The projects presents Android CI tutorial covering Docker and GitLab
Gitlab scripts - .gitlab-ci.yml All the scripts are stored in the folder GitLabCIScripts
Goal: To create a Docker image that contains the Android SDK command line tools installed in it.
-
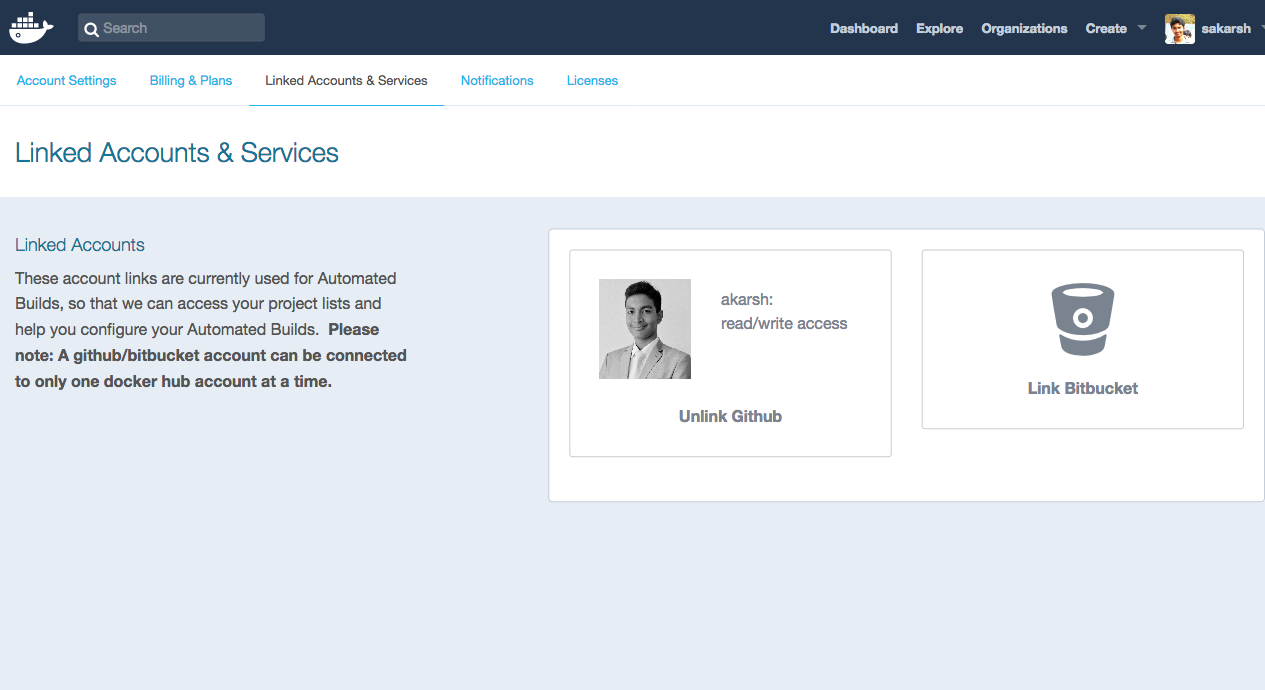
Create a account in Docker. Then go to Docker hub.
-
Next, link your Github or Bitbucket account to your Docker account.
