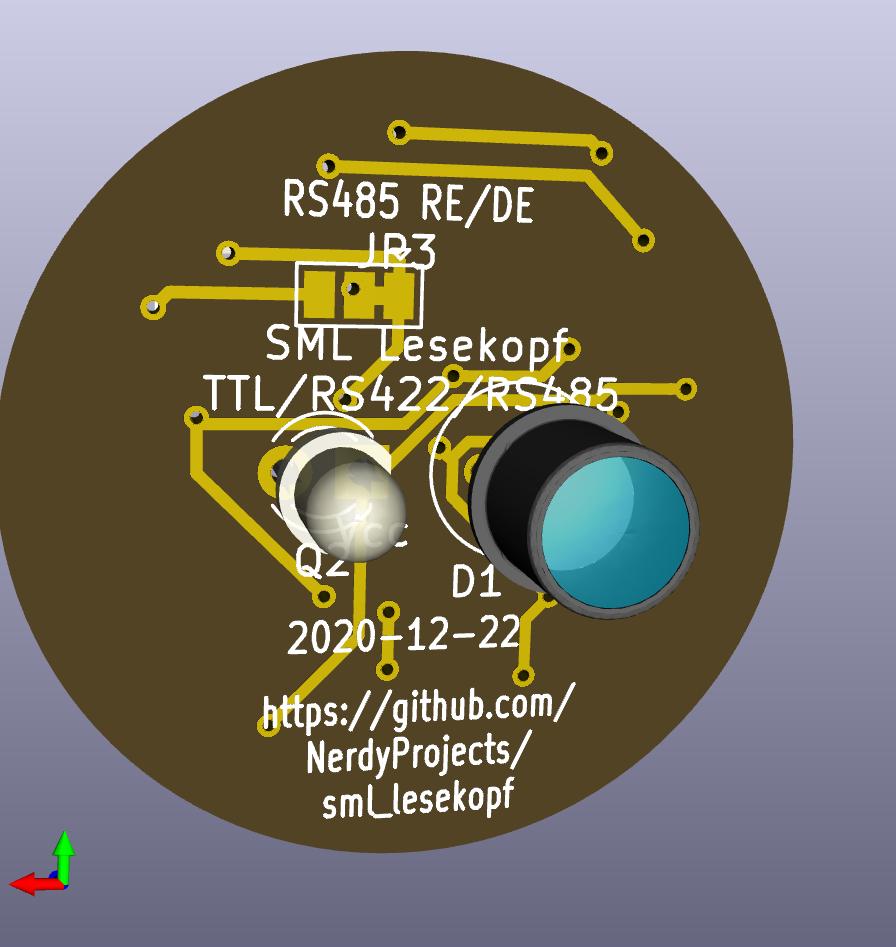
sml_lesekopf
This project implements the SML infrared read/write interface from Volkszaehler and adds generic RS422/RS485 capabilities.
The PCB is of 27mm diameter and meant to be used with a 27/16/5mm magnet.
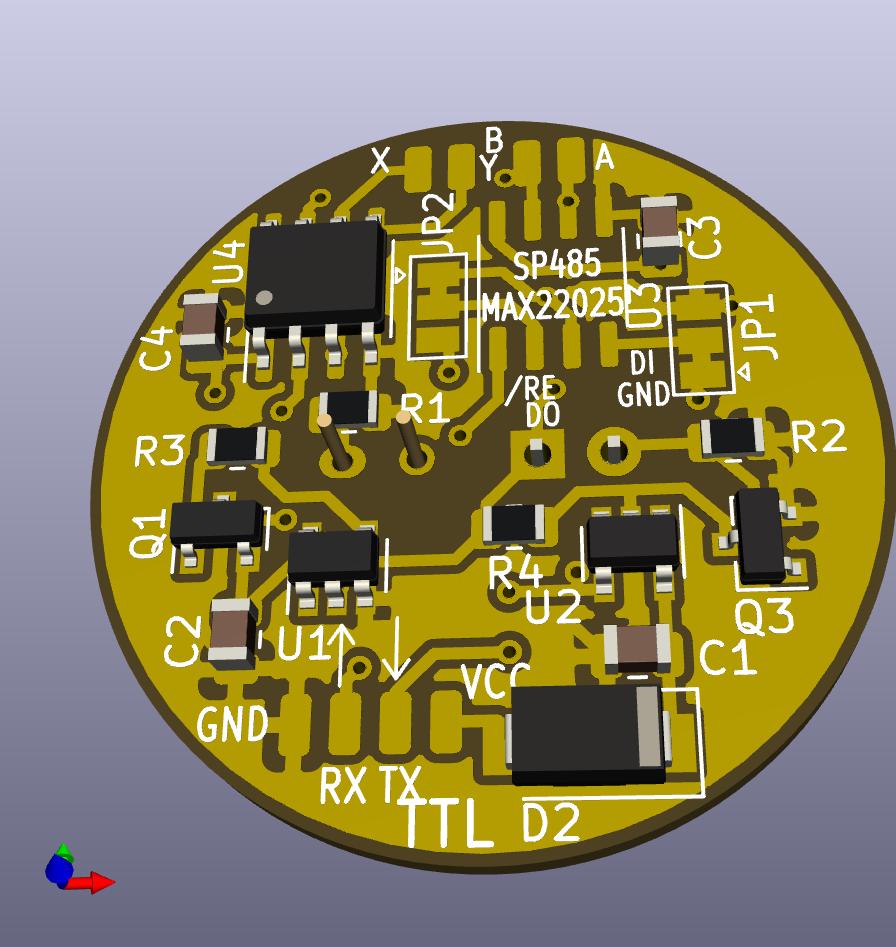
Building
The PCB can be used in different operating modes. Each of those can be used independently, just add all the variants together you want to have
Basic (reverse polarity protection)
- D2: Any SMA (or smaller) shottky diode (e.g. BAT46); if in doubt, also a silicon diode like 1N4148 is appropriate but has higher voltage drop
Infrared receiver
To read out smartmeters that send data themselves, you only need the infrared receiver part consisting of:
- C1: 1µF 0805 ceramic capacitor
- R2: 13k Ohms 0805 resistor
- R4: 13k Ohms 0805 resistor
- Q3: Any SOT23 NPN transistor, e.g. BC817
- Q2: SFH309 FA infrared phototransistor (860nm). If in doubt, take the -4 version.
- U2: 74LVC1G17 schmitt trigger buffer (can be omitted when the device has schmitt trigger inputs and you use short cables; bridge pins 2 and 4 in that case)
This outputs the received signal as a TTL signal on the TX pin. Feel free to use any supply voltage between 2 and 5.5V, your output signal will have the same voltage levels.
Infrared transmitter
Some smartmeters require a signal sent to them to start transmitting data, so you need transmission capabilities:
- C2: 1µF 0805 ceramic capacitor
- R1: 180 Ohms 0805 resistor
- D1: SFH487 or any other ~860 nm infrared LED with a viewing angle of 30..60 degrees (e.g. Reichelt L-7104SF4BT KB)
- Q1: Any SOT23 PNP transistor, e.g. BC807
- R3: 13k Ohms 0805 resisotr
- U1: 74LVC1G17 schmitt trigger buffer (can be omitted when you use short cables, bridge pins 2 and 4 in that case)
