Backend Server of the Nesteo nesting box management application for ringing associations. - More Information
Useful links:
Please make sure you're running an up to date Linux distribution and have Docker as well as Docker-Compose installed:
To get up and running, please clone this repository to your pc and open the repository directory with a terminal:
git clone https://github.com/Nesteo/Nesteo-Server.git
cd Nesteo-Server
Now use the sample.env as a template to create a .env-file to configure docker-compose:
cp sample.env .env
nano .env
Please replace the database password and exit the editor with Crtl+O and Ctrl+X.
After that create a file at /root/nesteo/server/appsettings.json based on Nesteo.Server/appsettings-sample.json:
mkdir -p /root/nesteo/server/
cp Nesteo.Server/appsettings-sample.json /root/nesteo/server/appsettings.json
nano /root/nesteo/server/appsettings.json
Please replace the database password here, too.
Now execute the following commands to setup your database:
docker-compose up -d nesteo-db
<< Wait a few seconds while the database starts >>
docker-compose exec -T nesteo-db mysql -u root --password=DATABASE-PASSWORD -e 'CREATE DATABASE nesteo COLLATE utf8_general_ci;'
cat database.sql | docker-compose exec -T nesteo-db mysql -u root --password=DATABASE-PASSWORD nesteo
Now you can start all required services:
docker-compose up -d
In case you want to check the server logs, run docker-compose logs -f.
The backend is now available under http://localhost. See below for some useful URLs.
You can take all services down using:
docker-compose down
Before starting, take everything down:
docker-compose down
Now pull the latest changes:
git pull
docker-compose pull
And update your database:
docker-compose up -d nesteo-db
<< Wait a few seconds while the database starts >>
cat database.sql | docker-compose exec -T nesteo-db mysql -u root --password=DATABASE-PASSWORD nesteo
Now you can start the server as normal:
docker-compose up -d
The server, when started, serves different services at different URLs:
- / - Management website
- /api/v1 - The main API endpoint
- /api-docs - Fancy API documentation page
- /swagger - Swagger API testing tool
- /swagger/v1/swagger.json - Swagger API specification
- /health - Endpoint for health checks
When clicking Authorize in the API testing tool, you'll be asked for username and password. These have been set to the following values on first server start:
Username: Admin
Password: Admin123
You can use the following command to fill the database with generated sample data:
docker-compose exec nesteo-server /app/Nesteo.Server.SampleDataGenerator
This server is built on top of the open source .Net Core 3.0. At the time of writing, version 3.0 is going to be released in a few days. Please follow the installation instructions on the .Net Core downloads page to install the 3.0 SDK on your development machine.
To start developing on the server codebase, start with setting up your database as described above but skip the step for importing database.sql.
Instead of saving your modified appsettings.json to /root/nesteo/... put it into the project directory next to appsettings-sample.json.
Also don't run docker-compose up -d because it's sufficient when the database is running.
Now open Nesteo.Server.sln in the Jetbrains Rider IDE, add a Run configuration for the Nesteo.Server project and specify an environment variable called ASPNETCORE_ENVIRONMENT with Development as value.
Finally you should be able to startup the server and start hacking.
You need the dotnet ef cli tool to create database migrations and update your database (see below). Use this command to install it:
dotnet tool install --global dotnet-ef --version 3.0.0-*
When you've done changes to the database structure you'll have to create a database migration to update your database and enable other users to update their's, too.
Execute this command in the solution root directory to list existing migrations:
dotnet ef --project=Nesteo.Server migrations list
To create a new migration:
dotnet ef --project=Nesteo.Server migrations add TitleOfMyChange
dotnet ef --project=Nesteo.Server migrations script --idempotent --output database.sql
Now update your own database:
dotnet ef --project=Nesteo.Server database update
In case you want to drop your database to clear all data, execute dotnet ef --project=Nesteo.Server database drop before doing the update.
Now you can start the server and work with the updated database structure.
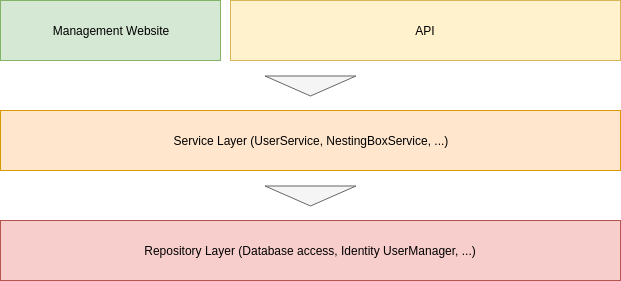
The main application code is split up into three layers:
- Management Website & API: This layer primarily consists of the API Controllers and the management website Pages. It only communicates with the interfaces of the service layer (for example
IUserService) and doesn't know anything about implementation details of the service classes or the repository layer. The code inside of this layer should be focused only on simple user interface or API tasks like handling authorization or returning appropriate HTTP responses. Don't implement any application logic here, because it will not be well testable. - Service Layer: All services are abstractly defined by interfaces and implemented by a "service class" that communicates with the repository layer to retrieve data or do data updates. The service layer contains the main application logic and doesn't know anything about the above layer. It uses a mapping library (
AutoMapper) to map between "entity" types (from the service layer) and normal "model" types that are returned to the above layer. - Repository Layer: This is anything that's directly related with databases and data storage. It's mostly implemented by a few entity classes and all the data management logic that's provided by Entity Framework Core. The user management, that's implemented using the inbuilt Identity framework, is also located here. This layer doesn't know anything about the above layers.
The dependencies of all implementation classes inside of these layers are resolved using a powerful Dependency Injection framework. This makes e.g. service implementations interchangeable and greatly improves code testability.