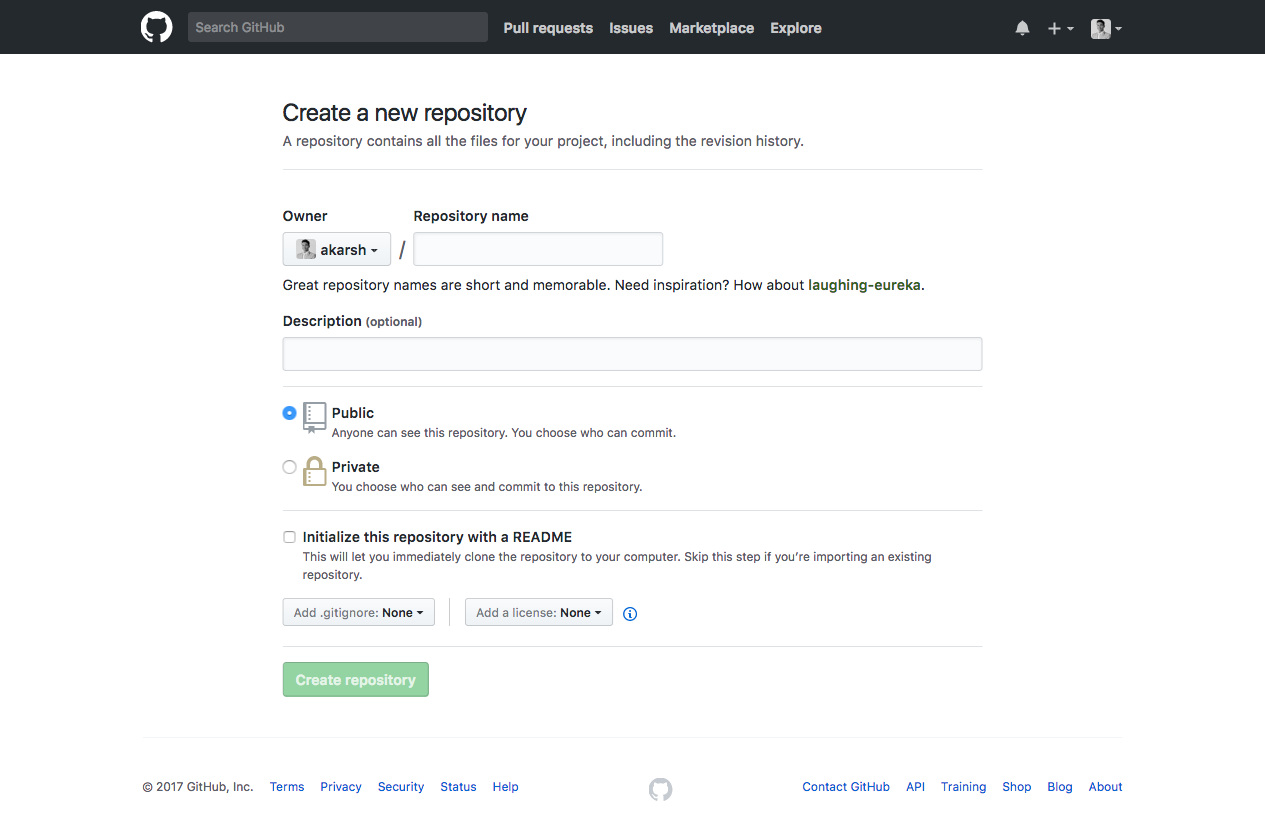
- Then, go to Github or Bitbucket to create a new repository that contains Docker file. Because, Docker currently supports only Github and Bitbucket for creating automation builds.
-
After creating a repository in Github or Bitbucket. Create a new file. Name the file as
Dockerfilewithout any extensions.
