
verify \
--concurrency=10 `# process at most 10 contracts concurrently` \
--chainId=1 `# verify contracts from chainId 1` \
--failFast `# exit on the first failure`Verify contract in a directory
# verify a single contract
node dist/bin.js \
verify \
--dirs=~/my-contract `# the contract's directory` \
--save `# save verified metadata to the contract's directory`Verify contracts in many directories
# verify contracts from the piped directories
find ~/my-contracts/ -mindepth 1 -maxdepth 1 -type d \
| head -n 1000 `# first 1000 contracts` \
| node dist/bin.js \
verify \
--concurrency=1 `# process one contract at a time` \
--dirs=- `# read directories from stdin` \
--save `# save verified metadata to contract directories`Summarise
The summarise command collects hashes, used compilers, and addresses from all verified addresses and saves them to the ./summary/<chainId>/<output type>.
- summary/
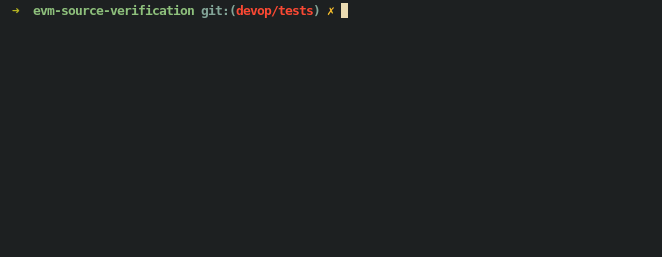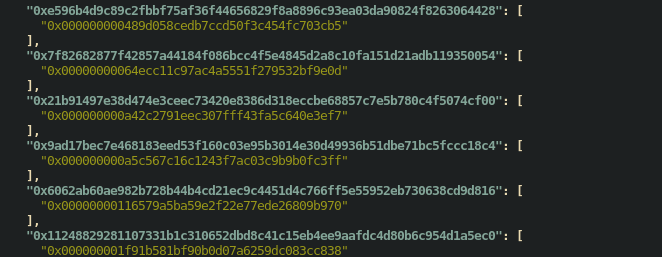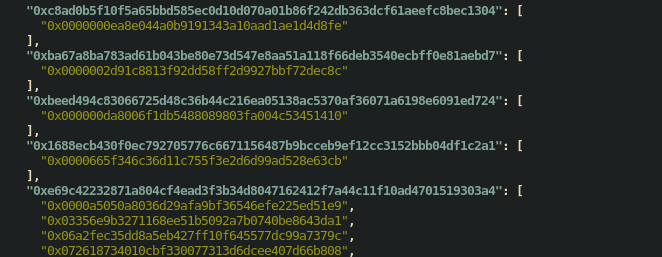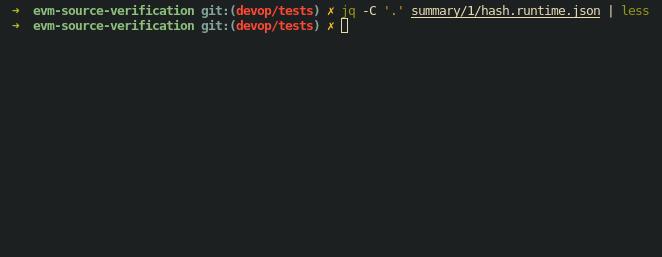
<chainId>/hash.runtime.json: JSON object whose keys are the runtime hashes of contracts and values are an array of contracts with that runtime hash. - summary/
<chainId>/hash.opcodes.json: JSON object whose keys are the opcode hashes of contracts and values are an array of contracts with that opcode hash. - summary/
<chainId>/hash.metaless.json: JSON object whose keys are the metaless hashes of contracts and values are an array of contracts with that metaless hash. - summary/
<chainId>/verified.json: JSON array of with all the verified addresses. - summary/
<chainId>/compilres.json: JSON object whose keys are the metaless hashes of contracts and values are arrays of contracts with that metaless hash.
bin.js summarise
rebuild the summary of all verified contractsPull Contracts
Used by CI to verify contracts added in a pull request Submitting contracts by pull request for more.
Rebuild Tests
Cleans and rebuilds contracts used for testing.