Alternatively, you can use a 74LVC1G14 (Inverter) and leave out R3/Q1 (bridging R3 and bridging pins 1 and 3 of Q1)
RS485/RS422 infrared receiver/bus transmitter only (single device on the bus)
To transmit the signal over wires longer than a few metres (up to 200m or even further), you can put a RS422/RS485 bus transceiver for U3. There is many options regarding your supply voltage and the bus voltage levels. In any case, you also need to supply C3. A transceiver with a lower maximum data rate has better EMI performance as well as better performance with long, unterminated bus wires (e.g. the SP3072E) Use the A/B connection for data transfer, RX/TX stay unconnected in this case.
- C3: 1µF 0805 ceramic capacitor
- U3: SN75176BD (5V, ~50mA standby current); SP485CNL(5V, low power); ADM485 (5V, 2 mA standby current); MAX485CSA (5V, low power); SP3072E(3,3V, <2 mA)
RS422 bidirectional
RS422/RS485 full duplex interfaces transmit and receive at the same time. You need to connect 2 wires for TX/RX each and the supply voltage.
- C4: 1µF 0805 ceramic capacitor
- U4: DS89C21(5V, <10 mA); SP3071E(3,3V, <2 mA)
RS485 auto direction
A MAX22025 auto direction RS485 transceiver can be used to use a half duplex, bidirectional RS485 transfer using only 4 wires in total. Change both solder jumpers JP1 and JP2 on the top side of the PCB.
RS485/RS422 PC interface
By changing the solder jumper JP3 (on the back side of the PCB), the half duplex RS485 transceiver U3 is put into receive mode. Placing the components D2, C3 and U3 allows the PCB to be used as a TTL to RS485 (receive only) interface. Input pin "RX/J3/DI" of the TTL side is then used as the TTL TX pin towards a computer or another device.
Case
In the 3d folder, there is a printable case where you can put the magnet and the PCB in. The PCBs might fight very tightly, I suggest printing it at 102% scale.