Here is the code for Dockerfile
#
# GitLab CI: Android
# Version: 1.0.0
#
# https://hub.docker.com/r/sakarsh/gitlab-ci-android-akarsh-seggemu/
#
FROM ubuntu:18.04
MAINTAINER Akarsh Seggemu <sakarshkumar@gmail.com>
ENV VERSION_SDK_TOOLS "3859397"
ENV ANDROID_HOME "/sdk"
ENV PATH "$PATH:${ANDROID_HOME}/tools"
ENV DEBIAN_FRONTEND noninteractive
RUN apt-get -qq update && \
apt-get install -qqy --no-install-recommends \
bzip2 \
curl \
git-core \
html2text \
openjdk-8-jdk \
libc6-i386 \
lib32stdc++6 \
lib32gcc1 \
lib32ncurses5 \
lib32z1 \
unzip \
&& rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/* /tmp/* /var/tmp/*
RUN rm -f /etc/ssl/certs/java/cacerts; \
/var/lib/dpkg/info/ca-certificates-java.postinst configure
RUN curl -s https://dl.google.com/android/repository/sdk-tools-linux-${VERSION_SDK_TOOLS}.zip > /sdk.zip && \
unzip /sdk.zip -d /sdk && \
rm -v /sdk.zip
RUN mkdir -p $ANDROID_HOME/licenses/ \
&& echo "8933bad161af4178b1185d1a37fbf41ea5269c55\nd56f5187479451eabf01fb78af6dfcb131a6481e" > $ANDROID_HOME/licenses/android-sdk-license \
&& echo "84831b9409646a918e30573bab4c9c91346d8abd" > $ANDROID_HOME/licenses/android-sdk-preview-license
ADD packages.txt /sdk
RUN mkdir -p /root/.android && \
touch /root/.android/repositories.cfg && \
${ANDROID_HOME}/tools/bin/sdkmanager --update
RUN while read -r package; do PACKAGES="${PACKAGES}${package} "; done < /sdk/packages.txt && \
${ANDROID_HOME}/tools/bin/sdkmanager ${PACKAGES}
The Dockerfile code contains the following,
-
The base OS image is defined in FROM
-
The maintainer of the docker in MAINTAINER
-
The Android SDK tools is update after evey new release. With every new update the version number in the download link is updated. Having a variable ENV VERSION_SDK_TOOLS for the version number reduces the effort in long run for maintaining the Dockerfile.
-
ENV ANDROID_HOME is used for storing sdk folder name.
-
ENV PATH is used for storing the android sdk tools path.
-
DEBIAN_FRONTEND is used for installing the packages in Docker.
-
RUN apt-get -qq update and the consecutive commands are used to update the packages and install packages.
-
RUN rm -f /etc/ssl/certs/java/cacerts; is used for java ceritifcate.
-
RUN curl -s https://dl.google.com/android/repository/sdk-tools-linux-${VERSION_SDK_TOOLS}.zip for downloading the Android SDK tools
-
RUN mkdir -p $ANDROID_HOME/licenses/ is used for creating a directory to accept Android SDK license during installation of Android SDK Tools.
-
ADD packages.txt /sdk this command adds the file packages.txt ti the sdk folder.
-
The packages.txt contains the additional packages such as Google play services to be installed.
-
Create a new file in the repository and name it as
packages.txtand add the following code,
add-ons;addon-google_apis-google-24 build-tools;26.0.2 extras;android;m2repository extras;google;m2repository extras;google;google_play_services extras;m2repository;com;android;support;constraint; constraint-layout;1.0.2 extras;m2repository;com;android;support;constraint; constraint-layout-solver;1.0.2 platform-tools platforms;android-26
-
-
RUN mkdir -p /root/.android && is used to create a folder and the subsequent commands are used to update the Android SDK.
-
RUN while read -r package; do PACKAGES="${PACKAGES}${package} is used to run the packages.txt file. Next, the packages are downloaded and installed.
