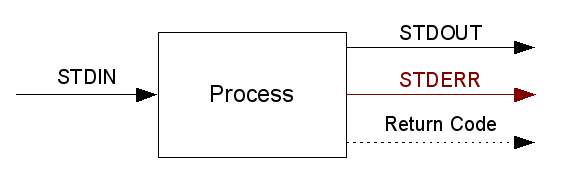
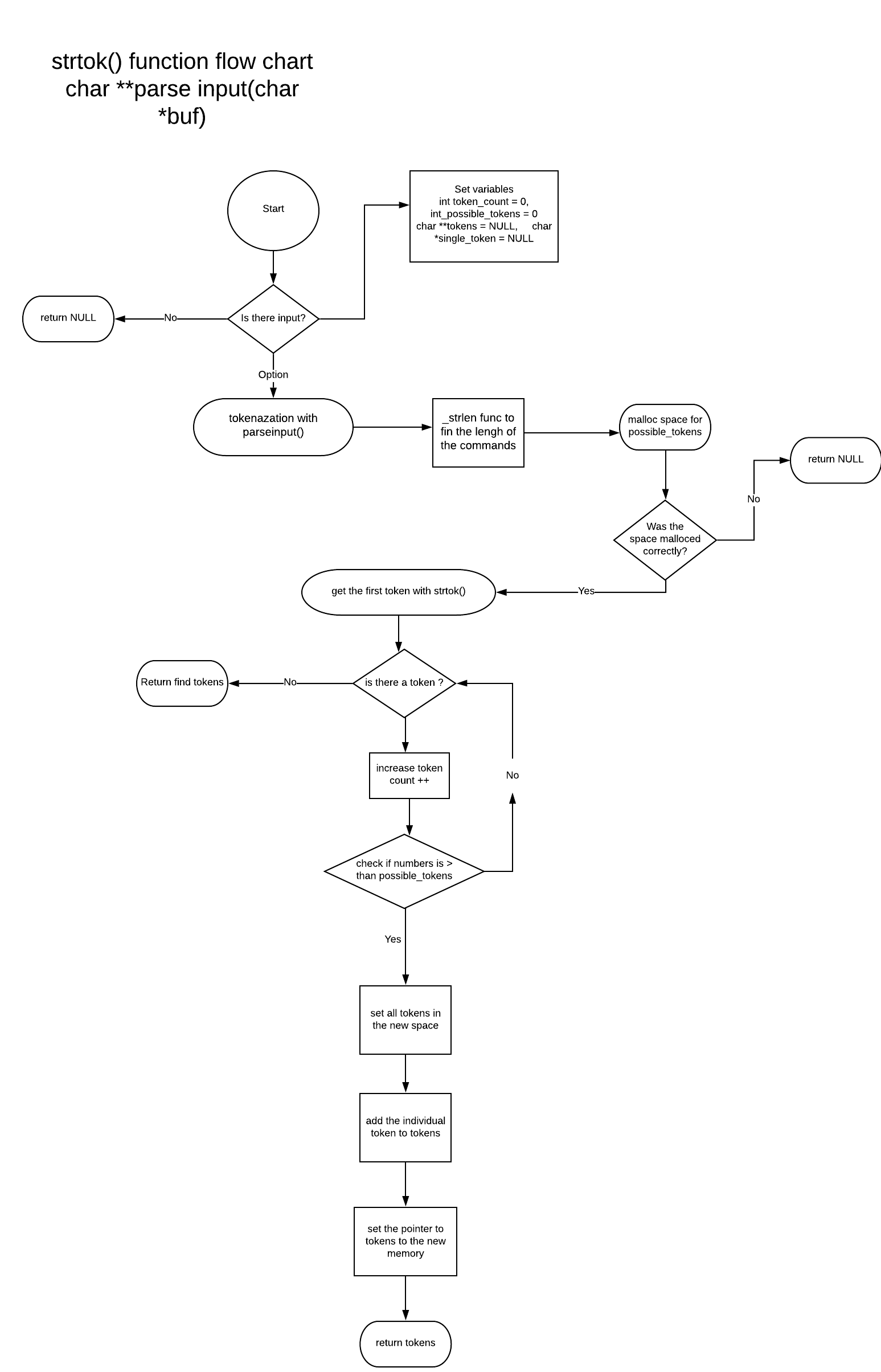
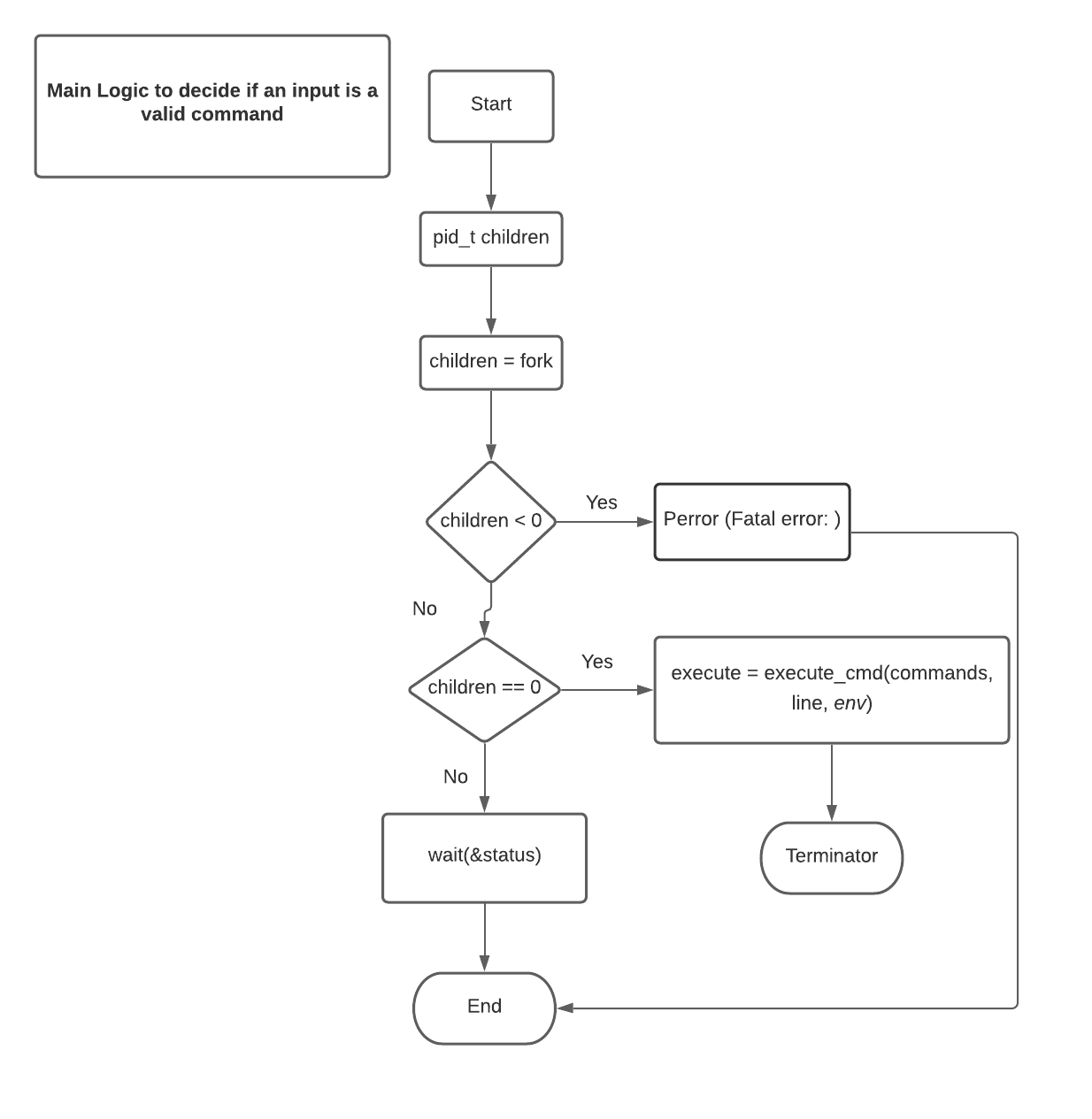
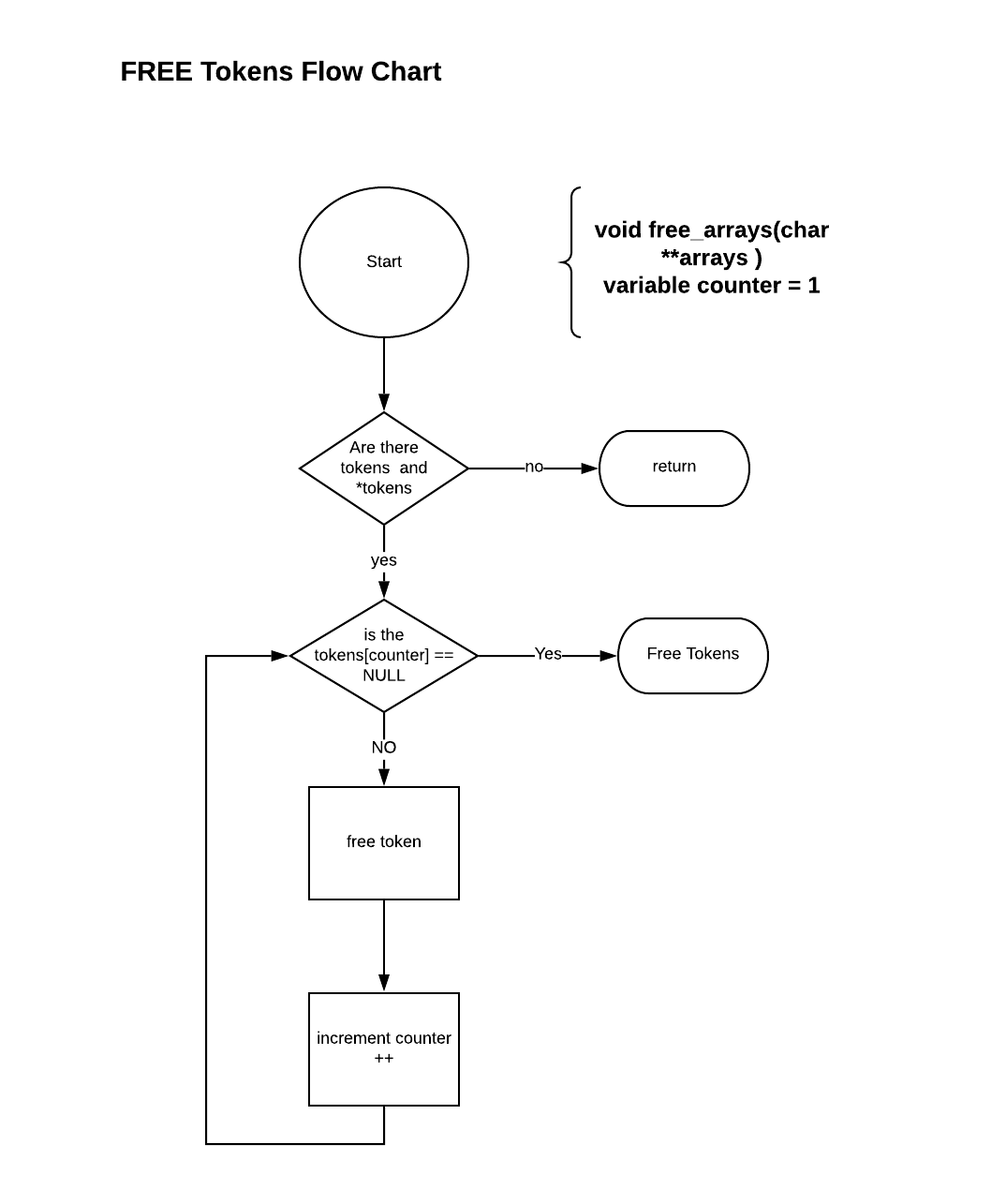
Read or watch:
man ./man_page
- All files will be compiled on Ubuntu 14.04 LTS
- C programs and functions will be compiled with
**gcc**using the flags-Wall-Werror``-Wextraand -pedantic - Files should end with a new line
- Use the
Bettystyle. - The shell should not have any memory leaks
- No more than 5 functions per file
- All header files should be include guarded
- Use system calls only when if needed to (why?)