-
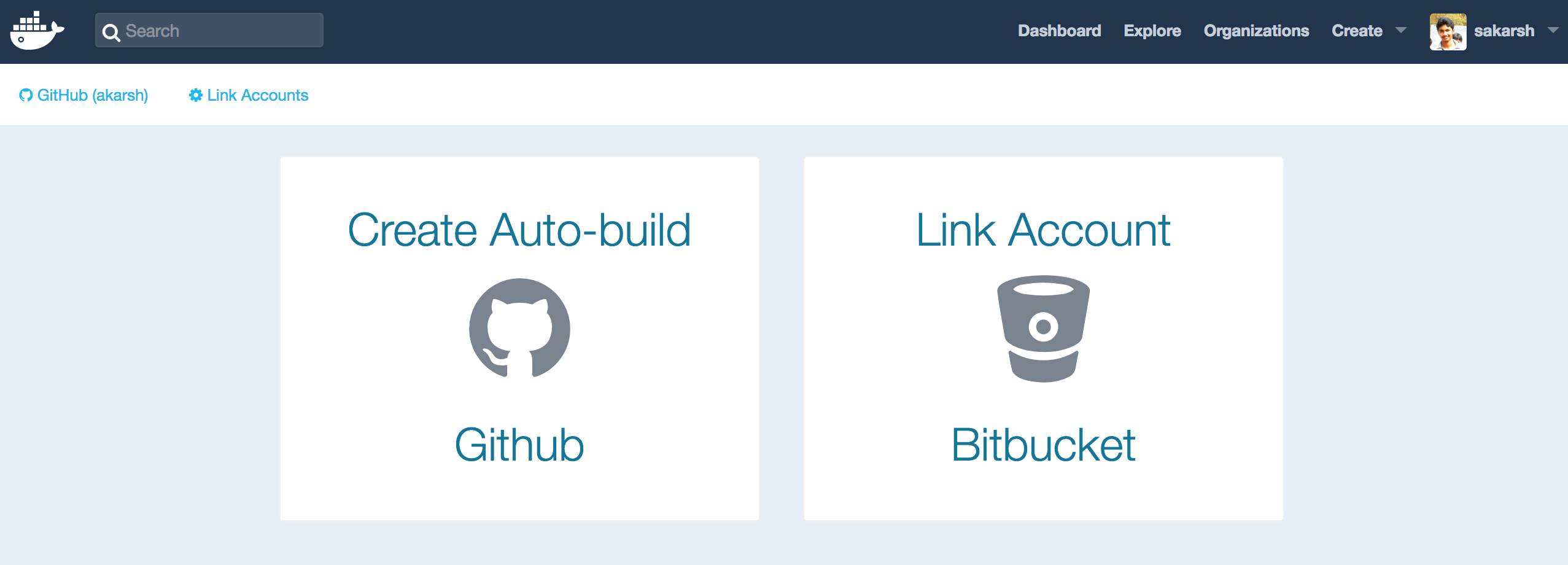
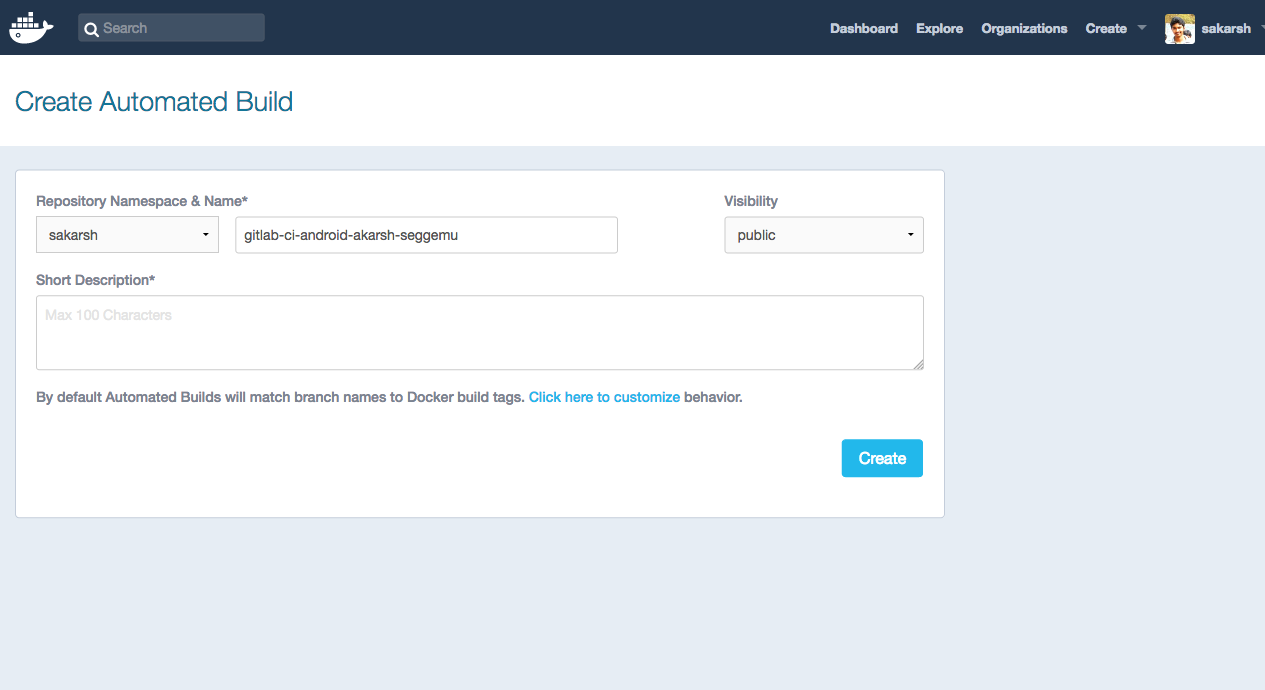
After the creating the Dockerfile and adding the mentioned code above. Next, go to Docker hub and click on create a automated build
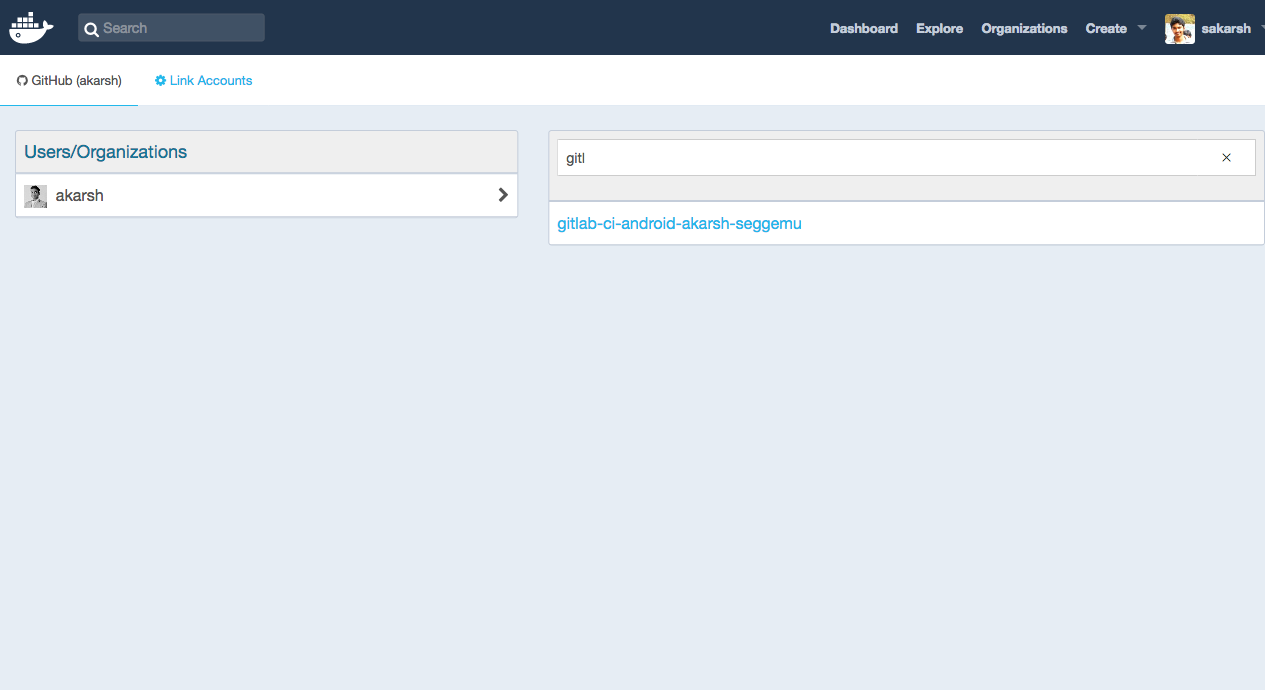
- Select the linked Github or bitbucket account to access the Github or Bitbucket repository.
- Select the Github or Bitbucket repository.
- Add a short description for the automated build and click on create.