access(man 2 access)chdir(man 2 chdir)close(man 2 close)closedir(man 3 closedir)execve(man 2 execve)exit(man 3 exit)_exit(man 2 _exit)fflush(man 3 fflush)fork(man 2 fork)free(man 3 free)getcwd(man 3 getcwd)getline(man 3 getline)isatty(man 3 isatty)kill(man 2 kill)malloc(man 3 malloc)open(man 2 open)opendir(man 3 opendir)perror(man 3 perror)read(man 2 read)readdir(man 3 readdir)signal(man 2 signal)stat(__xstat) (man 2 stat)lstat(__lxstat) (man 2 lstat)fstat(__fxstat) (man 2 fstat)strtok(man 3 strtok)wait(man 2 wait)waitpid(man 2 waitpid)wait3(man 2 wait3)wait4(man 2 wait4)write(man 2 write)
- Who designed and implemented the original Unix operating system
- Who wrote the first version of the UNIX shell
- Who invented the B programming language (the direct predecessor to the C programming language)
- Who is Ken Thompson
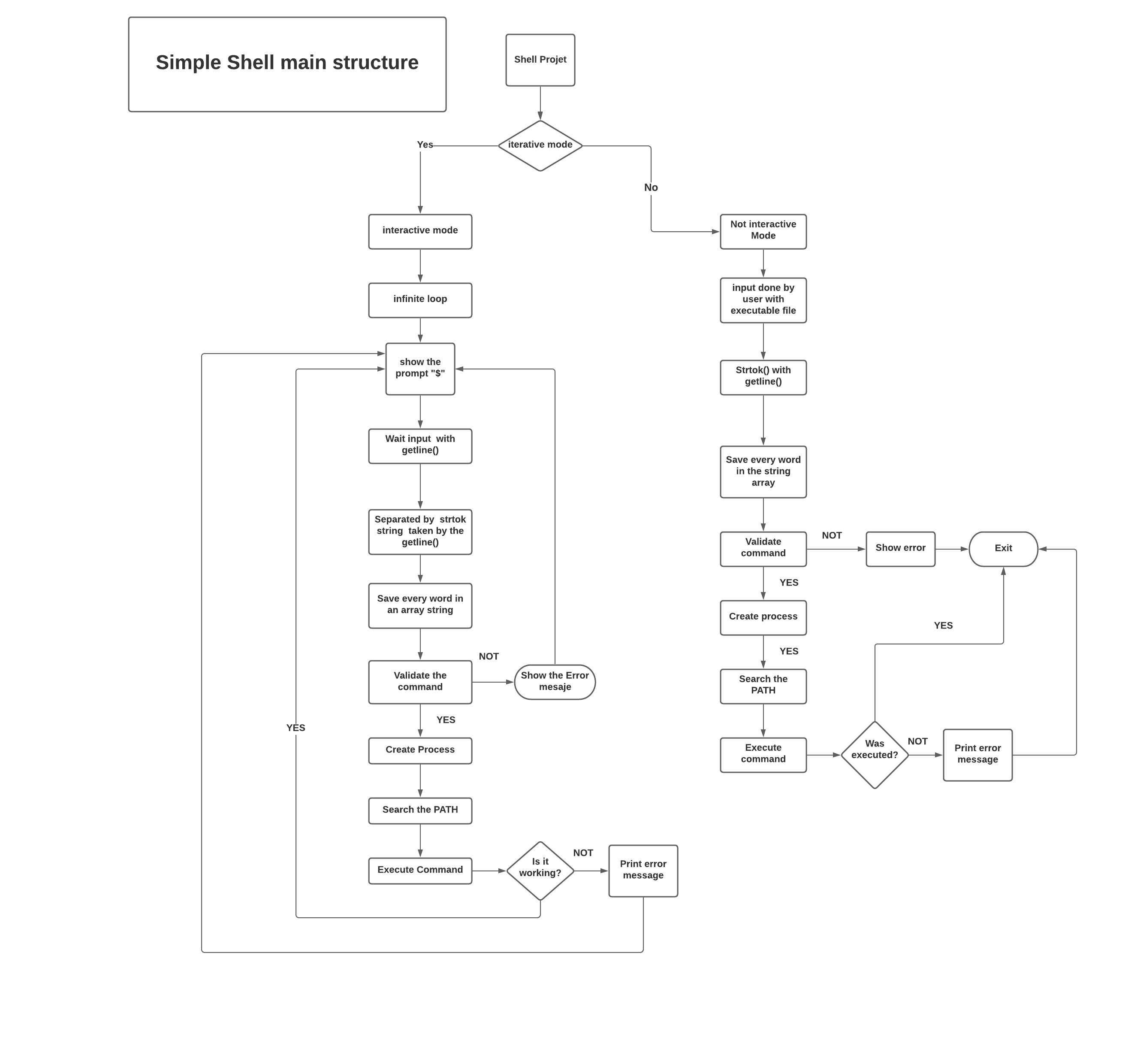
- How does a shell work
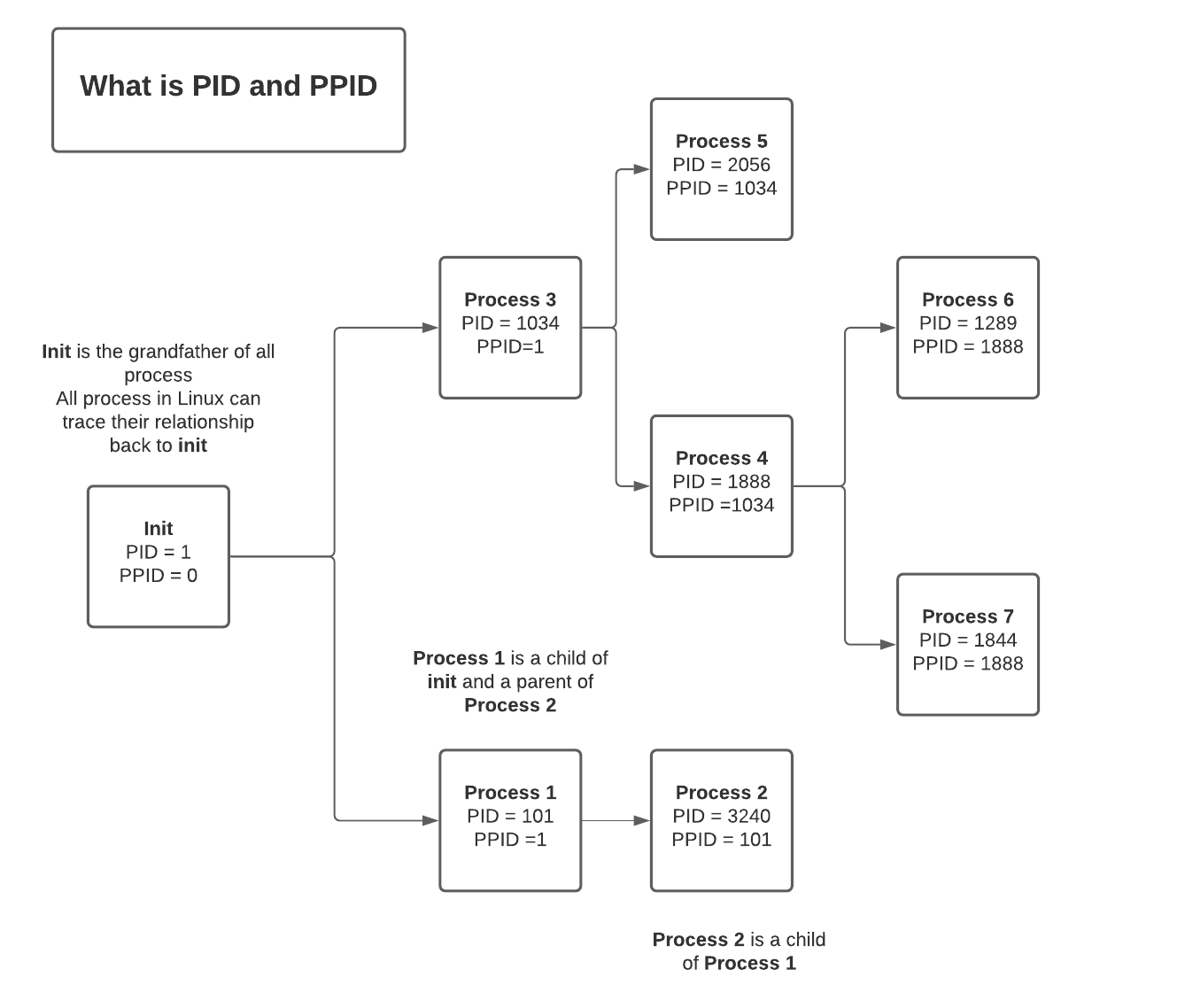
- What is a pid and a ppid
- How to manipulate the environment of the current process
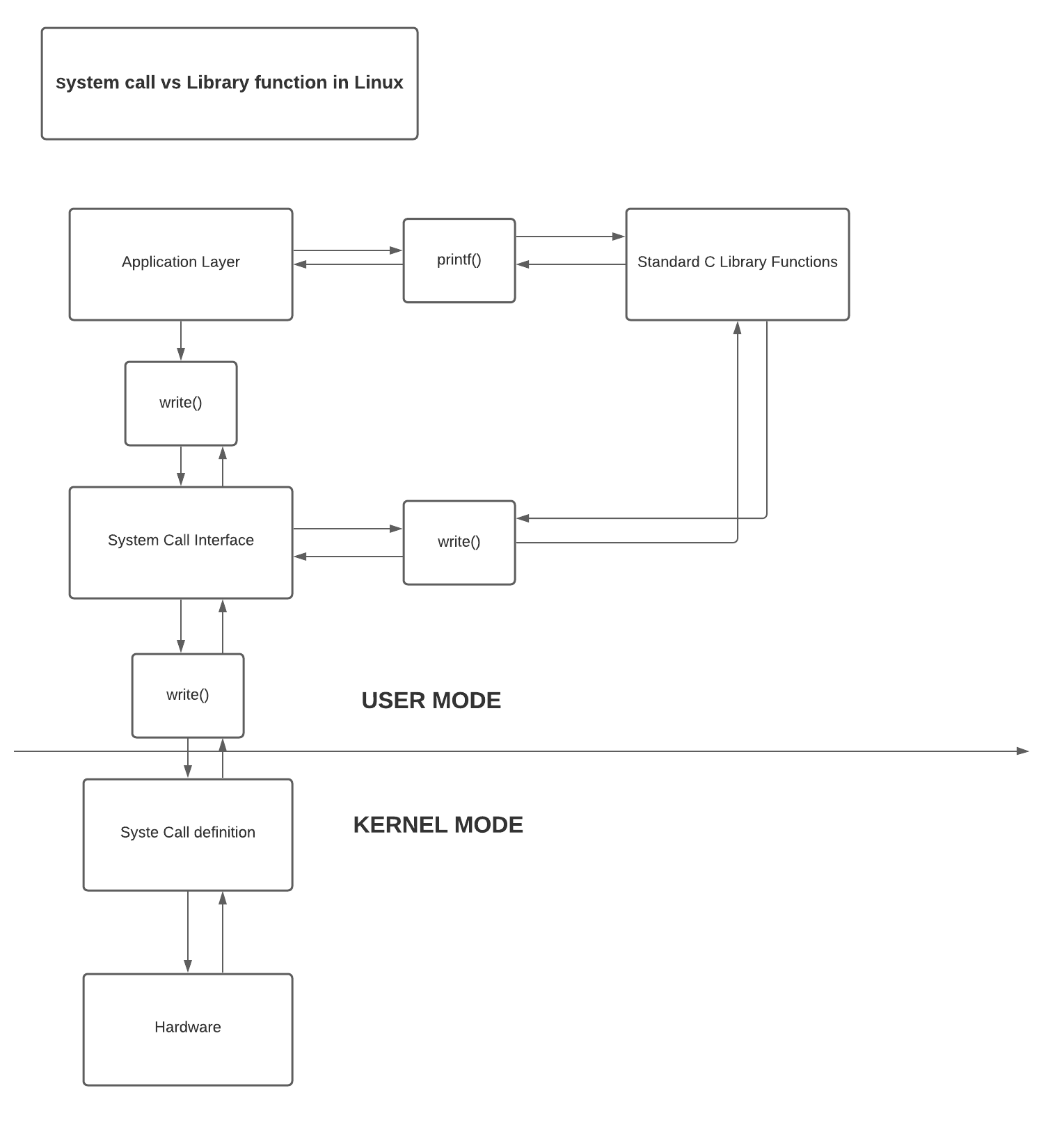
- What is the difference between a function and a system call
- How to create processes
- What are the three prototypes of
main - How does the shell use the
PATHto find the programs - How to execute another program with the
execvesystem call - How to suspend the execution of a process until one of its children terminates
- What is
EOF/ “end-of-file”?
Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, Brian Kernighan and Douglas McIlroy at Bell Labs
The development began in 1969 and published internally in November 1971 and then announced to the world in October 1973 by Bell Labs.
The first Unix shell was the sh, written by Ken Thompson computer programmer at Bell Labs and distributed with Versions 1 through 6 of Unix, from 1971 to 1975. Tough rudimentary by modern standards, it introduced many of the basic features common to all later Unix shells, including piping, simple control structures using if and goto, and filename wildcarding. Though not in current use, it is still available as part of some [Ancient UNIX Systems] ("Ancient UNIX Systems").