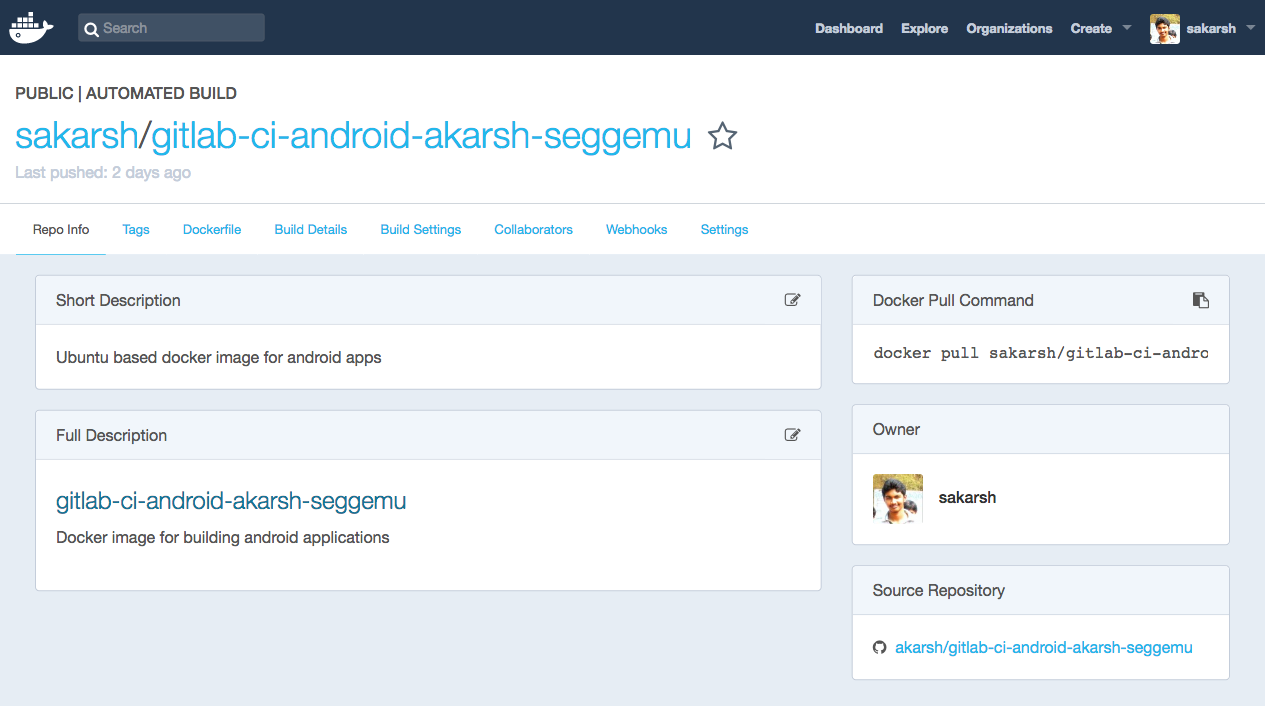
- Build page will be shown after completing the creation of automated build.
- Next, click on Build Settings tab and click on trigger to trigger a build job.
- When the build job is completed. Click on Build Details to see the status of the build. Success indicated the build is successfully built the docker image. Now, the Docker image is ready.
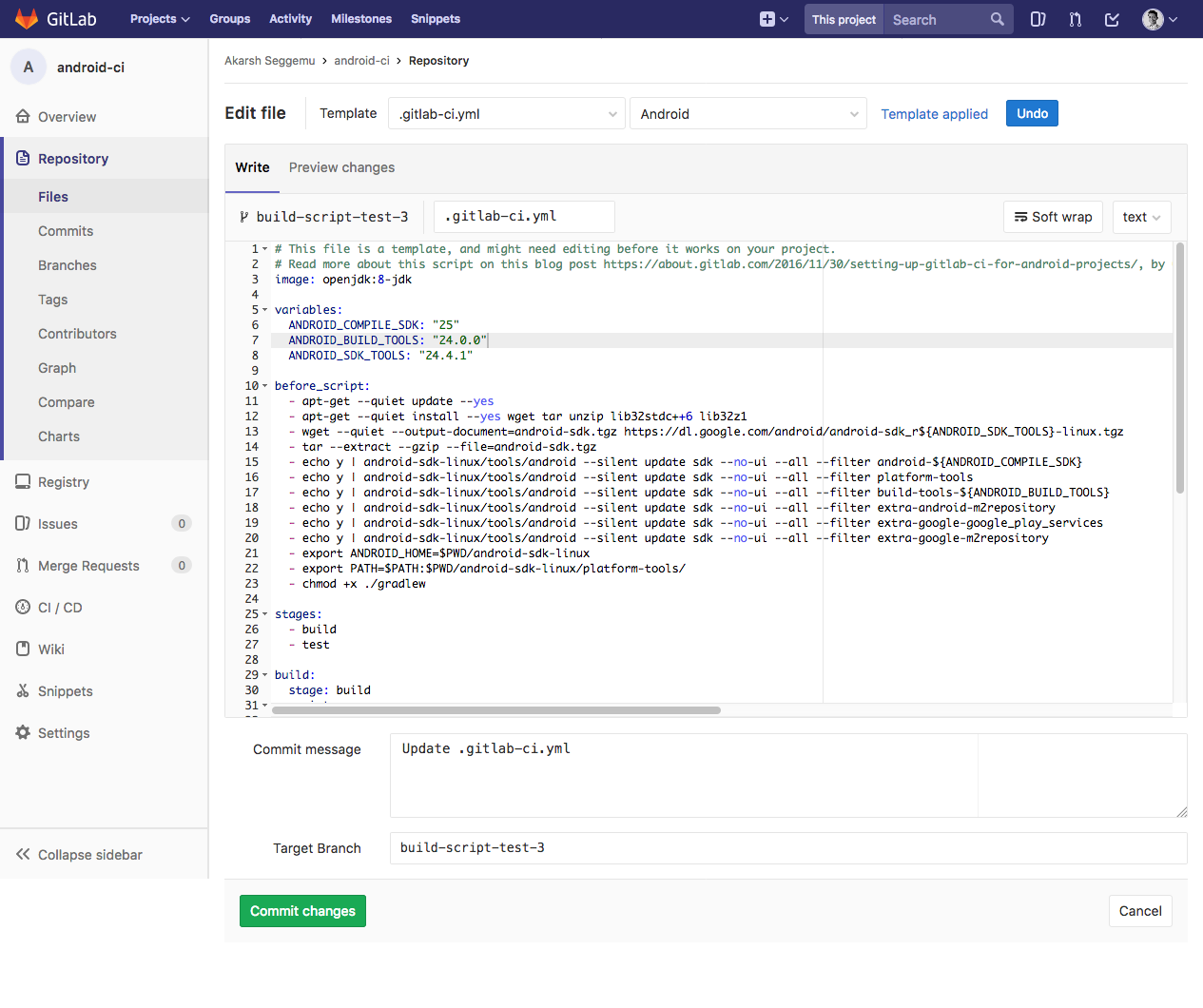
Follow the instructions on GitLab Documentation about Creatin .gitlab-ci.yml file.
A standard template file for Android application development provided by GitLab as follows,