Kenneth Lane Thompson is an American pioneer of computer science. He worked at Bell Labs where he designed and implemented the original Unix operating system. He also invented the B programming language, the direct predecessor to the C programming language, and was one of the creators and early developers of the Plan 9 operating systems. Since 2006, Thompson works at Google, where he co-invented the Go programming language.
The shell uses an environment list that is used to store eviroment variables. This list is an array of strings, with the following format: var=value, where var is the name of the variable and valueits value. As a reminder, you can list the environment with the command printenv.
Actually, every process comes with an environment. When a new process is created, it inherits a copy of its parent’s environment. To access the entire environment within a process. Find the options below:
- via the
mainfunction - via the global variable
environ(man environ)
An environment variable is a variable whose value is set outside the program, typically through functionality built into the operating system or microservice. An environment variable is made up of a name/value pair, and any number may be created and available for reference at a point in time.
- At runtime, the reference to the environment variable name is replaced with its current value.
The main difference between system call and function call is that a system call is a request for the kernel to access a resource while a function call is a request made by a program to perform a specific task.
The system call fork creates a new child process, almost identical to the parent (the process that calls fork). Once fork successfully returns, two processes continue to run the same program, but with different stacks, datas and heaps.
Using the return value of fork, it is possible to know if the current process is the father or the child: fork will return 0 to the child, and the PID of the child to the father.
Shell commands have a very specific purpose. More complicated commands can be constructed by combining simpler commands in a pipeline (|), so the output of one command becomes the input to another command. The standard shell syntax for pipelines(|) is to list multiple commands. When the shell runs commands forks new processes using exec, so the new process executes the program.
`* int main(void)
- int main(int ac, char **av)`
- int main(int ac, char **av, char **env)
There are two types of files those that just contain information and those that are executable (files that are used to run functions and operations in the machine). The PATH variable is basically a list of directories that the computer search in to find an executable that has been requested. Any command name that is not built-in, is assumed to be the name of an executable program file, and the shell attempts to find an executable file with that name and runs it. (Shells find and run commands.)
If the command name contains no slashes (like most command names, e.g. date), the shell looks for the executable file with that exact name in the list of directories kept in the PATH environment variable. Because PATH is a shell environment variable, you can change the list, and the list is usually exported and inherited by child processes of the shell. Directories in PATH are separated by colons, e.g. the following PATH variable contains three directories separated by colons:
$ echo "$PATH"
/usr/local/bin:/bin:/usr/bin
When typing a file with no slashes, shell goes looking for the executable file in the list of directories kept in the PATH environment variable, looking for an executable file named to execute. The shell tries each directory in the PATH`, left-to-right, and runs the first executable program with the matching command name that it finds.
The shell next tries the second directory name in the PATH variable (/bin) and looks for an executable file named /bin/ls, and this is the usual location of the ls.
Since this file exists, the shell runs this executable program and ls appears
The slashes in the pathname prevent the shell from using PATH to look up the command name, so the shell executes it directly.
The system call execve allows a process to execute another program. This system call loads the new program into the current process’ memory in place of the “previous” program: on success execve does not return to continue the rest of the “previous” program. The program invoked inherits the calling process’s PID, and any open file descriptors that are not set to close-on-exec. Signals pending on the calling process are cleared. Any signals set to be caught by the calling process are reset to their default behaviour.
A call to wait() blocks the calling process until one of its child processes exits or a signal is received. After child process terminates, the parent continues its execution after wait system call instruction.
Child process may terminate due to any of these:
- It calls exit();
- It returns (an int) from main
- It receives a signal (from the OS or another process) whose default action is to terminate.
It is an acronym for ‘End Of File’. It refers to a state that may occur while reading a file, or anything that can be read using the semantics of file IO, such as reading from devices or streams in Linux. The state can be represented in some cases by a value which equates to that state. There is a C function, feof(), which can be used to test whether reading from a stream has caused the EOF state to be reached. In certain cases, it is possible to generate an EOF state, such as by typing Ctrl-D to terminate standard input to a process, such as a shell.
Execute the following commmand in your terminal:
git clone https://github.com/Andres802/simple_shell.git
gcc -Wall -Werror -Wextra -pedantic simple_shell/*.c -o hsh
After installing the shell you can run it in interactive mode or non-interactive mode
cd simple_shell/
./hsh
$ls
$exit
cd simple_shell/
echo "ls" | ./hsh
To run the example file use:
cd simple_shell/
Example/./test