# This file is a template, and might need editing before it works on your project.
# Read more about this script on this blog post https://about.gitlab.com/2016/11/30/setting-up-gitlab-ci-for-android-projects/, by Greyson Parrelli
image: openjdk:8-jdk
variables:
ANDROID_COMPILE_SDK: "25"
ANDROID_BUILD_TOOLS: "24.0.0"
ANDROID_SDK_TOOLS: "24.4.1"
before_script:
- apt-get --quiet update --yes
- apt-get --quiet install --yes wget tar unzip lib32stdc++6 lib32z1
- wget --quiet --output-document=android-sdk.tgz https://dl.google.com/android/android-sdk_r${ANDROID_SDK_TOOLS}-linux.tgz
- tar --extract --gzip --file=android-sdk.tgz
- echo y | android-sdk-linux/tools/android --silent update sdk --no-ui --all --filter android-${ANDROID_COMPILE_SDK}
- echo y | android-sdk-linux/tools/android --silent update sdk --no-ui --all --filter platform-tools
- echo y | android-sdk-linux/tools/android --silent update sdk --no-ui --all --filter build-tools-${ANDROID_BUILD_TOOLS}
- echo y | android-sdk-linux/tools/android --silent update sdk --no-ui --all --filter extra-android-m2repository
- echo y | android-sdk-linux/tools/android --silent update sdk --no-ui --all --filter extra-google-google_play_services
- echo y | android-sdk-linux/tools/android --silent update sdk --no-ui --all --filter extra-google-m2repository
- export ANDROID_HOME=$PWD/android-sdk-linux
- export PATH=$PATH:$PWD/android-sdk-linux/platform-tools/
- chmod +x ./gradlew
stages:
- build
- test
build:
stage: build
script:
- ./gradlew assembleDebug
artifacts:
paths:
- app/build/outputs/
unitTests:
stage: test
script:
- ./gradlew test
functionalTests:
stage: test
script:
- wget --quiet --output-document=android-wait-for-emulator https://raw.githubusercontent.com/travis-ci/travis-cookbooks/0f497eb71291b52a703143c5cd63a217c8766dc9/community-cookbooks/android-sdk/files/default/android-wait-for-emulator
- chmod +x android-wait-for-emulator
- echo y | android-sdk-linux/tools/android --silent update sdk --no-ui --all --filter sys-img-x86-google_apis-${ANDROID_COMPILE_SDK}
- echo no | android-sdk-linux/tools/android create avd -n test -t android-${ANDROID_COMPILE_SDK} --abi google_apis/x86
- android-sdk-linux/tools/emulator64-x86 -avd test -no-window -no-audio &
- ./android-wait-for-emulator
- adb shell input keyevent 82
- ./gradlew cAT
In the template, openjdk:8-jdk Docker image is used and all the Android SDK tools and packages are installed during the build job. They are listed in before_script.
Instead of downloading and installing Android SDK tools and packages every time during the build job. We can use the Docker image built above in the .gitLab-ci.yml file.
The Docker image created above can be used as follows,
sakarsh/gitlab-ci-android-akarsh-seggemu:latest
By specifying the Docker hub username/Docker image. The :latest is used to get the latest build from Docker.
Using the Docker image mentioned above in .gitlab-ci.yml as follows,
image: sakarsh/gitlab-ci-android-akarsh-seggemu:latest
before_script:
- export GRADLE_USER_HOME=`pwd`/.gradle
- mkdir -p $GRADLE_USER_HOME
- chmod +x ./gradlew
stages:
- build
- test
build:
stage: build
script:
- ./gradlew assembleDebug
artifacts:
paths:
- app/build/outputs/
unitTests:
stage: test
script:
- ./gradlew test
functionalTests:
stage: test
script:
- wget --quiet --output-document=android-wait-for-emulator https://raw.githubusercontent.com/travis-ci/travis-cookbooks/0f497eb71291b52a703143c5cd63a217c8766dc9/community-cookbooks/android-sdk/files/default/android-wait-for-emulator
- chmod +x android-wait-for-emulator
- echo y | android-sdk-linux/tools/android --silent update sdk --no-ui --all --filter sys-img-x86-google_apis-${ANDROID_COMPILE_SDK}
- echo no | android-sdk-linux/tools/android create avd -n test -t android-${ANDROID_COMPILE_SDK} --abi google_apis/x86
- android-sdk-linux/tools/emulator64-x86 -avd test -no-window -no-audio &
- ./android-wait-for-emulator
- adb shell input keyevent 82
- ./gradlew cAT
Using an already configured Docker image with Android SDK tools and packages decreases the total build time.
- dockerfiles - contains various Dockerfiles.